Greenhouse Temperature Control The Guide To An Evaporative Cooling
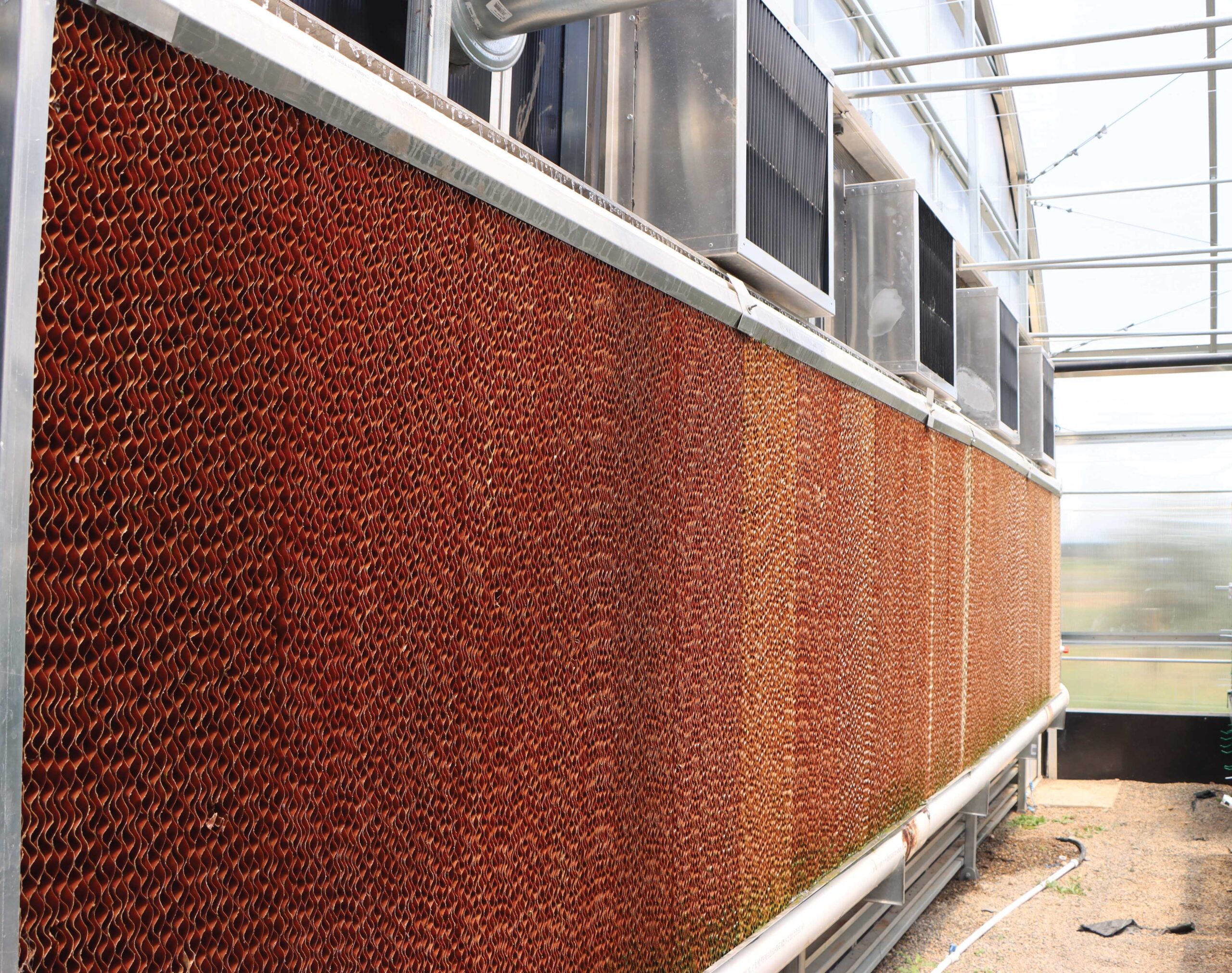

Greenhouse Temperature Control The Guide To An Evaporative Cooling Growspan’s evaporative cooling system uses a fan and pad technique. this method draws outdoor air into the greenhouse by exhaust fans. as the air passes through water soaked cooling pads, it is chilled, and then distributed across the greenhouse at crop level. this creates a constant, fresh stream of cooled air that simultaneously reduces the. Cut pipes, hoses, and rain gutters to desired lengths. cut rain gutter side pieces at a 45 degree angle as they will be the evaporative cooler’s frame. attach rain gutter caps for bottom piece of the frame (seal with silicone around the rubber) screw rain gutters into place. seal screws with silicone to avoid leaks.
