Frontotemporal Dementia Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis

Frontotemporal Dementia Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis There's currently no cure or treatment for frontotemporal dementia, although research into treatments is ongoing. medicines used to treat or slow alzheimer's disease don't seem to be helpful for people with frontotemporal dementia. some alzheimer's medicines may worsen the ftd symptoms. but certain medicines and speech therapy can help manage. Frontotemporal dementia (ftd) is a progressive brain disease. this means over time, it causes parts of your brain to deteriorate and stop working. depending on where it starts in your brain, this condition affects your behavior or ability to speak and understand others. it's not curable or treatable, but some symptoms might be treatable.

Frontotemporal Dementia Mayo Clinic Press Frontotemporal dementia (ftd) is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. this causes the lobes to shrink. ftd can affect behavior, personality, language, and movement. ftd is one of the most common dementias to strike at younger people. symptoms often start between the ages of 40. The most common symptoms of frontotemporal dementia involve extreme changes in behavior and personality. these include: increasingly inappropriate social behavior. loss of empathy and other interpersonal skills. for example, not being sensitive to another person's feelings. lack of judgment. loss of inhibition. Many possible symptoms can result, including unusual behaviors, emotional problems, trouble communicating, difficulty with work, or difficulty with walking. ftd is rare and tends to occur at a younger age than other forms of dementia. roughly 60% of people with ftd are 45 to 64 years old. But to confirm a diagnosis in someone with suspicious symptoms, a neurologist might order tests including: frontotemporal dementia treatment. ftd doesn’t have a cure or treatment. drugs that.
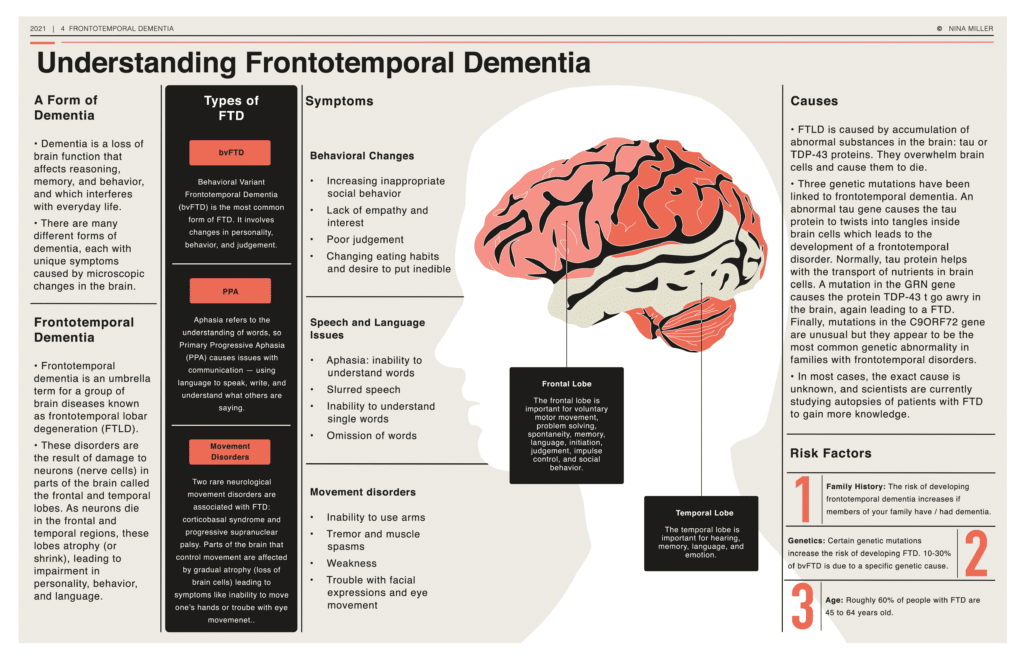
