Grassland Food Chain Examples And Diagram
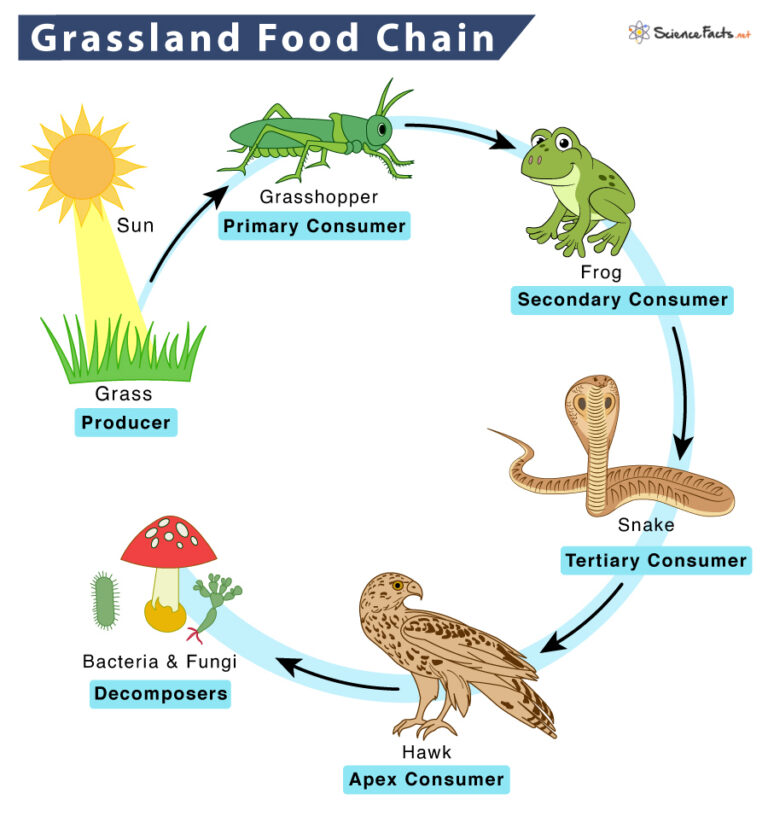
Grassland Food Chain Examples And Diagram The frog (carnivores) eats the insects, the secondary consumers in this food chain. in temperate grassland, the prairie dog is also a secondary consumer. finally, the snake is a tertiary consumer and feeds on the frog. coyotes are another example of the tertiary consumer in such a food chain. apex or quaternary consumers like vultures and hawk. In grasslands, examples of tertiary consumers include large predators like mountain lions and cheetahs. the significance of keystone species. keystone species are organisms that play a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem. in grassland food webs, the keystone species is often a top predator.
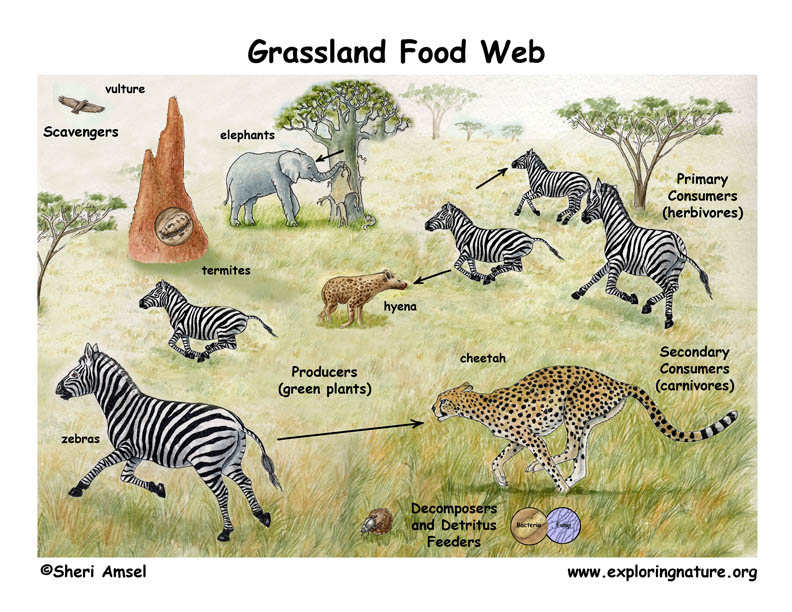
African Grassland Savanna Food Web The following is an example of a food chain in the grasslands:. producer: grass; primary consumer: grasshopper; secondary consumer: prairie dog; tertiary consumer: coyote; in this example, the. Food webs better represent the complexity of ecosystems, where most organisms consume multiple types of food and are preyed upon by various predators. for example: food chain example: grass → grasshopper → frog → snake → hawk. food web example: in a forest ecosystem, grasshoppers may be eaten by frogs, birds, and spiders, while snakes. Normally, food webs consist of a number of food chains meshed together. each food chain is a descriptive diagram including a series of arrows, each pointing from one species to another. This is an african savanna food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the trees, shrubs and grass. the primary consumers – the zebras and elephants. the secondary consumers – the cheetah, hyena. the scavengers – the termites, vultures and hyena.
