Gregor Mendels Pea Experiment

Mendel S Experiments On Pea Plant Study Material Mendelian inheritance is a term arising from the singular work of the 19th century scientist and austrian monk gregor mendel. his experiments on pea plants highlighted the mechanisms of inheritance in organisms that reproduce sexually and led to the laws of segregation and independent assortment. By experimenting with pea plant breeding, mendel developed three principles of inheritance that described the transmission of genetic traits, before anyone knew genes existed. mendel's insight.
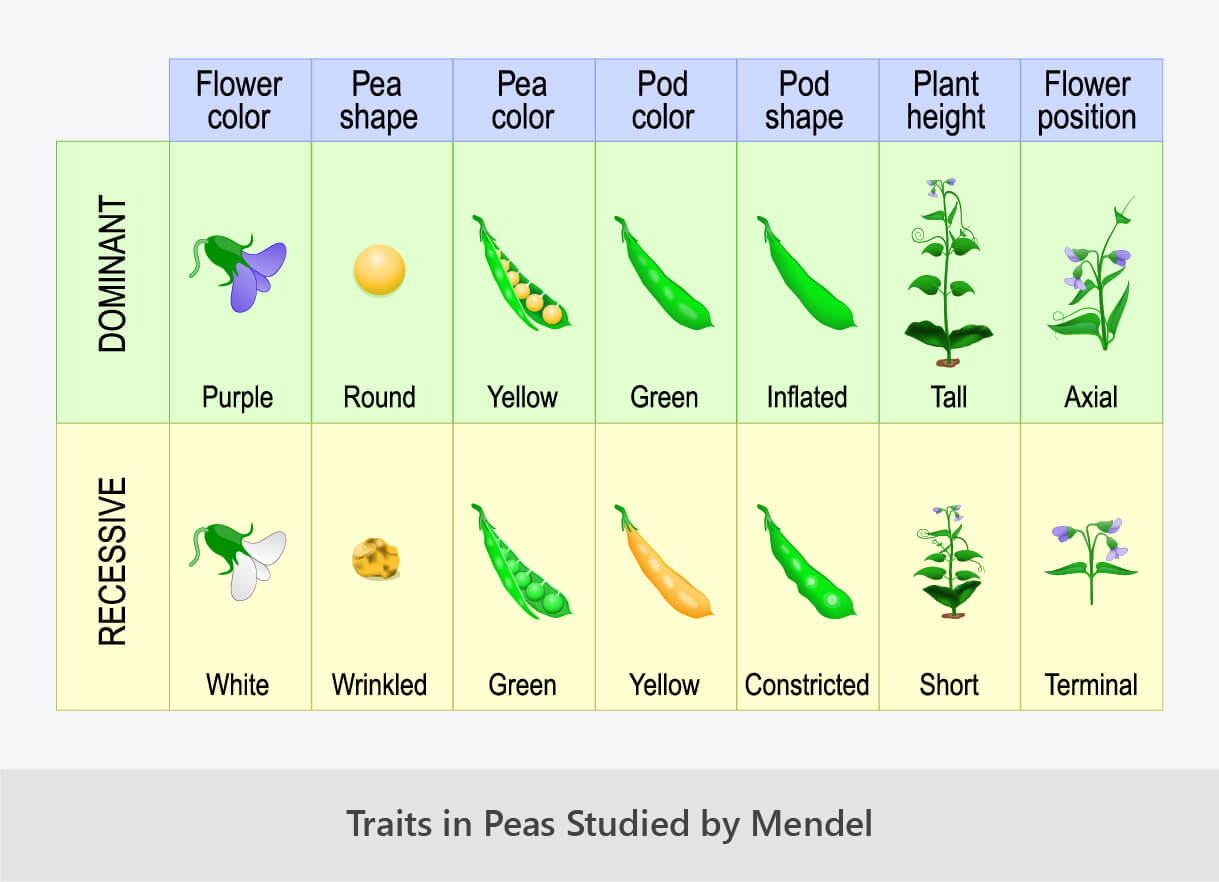
Mendelian Genetics Good Science Mendel’s findings were ignored. in 1866, mendel published the paper experiments in plant hybridisation (versuche über plflanzenhybriden). in it, he proposed that heredity is the result of each parent passing along 1 factor for every trait. if the factor is dominant, it will be expressed in the progeny. if the factor is recessive, it will not. Course: ap®︎ college biology > unit 5. lesson 2: mendelian genetics. introduction to heredity. fertilization terminology: gametes, zygotes, haploid, diploid. alleles and genes. worked example: punnett squares. mendel and his peas. the law of segregation. the law of independent assortment. Mendel carried out his key experiments using the garden pea, pisum sativum, as a model system. pea plants make a convenient system for studies of inheritance, and they are still studied by some geneticists today. useful features of peas include their rapid life cycle and the production of lots and lots of seeds. Key principles of genetics were developed from mendel’s studies on peas. 1. fundamental theory of heredity. inheritance involves the passing of discrete units of inheritance, or genes, from parents to offspring. mendel found that paired pea traits were either dominant or recessive. when pure bred parent plants were cross bred, dominant traits.
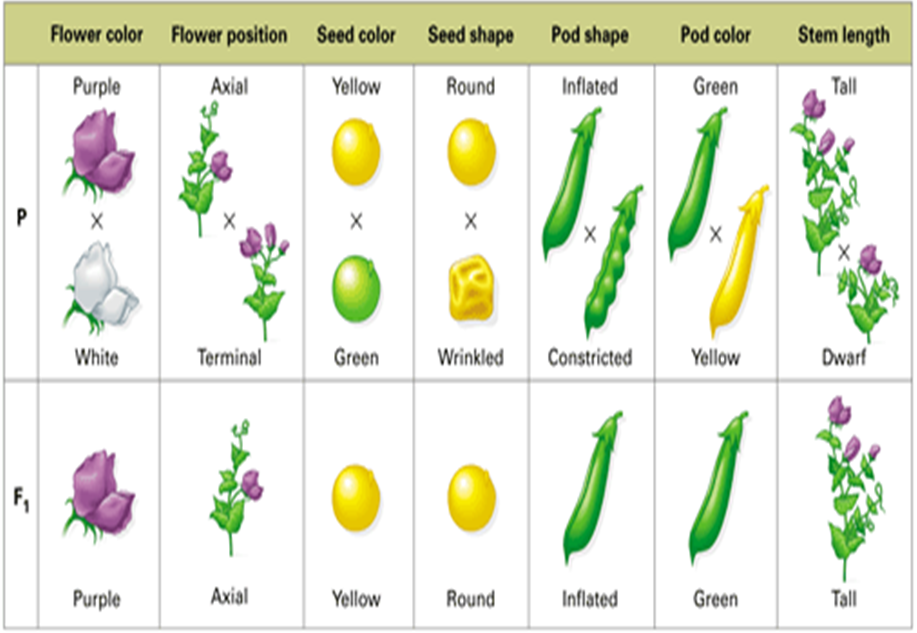
