Fundamental Accounting Equation Elements Example With Transactions
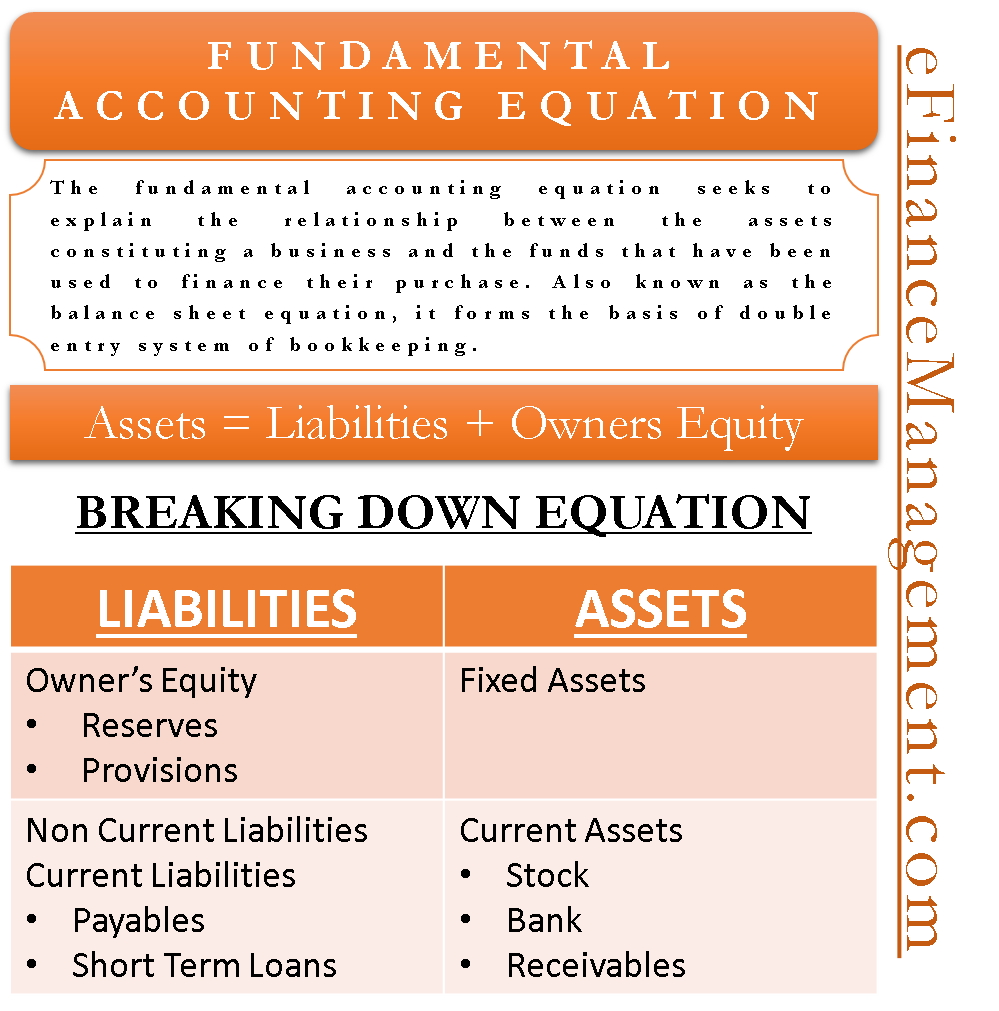
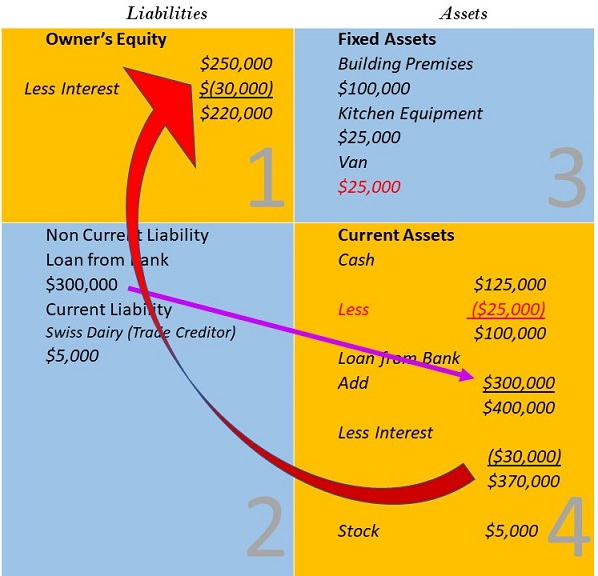
Fundamental Accounting Equation Elements Example With Transactions Transaction 4. john sees that his liquid cash balances have started to reduce because of ongoing business. therefore, as a precautionary measure, he decides to borrow a loan from a financial institution to maintain a buffer of funds. he borrows an amount equal to $300,000. the interest is payable at the rate of 10%. The accounting equation is a basic principle of accounting and a fundamental element of the balance sheet. the equation is as follows: assets = liabilities shareholder’s equity. this equation sets the foundation of double entry accounting, also known as double entry bookkeeping, and highlights the structure of the balance sheet.
