High Rates Of Teen Anxiety And Depression Due To Coronavirus Pandemic
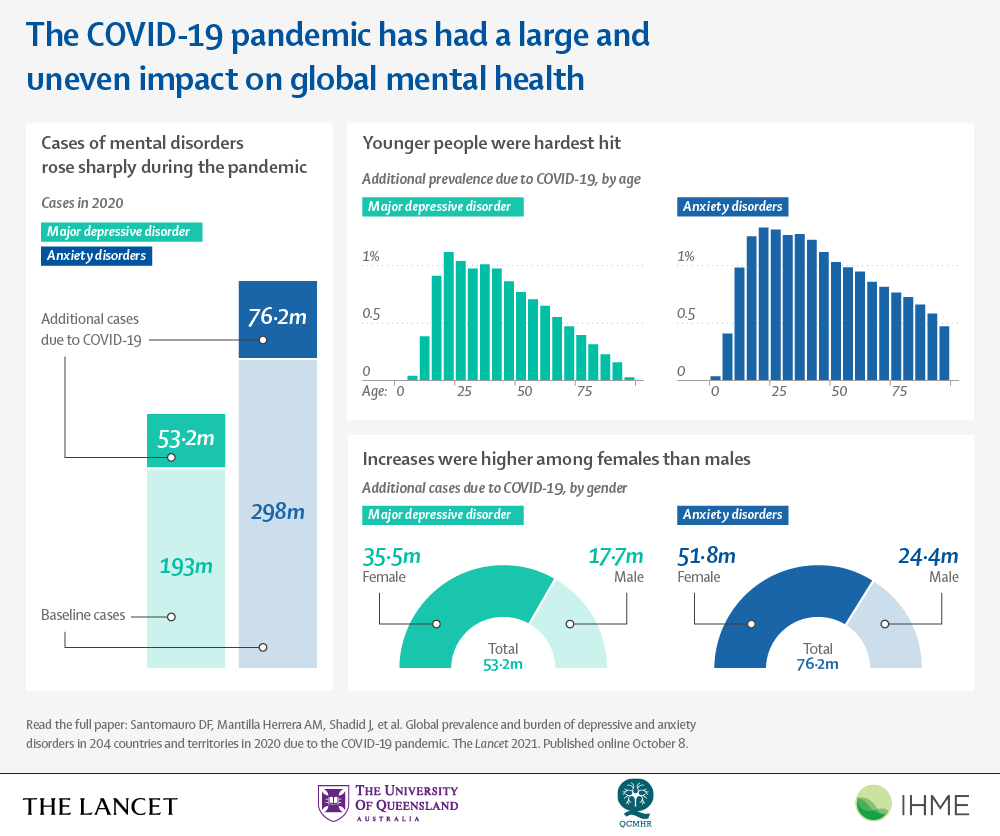
Covid 19 Pandemic Led To Stark Rise In Depression And Anxiety Disorders The kids are not all right, a new analysis suggests. during the covid 19 pandemic, depression and anxiety in youth doubled compared to pre pandemic levels, according to the research. one in 4. Rates of teen anxiety and depression are on the rise; between 2003 and 2021, depression and anxiety rates in teenagers have skyrocketed from 5.4% to 20% of all u.s. teens experiencing symptoms. (muiruri, 2021) covid 19 has impacted teens differently than adults because of the stage of development that teens are currently undergoing.