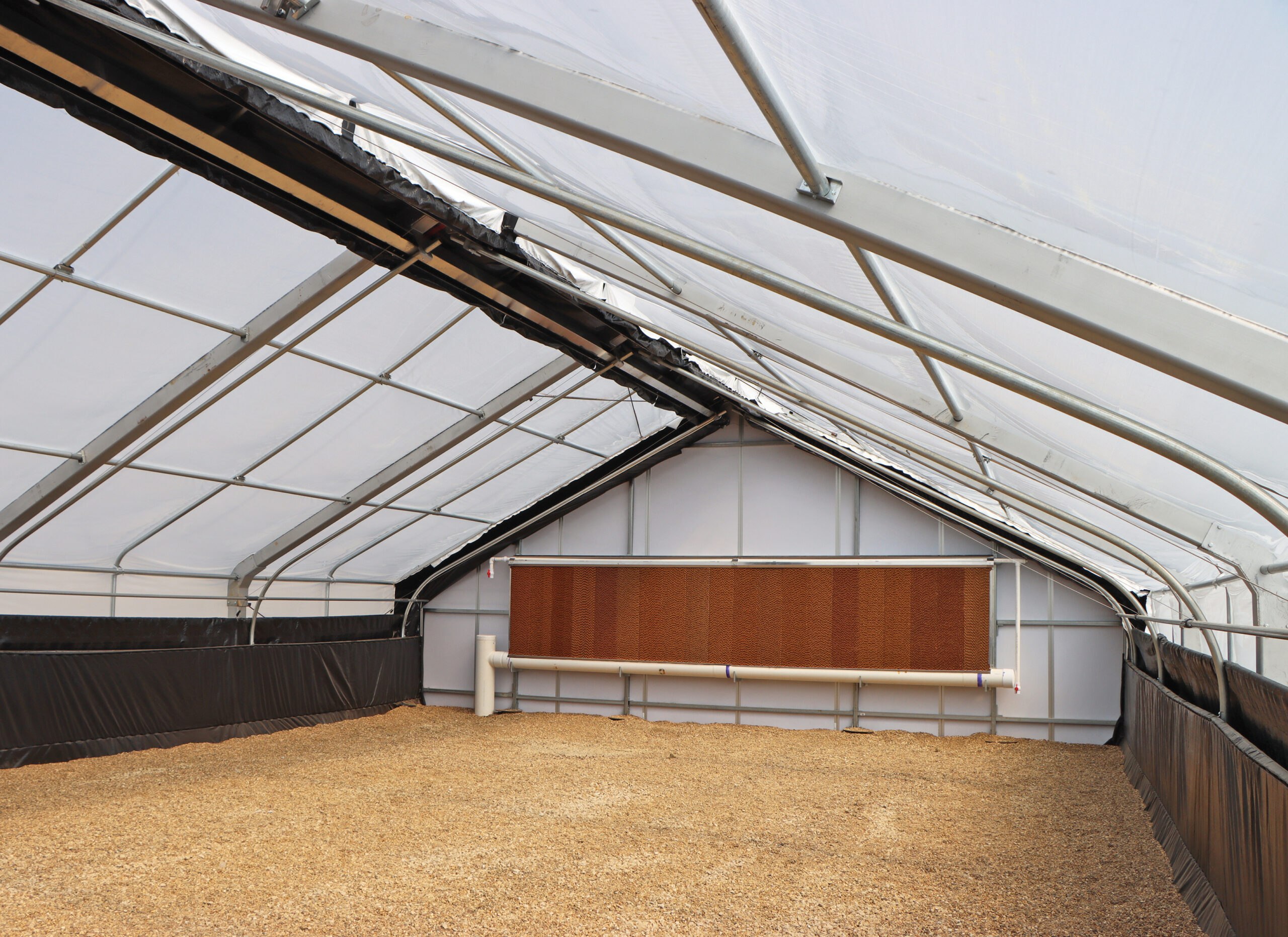

Greenhouse Temperature Control The Guide To An Evaporative Cooling 5. the maximum practical distance in the greenhouse from pad to fan should never exceed 200 feet. distances of 150 feet or fewer reduce the amount of temperature increase across the greenhouse. for most greenhouses, approximately one foot of pad height is required for every 20 feet of pad to fan distance. 6. Evaporative cooling: forced ventilation may reduce air temperature, but a greenhouse can still be hotter than outside during summer. in this situation, evaporative cooling can be used to cool a greenhouse. this method uses moist cooling pads to reduce the temperature of air entering the greenhouse. water added continuously. It should be clear that, like many other greenhouse systems, the design and control strategy for evaporative cooling systems requires some thought and attention. physical properties of air to use a psychrometric chart (figure 1) to help determine the maximum temperature drop resulting from the operation of an evaporative cooling system, it is. Control inside the greenhouse can be a challenge. greenhouses located in dry, dessert environments benefit greatly from evaporative cooling systems because large amounts of water can be evaporated into the incoming air, resulting in significant temperature drops. ity control since the relative humidity alone does not.