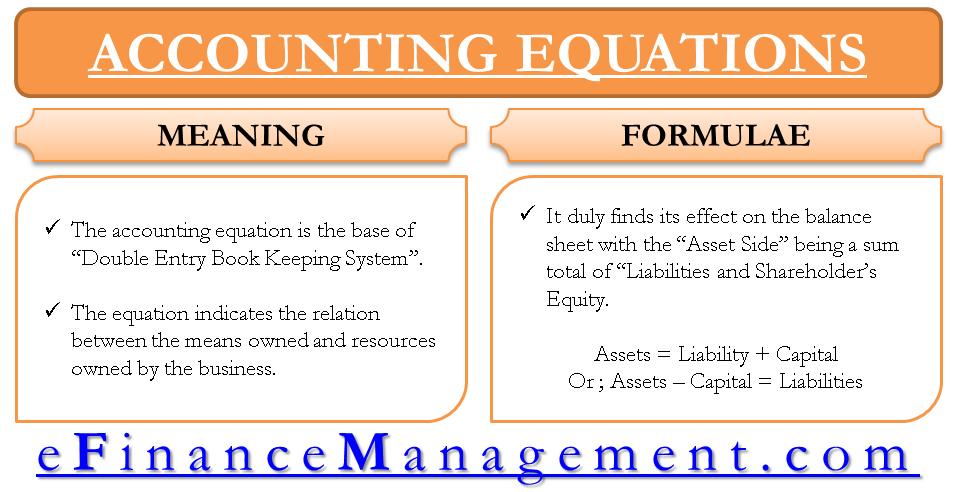
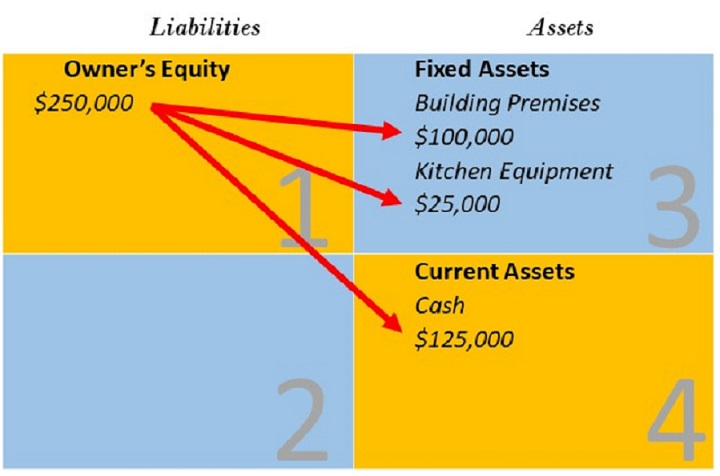
Fundamental Accounting Equation Elements Example With Transactions In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation. notice that each transaction changes the dollar value of at least one of the basic elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner’s equity) but the equation as a whole does not lose its balance. Every financial transaction impacts at least two accounts, keeping the equation balanced. for example, if a company borrows money (increases liabilities), it also increases its cash (assets). while the accounting equation is fundamental to accounting, it does not provide insights into a company's liquidity, profitability, or operational efficiency. The basic accounting equation is: assets = liabilities capital. sample business transactions. here are more examples to further illustrate how the accounting equation works. below are additional transactions following example 1, 2 and 3 in the previous lesson: rendered services and received the full amount in cash, $500. As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect. often, more than one element of the accounting equation is impacted but sometimes, like with transaction 3, the same part of the equation (in this case assets) goes up and down, making it look like nothing has happened.