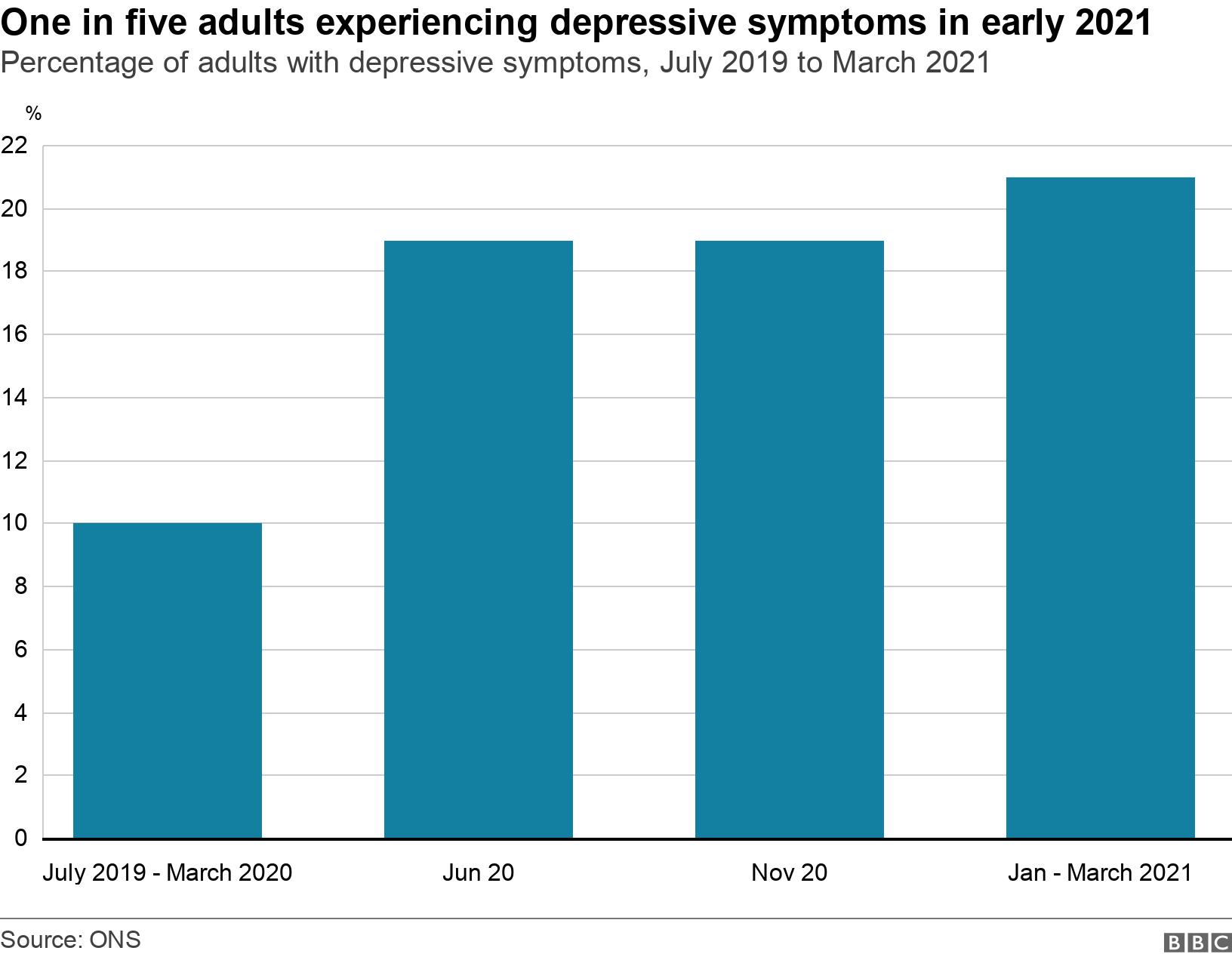
Covid Depression Rises In Young And Women During Second Peak According to the new data, in 2021, more than a third (37%) of high school students reported they experienced poor mental health during the covid 19 pandemic, and 44% reported they persistently felt sad or hopeless during the past year. the new analyses also describe some of the severe challenges youth encountered during the pandemic:. An emerging literature suggests that depression and anxiety symptoms may be elevated during the covid 19 pandemic, and that certain populations (e.g. women, individuals living in areas with a high density of covid 19 cases) are more vulnerable to worsening mental health during the pandemic (torales, o'higgins, castaldelli maia, & ventriglio. Compared to carefully matched peers assessed before the pandemic, adolescents who lived through the pandemic related shutdowns and continued to experience covid 19’s ongoing disruptions had greater cortical thinning and larger hippocampal and amygdala volumes—neural alterations that may reflect accelerated brain aging. The incidence of anxiety without depression also increased, from 1.77% in 2017 to 2.32% in 2021, a 31.1% rise. similar to depression, the incidence of anxiety without depression was highest among.
