Grassland Food Chain Diagram
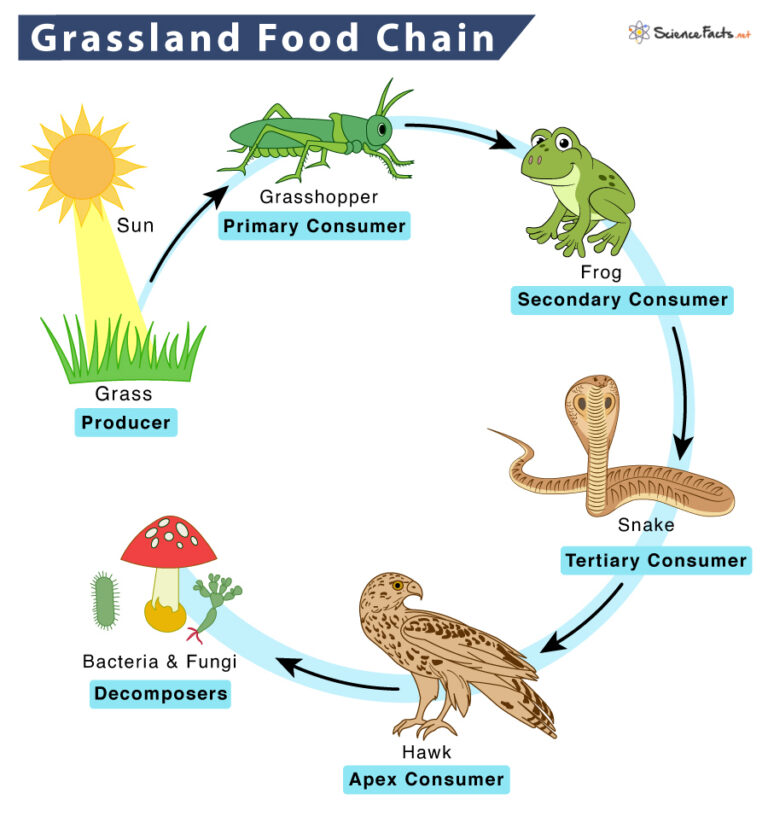
Grassland Food Chain Examples And Diagram Learn how grass, insects, frogs, snakes, coyotes, vultures and hawks form a food chain in a grassland ecosystem. see a diagram and examples of each tropic level and how they interact. A grassland food web is a complex network of interrelated food chains that illustrates the feeding relationships between different organisms in a grassland ecosystem. it showcases how energy and nutrients flow through the ecosystem, starting from producers (plants) to various levels of consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores) and decomposers.
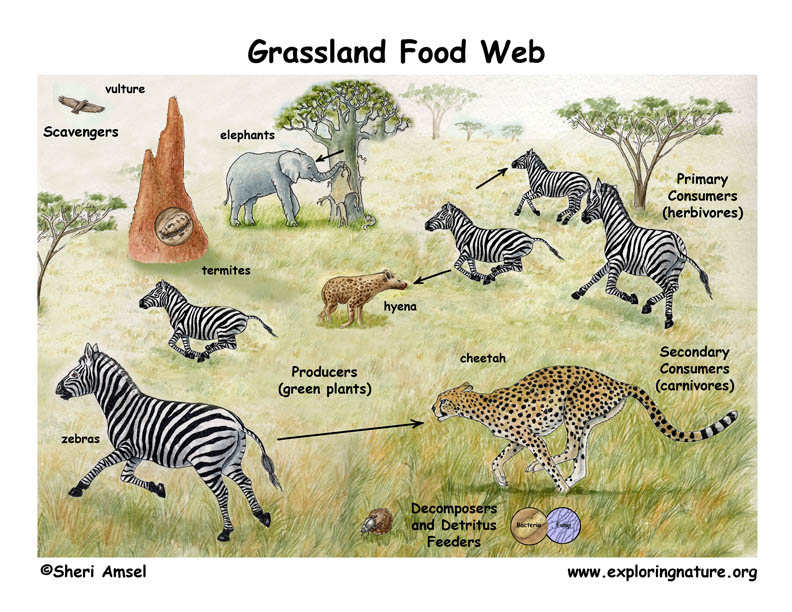
African Grassland Savanna Food Web A food chain is a feeding relationship between organisms in the form of a linear flow of energy that shows 'who eats whom' within an ecosystem. in a food chain, nutrients are passed from one. Learn how food webs illustrate the feeding relationships and energy flow among species in an ecosystem. see examples of grazing and detrital food chains, and different types of food webs based on species interactions. This is an african savanna food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the trees, shrubs and grass. the primary consumers – the zebras and elephants. the secondary consumers – the cheetah, hyena. the scavengers – the termites, vultures and hyena. A pyramid food chain diagram reminds us how it takes many organisms in lower trophic levels to support a just few organisms in higher trophic levels. food chains vary in length. some may be short, with as few as two tropic levels.