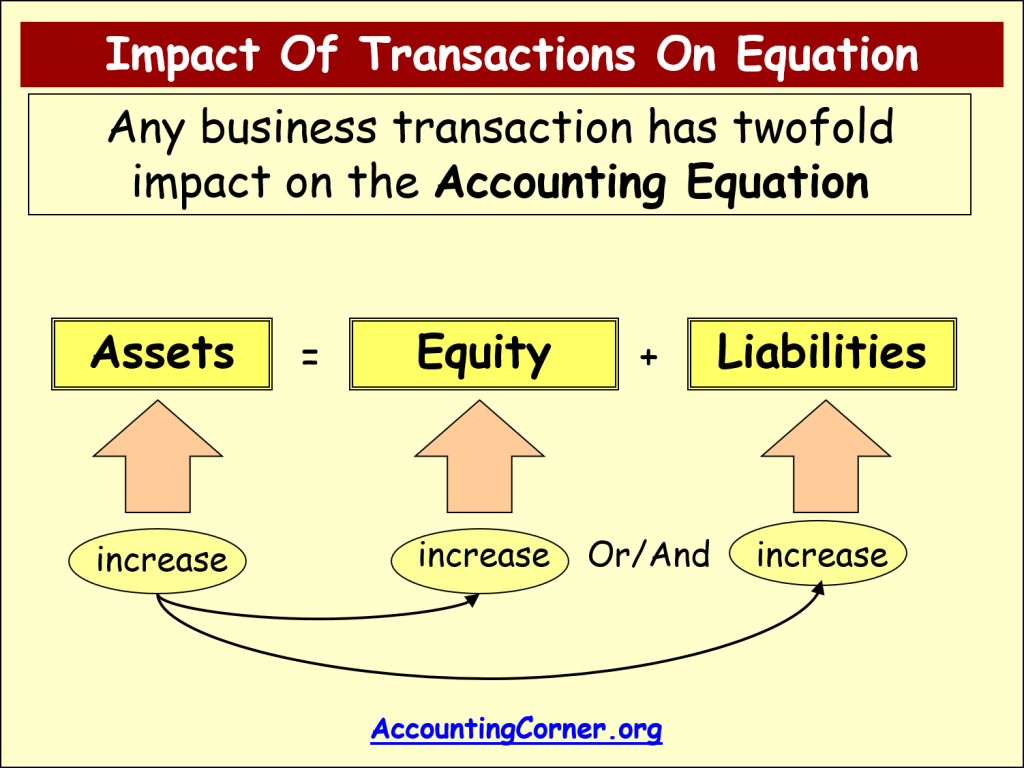
Accounting Equation Accounting Corner The basic accounting equation is: assets = liabilities capital. sample business transactions. here are more examples to further illustrate how the accounting equation works. below are additional transactions following example 1, 2 and 3 in the previous lesson: rendered services and received the full amount in cash, $500. As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect. often, more than one element of the accounting equation is impacted but sometimes, like with transaction 3, the same part of the equation (in this case assets) goes up and down, making it look like nothing has happened. The basic accounting equation is: assets = liabilities capital. when a business is put up, its resources (assets) come from two sources: contributions by owners (capital) and those acquired from creditors or lenders (liabilities). in other words, all assets initially come from liabilities and owners' contributions. At this point, let's consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. example 2. on 1 january 2016, sam started a trading business called sam enterprises with an initial investment of $100,000. at this time, there is external equity or liability in sam enterprise. the only.
Fundamental Accounting Equation Elements Example With Transactions The basic accounting equation is: assets = liabilities capital. when a business is put up, its resources (assets) come from two sources: contributions by owners (capital) and those acquired from creditors or lenders (liabilities). in other words, all assets initially come from liabilities and owners' contributions. At this point, let's consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. example 2. on 1 january 2016, sam started a trading business called sam enterprises with an initial investment of $100,000. at this time, there is external equity or liability in sam enterprise. the only.

Fundamental Accounting Equation Elements Example With Transactions
Fundamental Accounting Equation Elements Example With Transactions

Comments are closed.