Gcse Biology Trophic Levels Producers Consumers Herbivores Carnivores 86
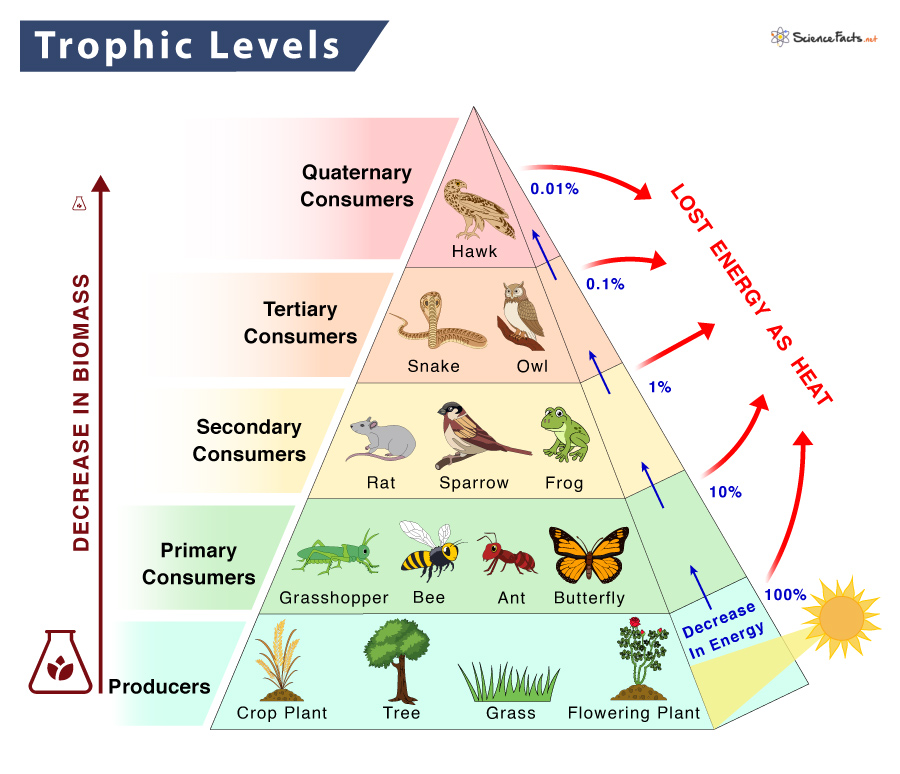
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram This video covers: the idea that trophic levels are just the different levels of a food chain trophic level 1 are called the producers trophic level 2 ar. Producers green plants they make glucose during photosynthesis. primary consumers usually eat plant material they are herbivores. for example rabbits, caterpillars, cows and sheep. secondary.
Organisation Trophic Levels Trophic Levels Food Chains Gcse Gcse biology trophic levels producers, consumers, herbivores & carnivores #86. Trophic levels are used to describe the feeding relationships between organisms. the sun is the source of energy for nearly all life on earth. energy flows from the sun to the first trophic level (producers) in the form of light. producers then convert light energy into chemical energy and it flows in this form from one consumer to the next. All at once. the idea that trophic levels are just the different levels of a food chain. the names of each trophic level e.g. 'producers', 'primary consumers' etc. the difference between 'herbivores', 'carnivores', and 'omnivores'. how detritivores break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients. gcse biology trophic levels producers. Trophic levels can be represented by numbers, starting at level 1 with plants and algae. further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. trophic levels table. energy flows from the sun to the first trophic level (producers) in the form of light. producers convert light energy into.

Trophic Levels Are Represented By All at once. the idea that trophic levels are just the different levels of a food chain. the names of each trophic level e.g. 'producers', 'primary consumers' etc. the difference between 'herbivores', 'carnivores', and 'omnivores'. how detritivores break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients. gcse biology trophic levels producers. Trophic levels can be represented by numbers, starting at level 1 with plants and algae. further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. trophic levels table. energy flows from the sun to the first trophic level (producers) in the form of light. producers convert light energy into. Trophic levels are used to describe where an organism is in a food chain. trophic level 1 – producers: these are green plants and algae that make their own food (glucose) using energy from the sun. trophic level 2 – primary consumers: this includes herbivores that feed only on the producers. trophic level 3 – secondary consumers: these. Food chain: level 4. carnivores that eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers. an apex predator is at the highest point in the food chain. food chains show feeding relationships and energy flows within a biological community. an organism’s trophic level describes where it fits into a food chain. trophic levels are given numbers:.

This Diagram Shows The Trophic Levels From Producers Or Plants To Trophic levels are used to describe where an organism is in a food chain. trophic level 1 – producers: these are green plants and algae that make their own food (glucose) using energy from the sun. trophic level 2 – primary consumers: this includes herbivores that feed only on the producers. trophic level 3 – secondary consumers: these. Food chain: level 4. carnivores that eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers. an apex predator is at the highest point in the food chain. food chains show feeding relationships and energy flows within a biological community. an organism’s trophic level describes where it fits into a food chain. trophic levels are given numbers:.

Comments are closed.