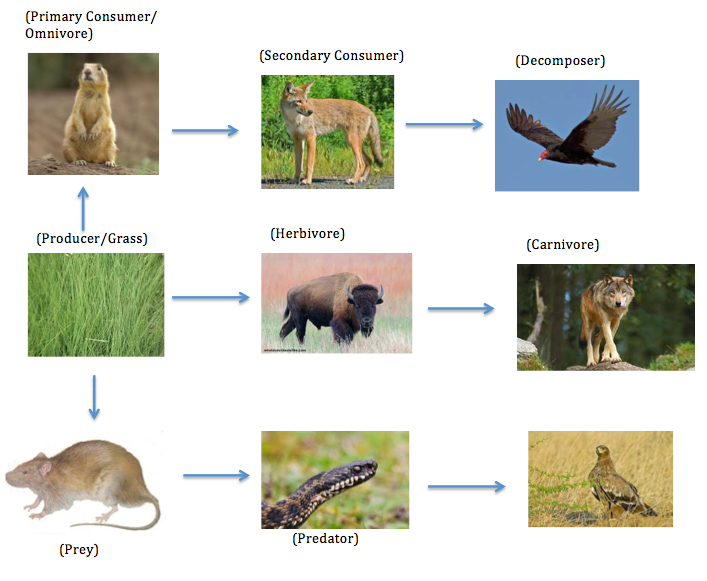
Food Chain Web Temperate Grassland This is an african savanna food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the trees, shrubs and grass. the primary consumers – the zebras and elephants. the secondary consumers – the cheetah, hyena. the scavengers – the termites, vultures and hyena. A pyramid food chain diagram reminds us how it takes many organisms in lower trophic levels to support a just few organisms in higher trophic levels. food chains vary in length. some may be short, with as few as two tropic levels. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. each organism in a food chain occupies a specific trophic level (energy level), its position in the food chain. the first trophic level in the food chain is the producers. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.
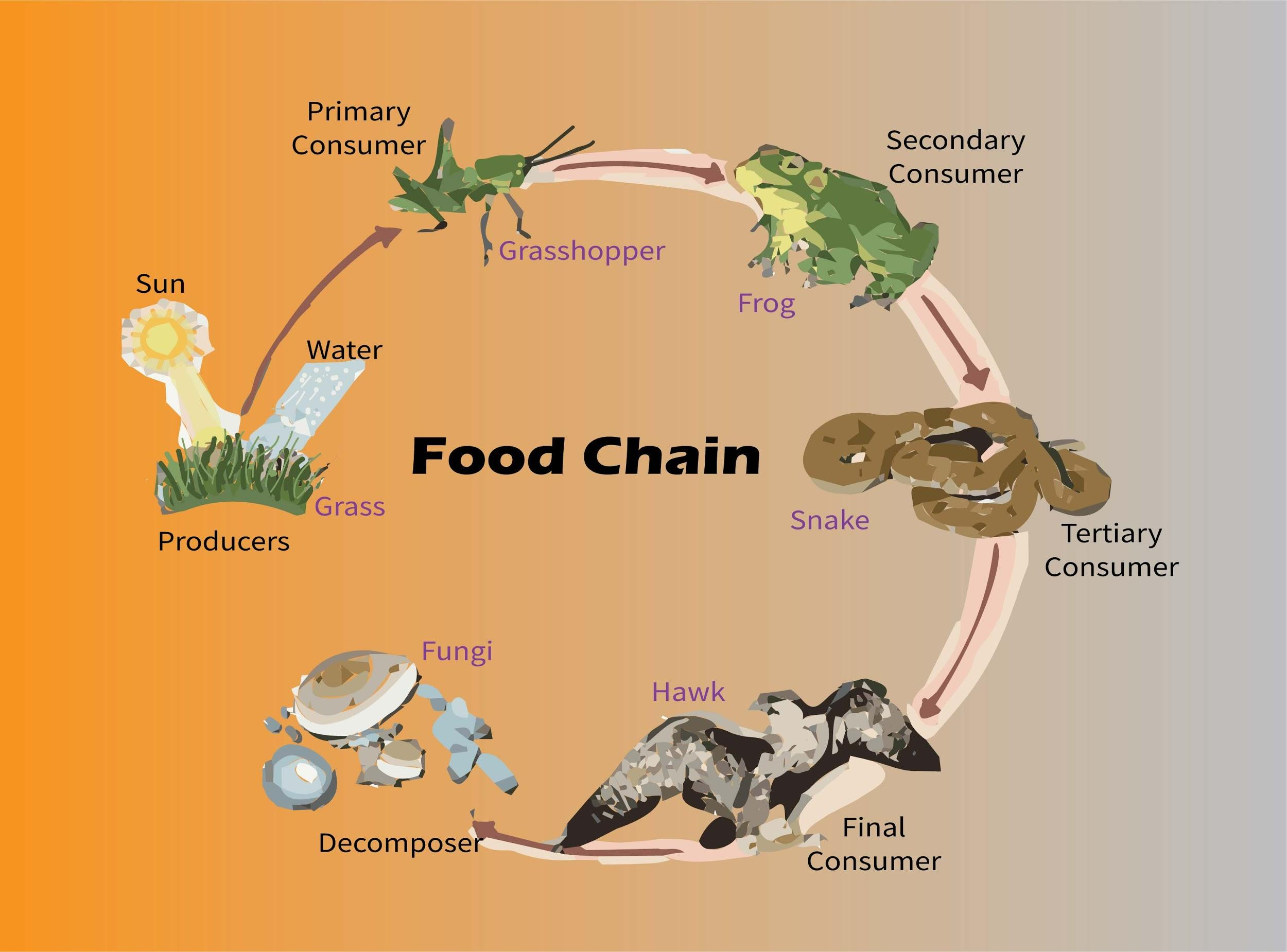
Grassland Ecosystem Food Web A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. each organism in a food chain occupies a specific trophic level (energy level), its position in the food chain. the first trophic level in the food chain is the producers. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Comments are closed.