H2o Covalent Bonding Water Formula Diagram Design For Chemistry Labs
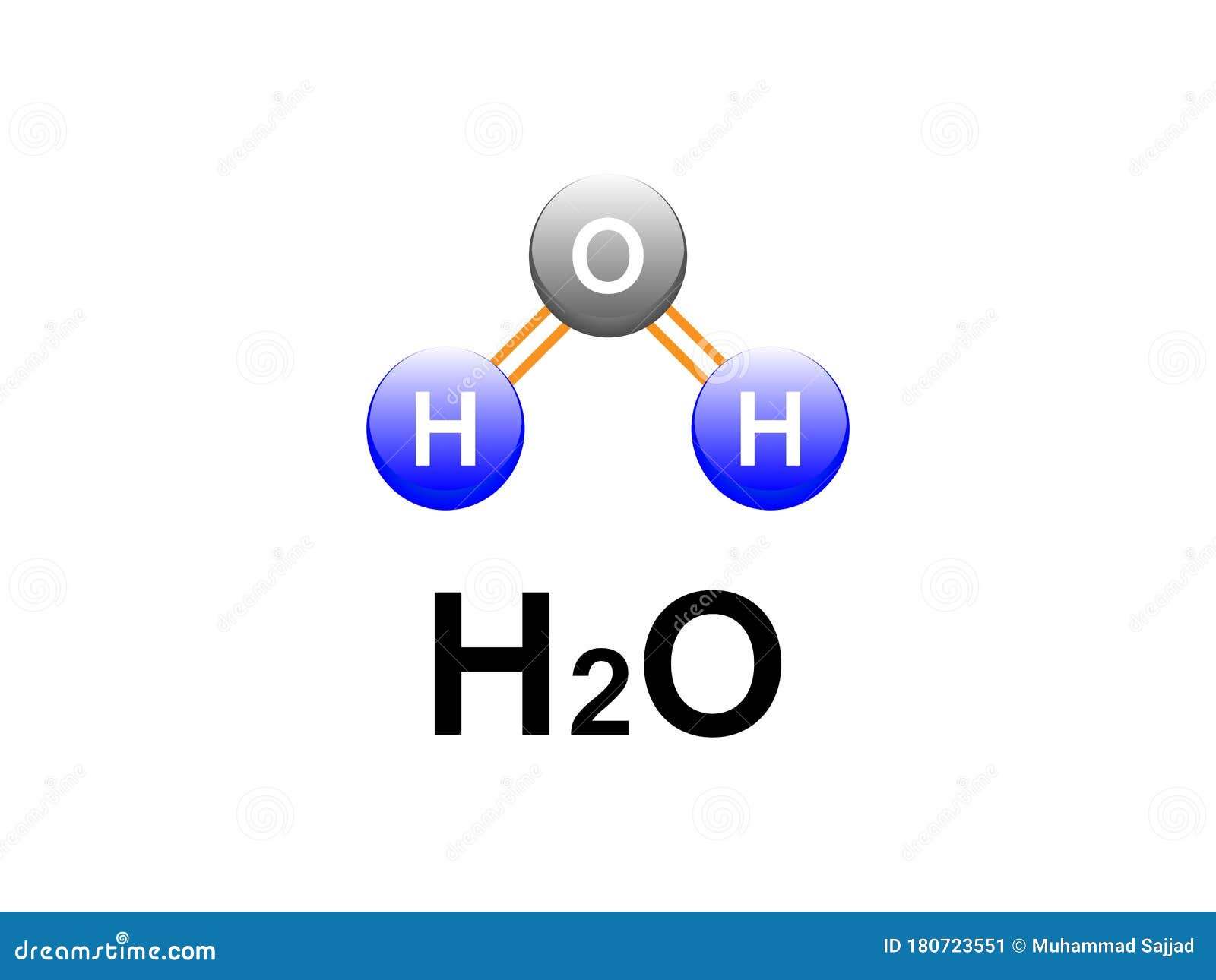
H2o Covalent Bonding Water Formula Diagram Design For Chemistry Labs This type of bonding would be a covalent bond. two combinations of atoms can produce this type of bonding: nonmetal nonmetal or metalloid nonmetal. in this class, we will not discuss the option of metallic bonding which is a form of covalent bonding. figure 4.8.1 4.8. 1: sharing is caring, especially for atoms that participate in covalent. The lewis structure of the triatomic h2o molecule shows two single sigma bonds between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. moreover, these bonds leave two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom that mainly contributes to the tetrahedral bent geometrical structure of the h2o molecule. it is the reason why the bond angle that should have.

H2o Covalent Bonding Water Formula Diagram Design For Chemistry Labs As a result, the water molecule’s molecular geometry is angular or v shaped. the bond angle in a water molecule (104.5°) hybridization of h 2 o. the lewis structure shows two single sigma bonds between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. besides that, these bonds leave the oxygen atom with two lone pairs of electrons. Hydrogen can only form 1 bond. two hydrogen atoms each share their 1 electron with oxygen to form two covalent bonds and make a water molecule (h 2 o). this is a picture of a water molecule. by sharing the two electrons where the shells touch each hydrogen atom can count 2 electrons in its outer shell and the oxygen atom can count 8 electrons. To determine the total number of valence electrons in water, we add up the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule. hydrogen (h) has 1 valence electron, and oxygen (o) has 6 valence electrons. since there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in water, the total number of valence electrons is: 2× (1) 6 = 8. Hydrogen bonds are the bonds between two water molecules. all molecules have covalent bonds, but only some molecules have hydrogen bonds. as an example, water has hydrogen bonds, but carbon dioxide does not. one of the requirements for hydrogen bonding is that the molecule must be polar. water molecules are polar because of two effects.
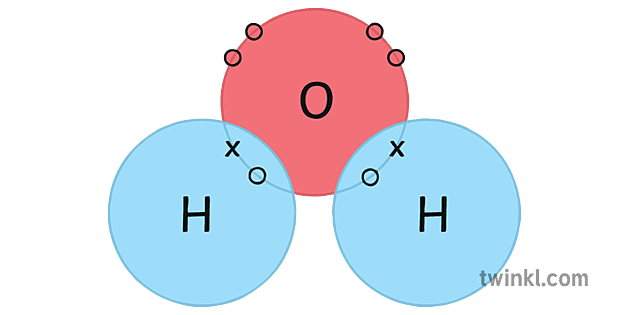
H2o Water Covalent Bonding Point Cross Diagram Science Ks4 Illustration To determine the total number of valence electrons in water, we add up the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule. hydrogen (h) has 1 valence electron, and oxygen (o) has 6 valence electrons. since there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in water, the total number of valence electrons is: 2× (1) 6 = 8. Hydrogen bonds are the bonds between two water molecules. all molecules have covalent bonds, but only some molecules have hydrogen bonds. as an example, water has hydrogen bonds, but carbon dioxide does not. one of the requirements for hydrogen bonding is that the molecule must be polar. water molecules are polar because of two effects. Relates to covalent bonding. add circles if necessary. extension draw a cluster diagram for each type of bond. lesson summary the octet rule in covalent bonding covalent compounds are most stable when each atom has eight electrons. single, double, and triple covalent bonds depend on the number of pairs of electrons shared between two atoms. Properties of water molecule. the water molecule, h2o, is made up of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. it is a small molecule, with a molecular weight of approximately 18 g mol. due to its unique structure and properties, water plays a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes. polarity: one of the key properties of.

Comments are closed.