Frontotemporal Dementia Penn Memory Center Many possible symptoms can result, including unusual behaviors, emotional problems, trouble communicating, difficulty with work, or difficulty with walking. ftd is rare and tends to occur at a younger age than other forms of dementia. roughly 60% of people with ftd are 45 to 64 years old. But to confirm a diagnosis in someone with suspicious symptoms, a neurologist might order tests including: frontotemporal dementia treatment. ftd doesn’t have a cure or treatment. drugs that. Prognosis. frontotemporal dementia (ftd) refers to sporadic and hereditary disorders that affect the frontal and temporal lobes, including pick disease. (see also overview of delirium and dementia and dementia.) dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition. frontotemporal dementia accounts for up to 10% of dementias. Frontotemporal dementia: clinical features and diagnosis; frontotemporal dementia: epidemiology, pathology, and pathogenesis; initial pharmacologic treatment of parkinson disease; management of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia; management of the patient with dementia; prognosis and treatment of dementia with lewy bodies.
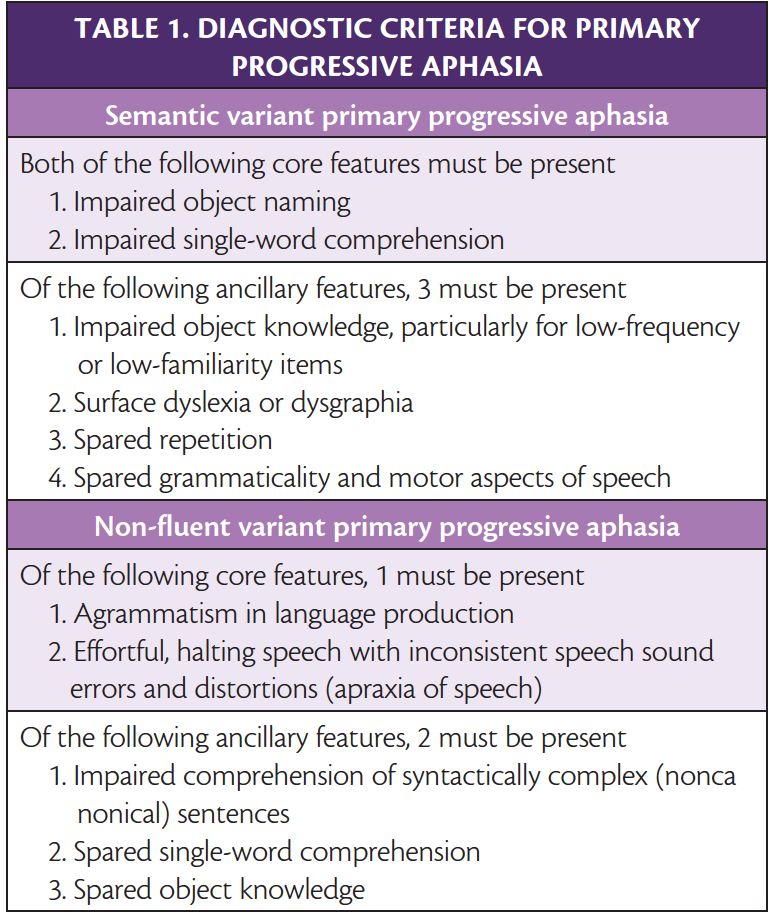
Frontotemporal Dementias Practical Neurology Prognosis. frontotemporal dementia (ftd) refers to sporadic and hereditary disorders that affect the frontal and temporal lobes, including pick disease. (see also overview of delirium and dementia and dementia.) dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition. frontotemporal dementia accounts for up to 10% of dementias. Frontotemporal dementia: clinical features and diagnosis; frontotemporal dementia: epidemiology, pathology, and pathogenesis; initial pharmacologic treatment of parkinson disease; management of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia; management of the patient with dementia; prognosis and treatment of dementia with lewy bodies.

What Is Frontotemporal Dementia Symptoms And Treatment Options

Comments are closed.