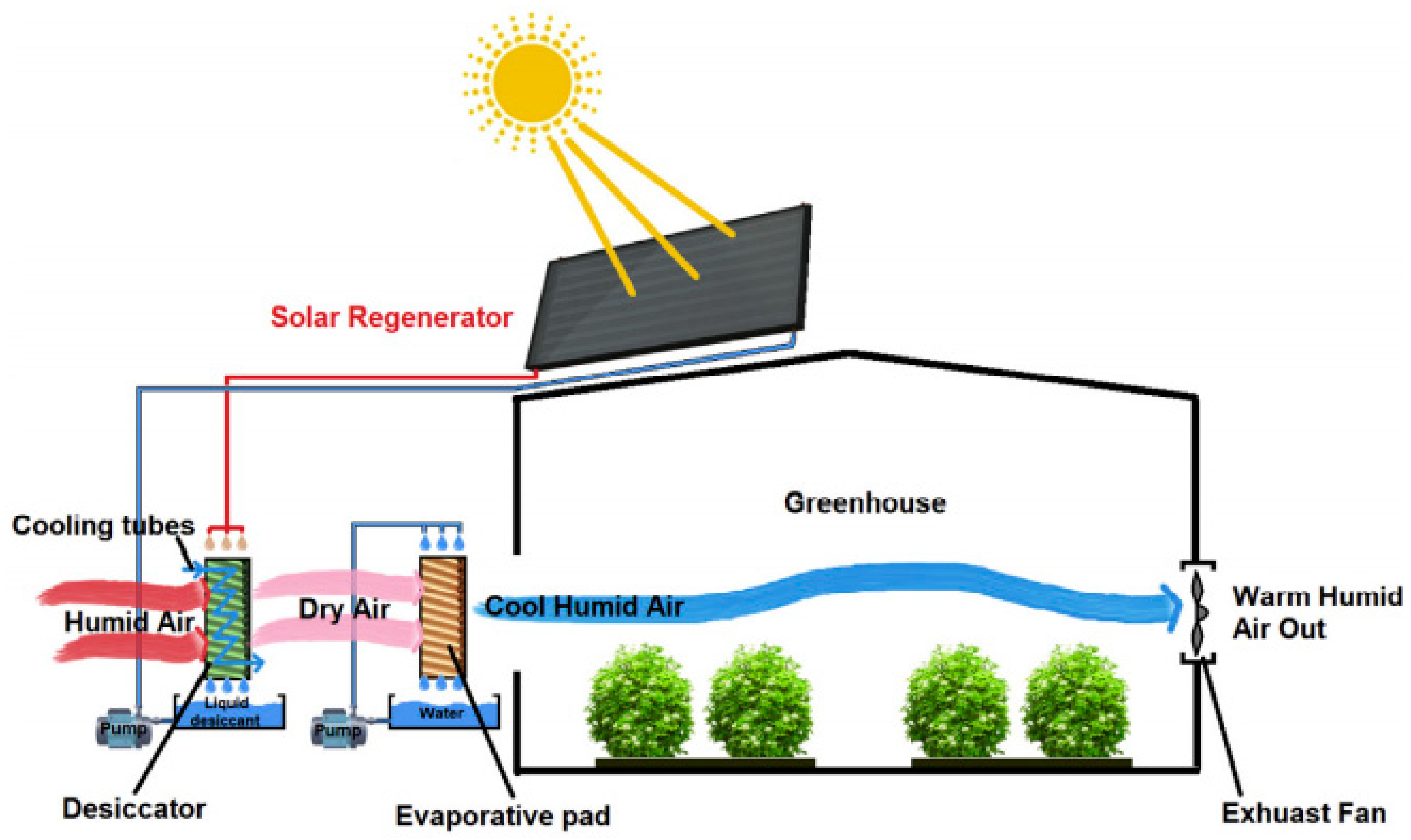
Evaporative Cooling System Greenhouse It should be clear that, like many other greenhouse systems, the design and control strategy for evaporative cooling systems requires some thought and attention. physical properties of air to use a psychrometric chart (figure 1) to help determine the maximum temperature drop resulting from the operation of an evaporative cooling system, it is. Control inside the greenhouse can be a challenge. greenhouses located in dry, dessert environments benefit greatly from evaporative cooling systems because large amounts of water can be evaporated into the incoming air, resulting in significant temperature drops. ity control since the relative humidity alone does not. Evaporative cooling, which uses the heat in the air to evaporate water from plants and other wetted surfaces can be used to cool the greenhouse as much as 10 to 20ºf below the outside temperature. although evaporative cooling is most effective in dryer climates, such as the southwest, it can provide cooling anywhere in the u.s. changing water from the liquid to the vapor phase absorbs. Unable to provide sufficient cooling for greenhouse temperature control, additional cooling is needed. two cooling systems, the pad and fan and the fog system, are commonly used in greenhouses and both make use of the cooling effect resulting from the evaporation of water (figures 2 and 3). the process of evaporation.