Mendel S Pea Plant Experiments Worksheet Answers Mendel carried out his key experiments using the garden pea, pisum sativum, as a model system. pea plants make a convenient system for studies of inheritance, and they are still studied by some geneticists today. useful features of peas include their rapid life cycle and the production of lots and lots of seeds. Key principles of genetics were developed from mendel’s studies on peas. 1. fundamental theory of heredity. inheritance involves the passing of discrete units of inheritance, or genes, from parents to offspring. mendel found that paired pea traits were either dominant or recessive. when pure bred parent plants were cross bred, dominant traits. The austrian monk gregor mendel experimented with pea plants. he did all of his research in the garden of the monastery where he lived. gregor mendel (figure 5.10.2) was born in 1822. he grew up on his parents’ farm in austria. he did well in school and became a friar (and later an abbot) at st. thomas’ abbey. E. mendelian inheritance (also known as mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by gregor mendel in 1865 and 1866, re discovered in 1900 by hugo de vries and carl correns, and later popularized by william bateson. [1] these principles were initially controversial.

Mendel S Experiments On Pea Plant Study Material The austrian monk gregor mendel experimented with pea plants. he did all of his research in the garden of the monastery where he lived. gregor mendel (figure 5.10.2) was born in 1822. he grew up on his parents’ farm in austria. he did well in school and became a friar (and later an abbot) at st. thomas’ abbey. E. mendelian inheritance (also known as mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by gregor mendel in 1865 and 1866, re discovered in 1900 by hugo de vries and carl correns, and later popularized by william bateson. [1] these principles were initially controversial.

Comments are closed.