Frontotemporal Dementia Emerging Therapies For Dementia

Frontotemporal Dementia Emerging Therapies For Dementia Youtube Frontotemporal dementia (ftd) is the most common age related dementia in people under 60 years of age 1 – 4. the clinical presentation of ftd is distinct from alzheimer’s disease (ad), the most common age related dementia, in that there is a major impairment of executive functioning in ftd rather than an impairment of memory functions as in ad. In this review, the authors explored the clinical features of frontotemporal dementia (ftd), focusing on treatment. the clinical features of ftd are unique, with disinhibition, apathy, loss of empathy, and compulsions common. motor changes occur later in the illness. the two major proteins that aggregate in the brain with ftd are tau and tdp 43, whereas a minority of patients aggregate fet.
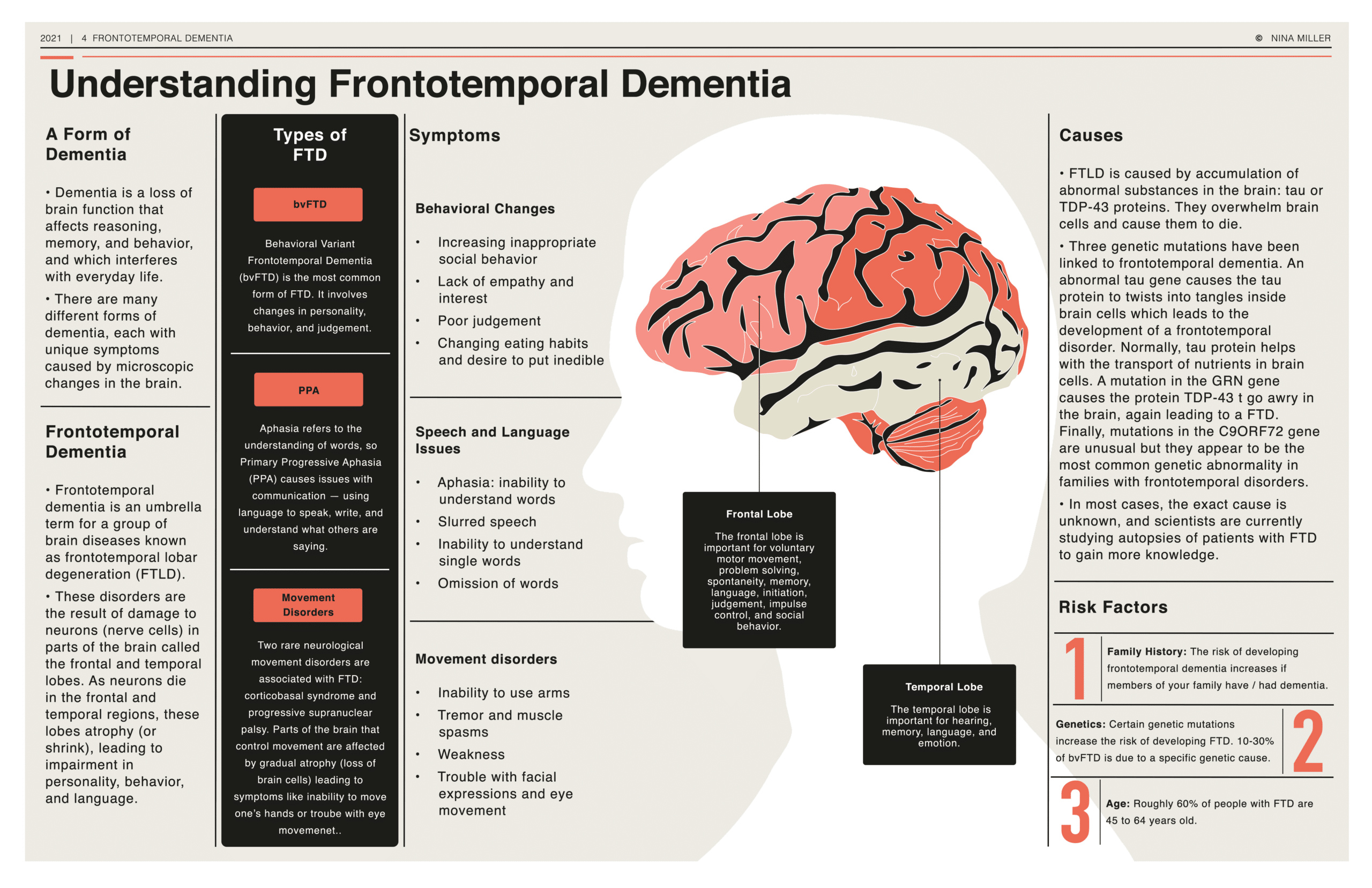
Frontotemporal Dementia Penn Memory Center A monash university led study has found a promising new treatment for patients with behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia, the second most common form of dementia in the under 60s. Frontotemporal dementia comprises a group of clinical syndromes that are characterised by progressive changes in behaviour, executive function, or language. the term frontotemporal lobar degeneration encompasses the neurodegenerative diseases that give rise to these clinical syndromes and involve proteinopathies associated with frontotemporal network dysfunction. improvements in clinical. Introduction. frontotemporal dementia (ftd) is a neuropathologically and clinically heterogeneous disorder characterized by focal degeneration of the frontal and or temporal lobes [1]. age of onset is typically in the late 50s or early 60s. Frontotemporal dementia (ftd) comprises a diverse group of clinical neurodegenerative syndromes characterized by progressive changes in behavior, personality, executive function, language, and motor function. approximately 20% of ftd cases have a known genetic cause. the three most common genetic mutations causing ftd are discussed. frontotemporal lobar degeneration refers to the heterogeneous.

Comments are closed.