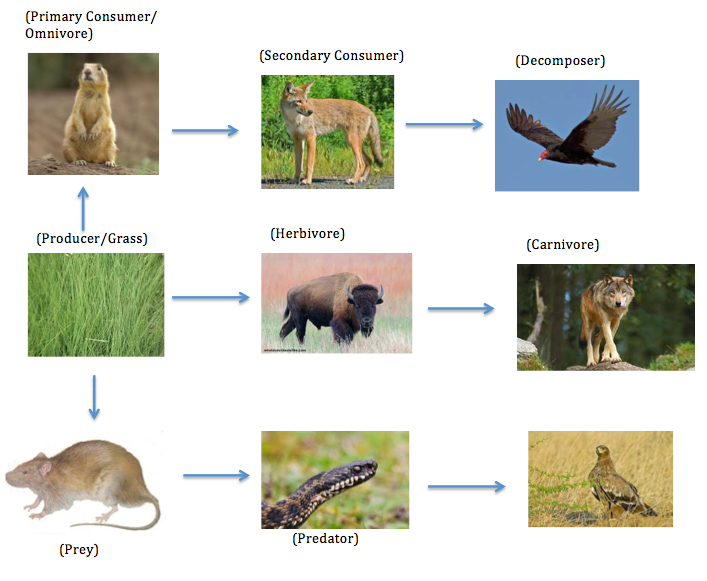
Food Chain Web Temperate Grassland Normally, food webs consist of a number of food chains meshed together. each food chain is a descriptive diagram including a series of arrows, each pointing from one species to another. This is an african savanna food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the trees, shrubs and grass. the primary consumers – the zebras and elephants. the secondary consumers – the cheetah, hyena. the scavengers – the termites, vultures and hyena. The food chains in an ecosystem intertwine to form a food web. this interactive shows a simplified grassland food web. each set of arrows links the organisms in one food chain. note that most organisms in a food web belong to multiple food chains. A food chain defines how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. it shows the feeding relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers in a habitat. producers, mainly