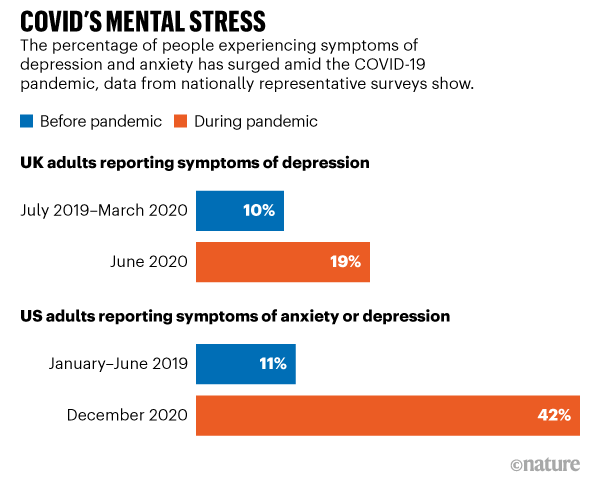
Covid S Mental Health Toll How Scientists Are Tracking A Surge In Compared to carefully matched peers assessed before the pandemic, adolescents who lived through the pandemic related shutdowns and continued to experience covid 19’s ongoing disruptions had greater cortical thinning and larger hippocampal and amygdala volumes—neural alterations that may reflect accelerated brain aging. The incidence of anxiety without depression also increased, from 1.77% in 2017 to 2.32% in 2021, a 31.1% rise. similar to depression, the incidence of anxiety without depression was highest among. Español. in the first year of the covid 19 pandemic, global prevalence of anxiety and depression increased by a massive 25%, according to a scientific brief released by the world health organization (who) today. the brief also highlights who has been most affected and summarizes the effect of the pandemic on the availability of mental health. Two longitudinal studies on adolescent mental health during the pandemic found increases in depression and anxiety over the course of the pandemic (4,5). in one study, these symptoms were predicted by covid 19–related worries, online learning difficulties, and increased conflict with parents ( 4 ).

