Foundation Engineering Building Foundation Types Build

Different Types Of Foundation Classification Of Building Foundation The ideal choice depends on the specific structural characteristics and soil conditions of your building construction. 1. mat (raft) foundation. consisting of a single large continuous rectangular or circular slab under a building, the mat (or raft) foundation carries and distributes an entire load of a structure. Types of building foundations: we explored the differences between shallow and deep foundations, highlighting their characteristics, uses, and examples. soil analysis and site investigation: the importance of soil testing and thorough site investigation was emphasized, detailing methods and tools used to ensure a stable foundation.
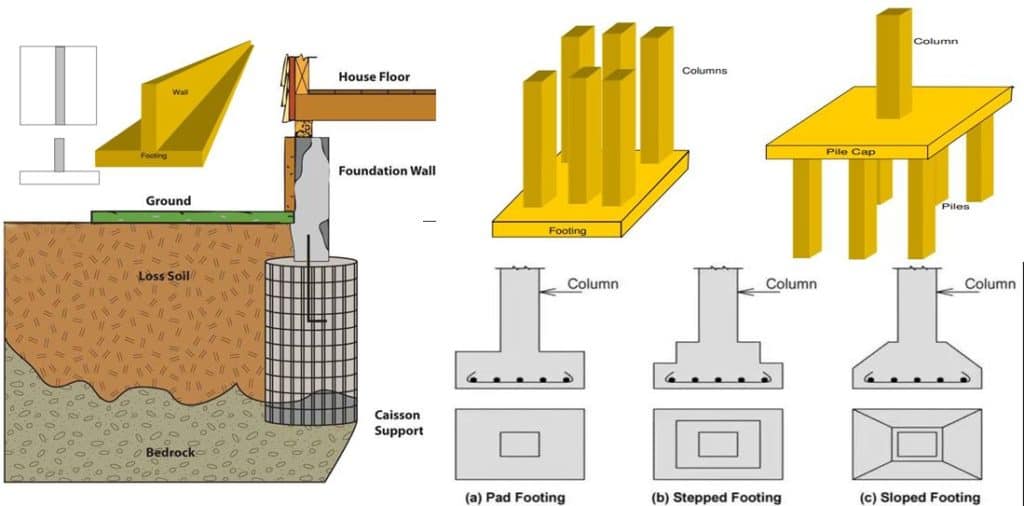
Types Of Foundation Their Uses In Building Construction Description: pier and beam foundations consist of a series of piers (columns) that support beams running across the structure. this type of foundation elevates the building and provides a crawl space underneath. advantages: provides access to plumbing and electrical systems. Definition of building foundation. foundations transfer forces from structural systems to some external source, typically the ground. the ground has essentially infinite stability, which makes it a great place to transfer the loads of your structure. in a structural model, foundations are often represented as supports, or boundary conditions. Types of building foundations. when planning a construction project, one of the first decisions you'll face is selecting the type of foundation. this choice is crucial, as the foundation supports the entire structure, distributing its weight to the ground. there are two main categories of foundations: shallow and deep. Foundation design is a critical aspect of structural engineering, as it ensures that a building or structure remains stable and secure by transferring its loads safely to the ground. a well designed foundation provides the necessary support to prevent excessive settlement, tilting, or failure over time. engineers must consider soil conditions.

Types Of Foundations In Building Construction Foundation Engineering Types of building foundations. when planning a construction project, one of the first decisions you'll face is selecting the type of foundation. this choice is crucial, as the foundation supports the entire structure, distributing its weight to the ground. there are two main categories of foundations: shallow and deep. Foundation design is a critical aspect of structural engineering, as it ensures that a building or structure remains stable and secure by transferring its loads safely to the ground. a well designed foundation provides the necessary support to prevent excessive settlement, tilting, or failure over time. engineers must consider soil conditions. A building’s foundation is a critical structural component that transfers loads from the building into the underlying soil or bedrock. as civil engineers, understanding the principles behind foundation design and the various types of foundations is key for any construction project. in this in depth guide, we’ll explore what building. Types of foundation and their uses. following are different types of foundations used in construction: shallow foundation. individual footing or isolated footing. combined footing. strip foundation. raft or mat foundation. deep foundation. pile foundation.

Types Of Foundation In Construction Work Types Of Footings Type Of A building’s foundation is a critical structural component that transfers loads from the building into the underlying soil or bedrock. as civil engineers, understanding the principles behind foundation design and the various types of foundations is key for any construction project. in this in depth guide, we’ll explore what building. Types of foundation and their uses. following are different types of foundations used in construction: shallow foundation. individual footing or isolated footing. combined footing. strip foundation. raft or mat foundation. deep foundation. pile foundation.

Comments are closed.