plants, convert energy from the sun into food through photosynthesis. primary consumers, primarily herbivores, then consume this organic matter.
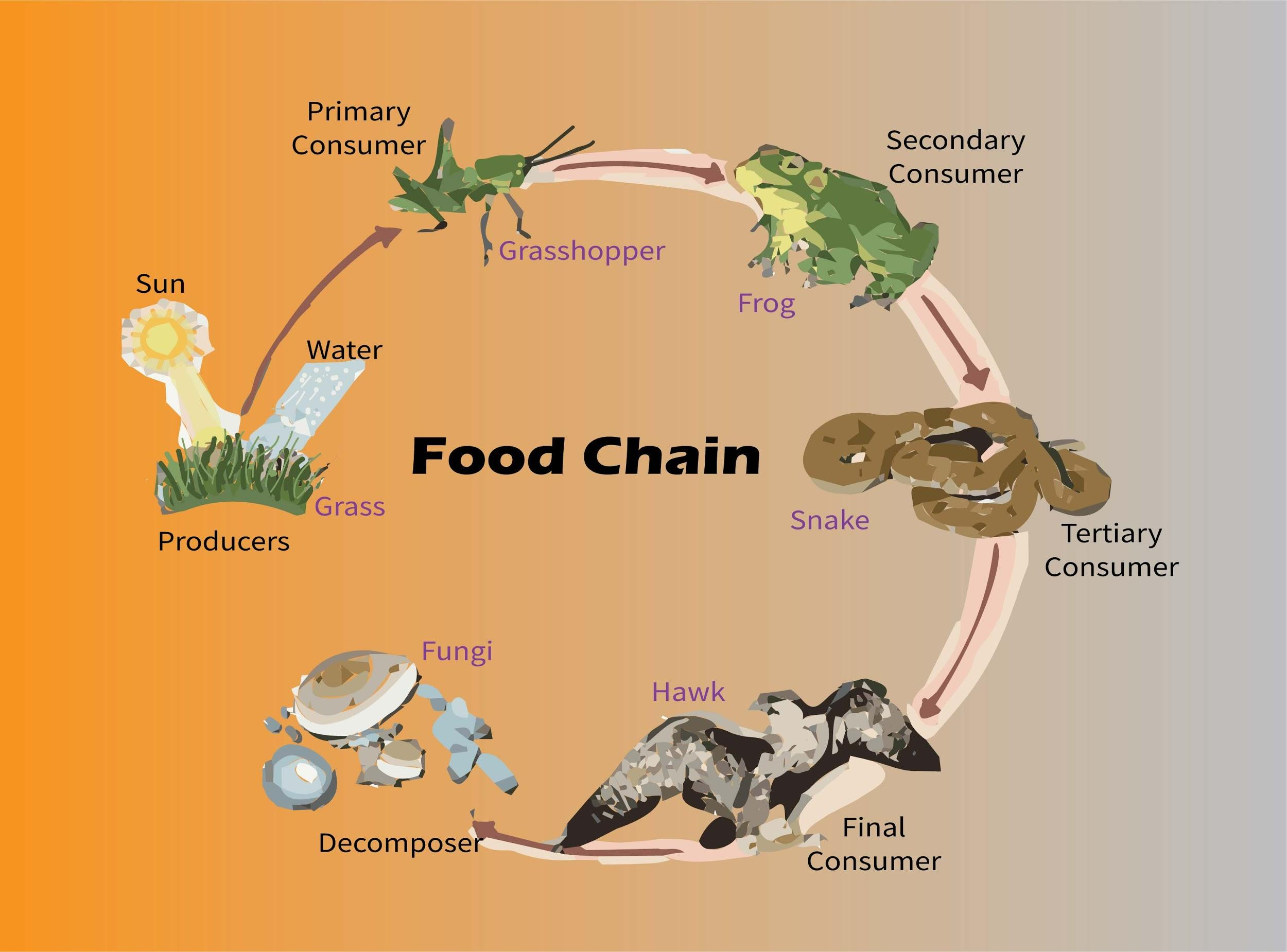
What Is The Correct Food Chain In Grassland A Grass Snake Insect Deer The food chains in an ecosystem intertwine to form a food web. this interactive shows a simplified grassland food web. each set of arrows links the organisms in one food chain. note that most organisms in a food web belong to multiple food chains. A food chain defines how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. it shows the feeding relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers in a habitat. producers, mainly plants, convert energy from the sun into food through photosynthesis. primary consumers, primarily herbivores, then consume this organic matter.
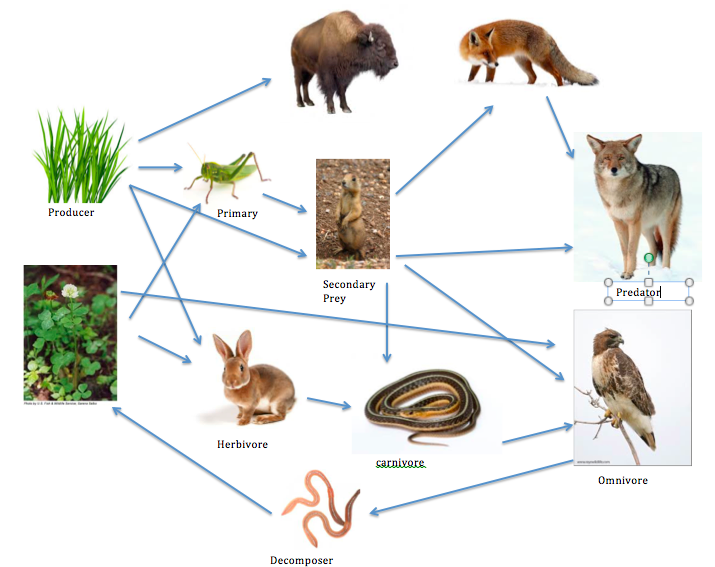
Food Chain And Food Web Temperate Grasslands

Comments are closed.