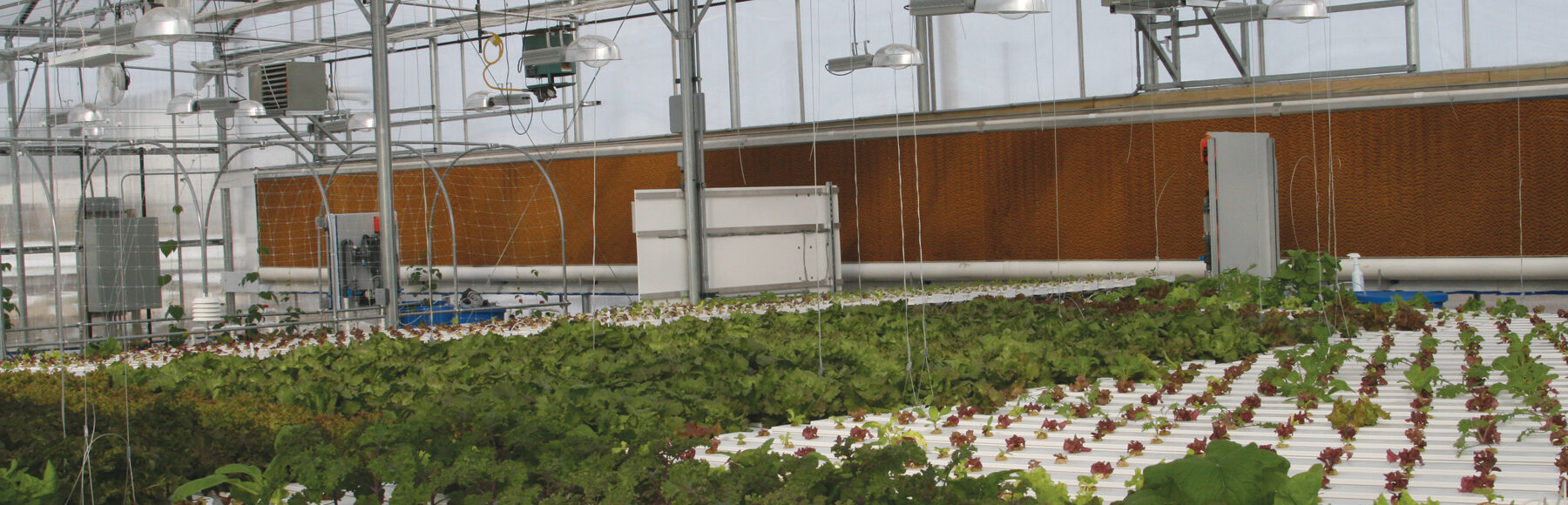

Greenhouse Temperature Control The Guide To An Evaporative Cooling Evaporative cooling, which uses the heat in the air to evaporate water from plants and other wetted surfaces can be used to cool the greenhouse as much as 10 to 20ºf below the outside temperature. although evaporative cooling is most effective in dryer climates, such as the southwest, it can provide cooling anywhere in the u.s. changing water from the liquid to the vapor phase absorbs. Unable to provide sufficient cooling for greenhouse temperature control, additional cooling is needed. two cooling systems, the pad and fan and the fog system, are commonly used in greenhouses and both make use of the cooling effect resulting from the evaporation of water (figures 2 and 3). the process of evaporation.

Guide To Evaporative Coolers In Greenhouses Greenhouse Info

Comments are closed.