Global Prevalence And Burden Of Depressive And Anxiety Disorders In 204 Español. in the first year of the covid 19 pandemic, global prevalence of anxiety and depression increased by a massive 25%, according to a scientific brief released by the world health organization (who) today. the brief also highlights who has been most affected and summarizes the effect of the pandemic on the availability of mental health. Two longitudinal studies on adolescent mental health during the pandemic found increases in depression and anxiety over the course of the pandemic (4,5). in one study, these symptoms were predicted by covid 19–related worries, online learning difficulties, and increased conflict with parents ( 4 ).
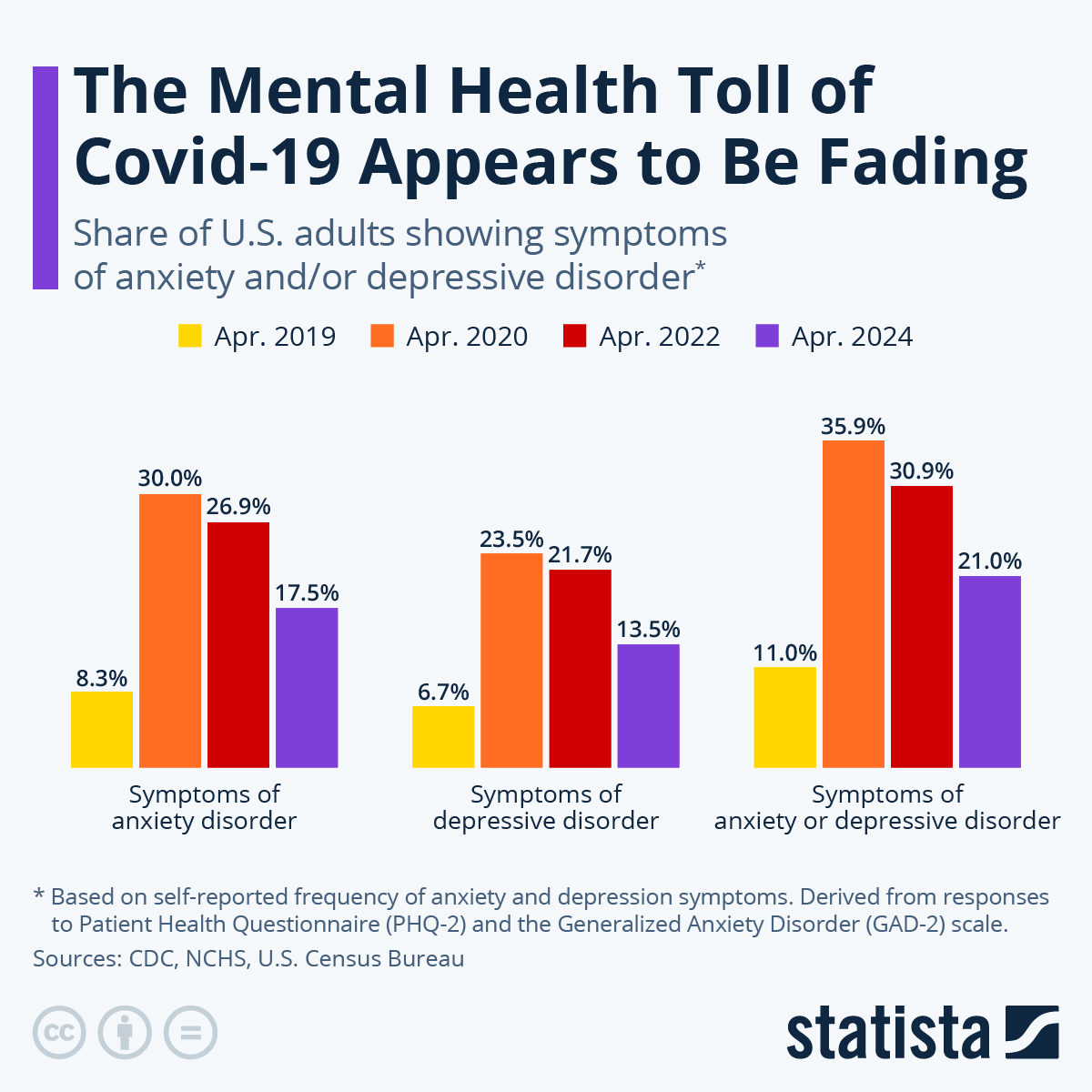
Chart The Mental Health Toll Of Covid 19 Appears To Be Fading Statista
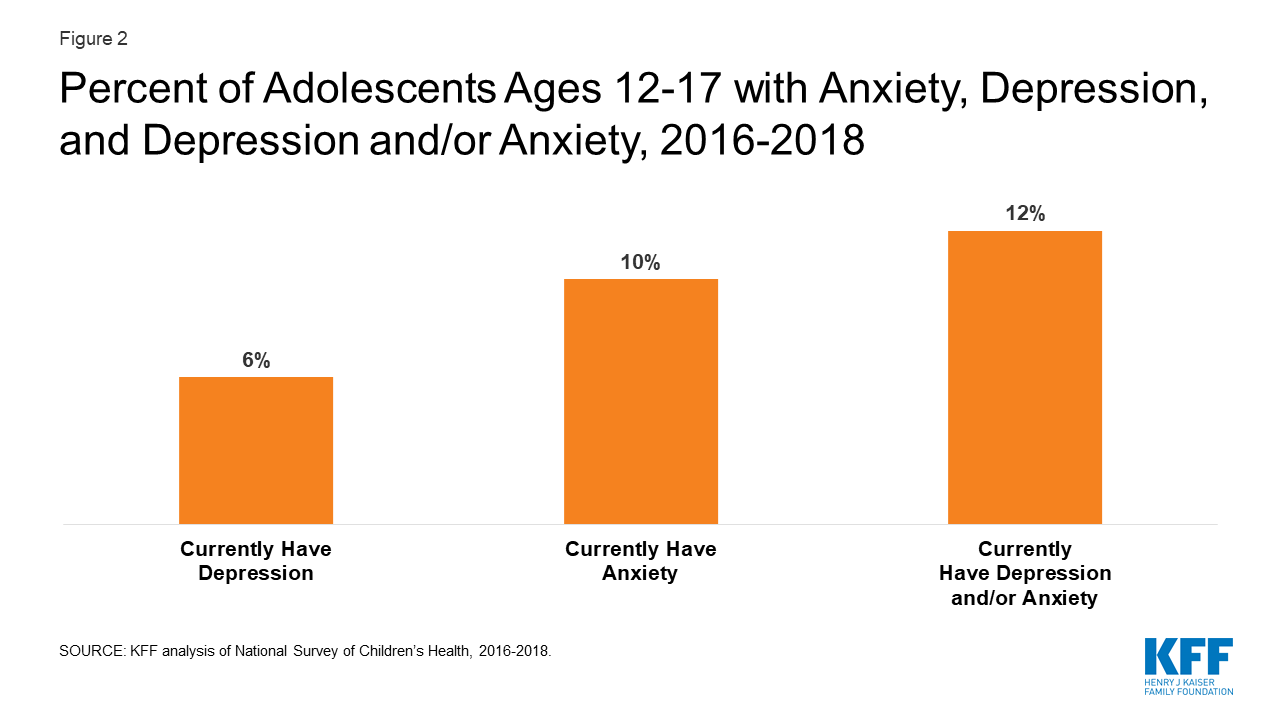
The Implications Of Covid 19 For Mental Health And Substance Use Kff

Comments are closed.