Grassland Food Chain Example Food Chain Grassland Ecology
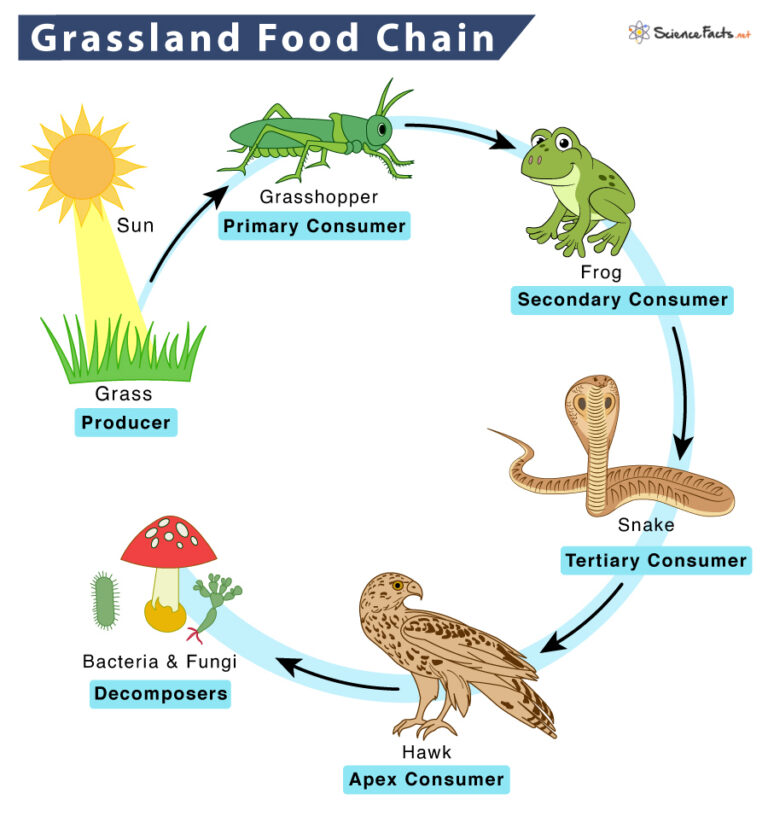
Grassland Food Chain Examples And Diagram The frog (carnivores) eats the insects, the secondary consumers in this food chain. in temperate grassland, the prairie dog is also a secondary consumer. finally, the snake is a tertiary consumer and feeds on the frog. coyotes are another example of the tertiary consumer in such a food chain. apex or quaternary consumers like vultures and hawk. Learn about the grassland food chain and see how it compares to the grassland food web. explore examples of grassland animals in the food web and food chain. updated: 11 21 2023.

Grassland Food Chain Example Food Chain Grassland Ecology A grassland food web is a complex network of interrelated food chains that illustrates the feeding relationships between different organisms in a grassland ecosystem. it showcases how energy and nutrients flow through the ecosystem, starting from producers (plants) to various levels of consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores) and decomposers. For example, the predators of a scorpion in a desert ecosystem might be a golden eagle, an owl, a roadrunner, or a fox. figure 1: a simple six member food web for a representative desert grassland. Food chains. a food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. Welcome to the grassland food webs learning object. food webs consist of a number of interlinking food chains within an ecosystem. a food chain indicates ‘who eats who’ and depicts a flow of energy. all food chains begin with a producer, an organism that can make its own food e.g. a plant. herbivores are organisms that eat plants and.
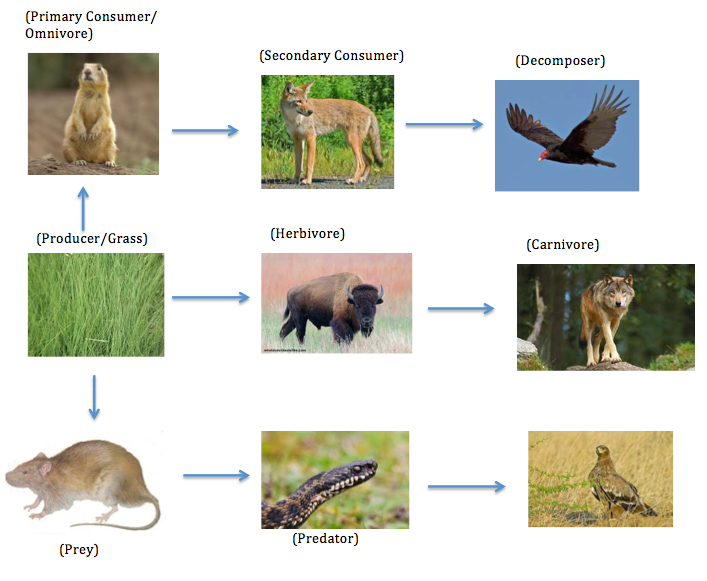
Grassland Food Chain Food chains. a food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. Welcome to the grassland food webs learning object. food webs consist of a number of interlinking food chains within an ecosystem. a food chain indicates ‘who eats who’ and depicts a flow of energy. all food chains begin with a producer, an organism that can make its own food e.g. a plant. herbivores are organisms that eat plants and. The food chains in an ecosystem intertwine to form a food web. this interactive shows a simplified grassland food web. each set of arrows links the organisms in one food chain. note that most organisms in a food web belong to multiple food chains. Food chain. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most.
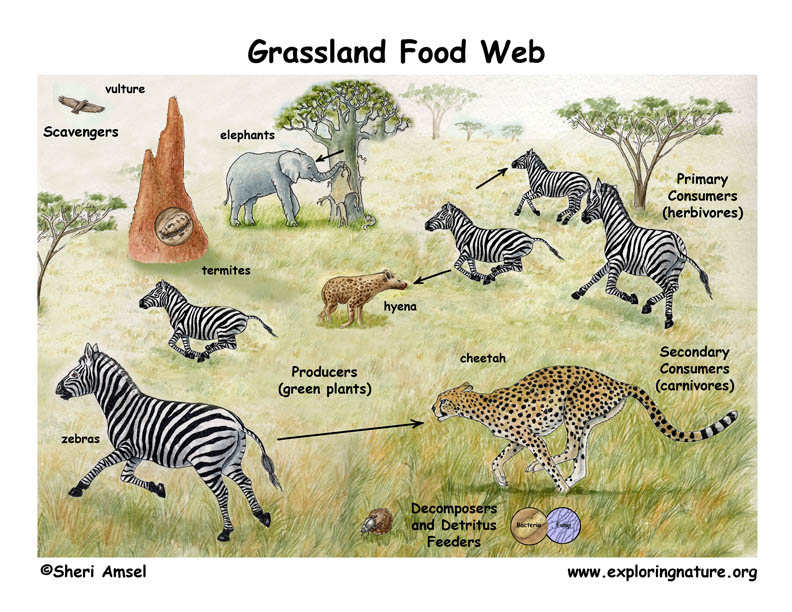
African Grassland Savanna Food Web The food chains in an ecosystem intertwine to form a food web. this interactive shows a simplified grassland food web. each set of arrows links the organisms in one food chain. note that most organisms in a food web belong to multiple food chains. Food chain. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most.

Comments are closed.