How Does Reverse Osmosis Work

How Does Reverse Osmosis Work Advanced Water Solutions Learn how reverse osmosis is used to desalinate seawater, recycle water, and produce energy. find out how pressure and membranes make water molecules move against their natural tendency. Reverse osmosis (ro) is a water purification process that uses a semi permeable membrane to separate water molecules from other substances. ro applies pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors even distributions and can remove dissolved or suspended chemical species as well as biological substances.

What Is Reverse Osmosis Water Purification Pure Water Systems Reverse osmosis is a water filtration method that uses pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane and remove contaminants. learn how reverse osmosis systems work, what they remove, and why they are beneficial for your water quality. Reverse osmosis is a technique that uses pressure to force solvent through a membrane from a low concentration to a high concentration region, leaving behind the solutes. learn how reverse osmosis works, its applications, and its advantages over distillation. Reverse osmosis is a filtration method that uses pressure to force water across a semipermeable membrane, removing ions and molecules from a solution. learn how reverse osmosis differs from diffusion and osmosis, and how it is used for water purification and desalination. Reverse osmosis is a water purification method that presses water through a semi permeable membrane. learn how it works, what it removes, and what are its advantages and disadvantages.

How Does Reverse Osmosis Work The Complete Guide On Ro Reverse osmosis is a filtration method that uses pressure to force water across a semipermeable membrane, removing ions and molecules from a solution. learn how reverse osmosis differs from diffusion and osmosis, and how it is used for water purification and desalination. Reverse osmosis is a water purification method that presses water through a semi permeable membrane. learn how it works, what it removes, and what are its advantages and disadvantages. There are four common stages of all reverse osmosis systems: a sediment pre filter, an activated carbon stage, the reverse osmosis membrane, and a post or polishing filter. 1. sediment pre filter. water contains a number of large sediment particles such as dust, rust, salt, and sand. Learn how reverse osmosis works opposite to osmosis by applying external pressure to separate pure water from impurities. find out the advantages and disadvantages of this technique and its uses in water purification, desalination, and more.
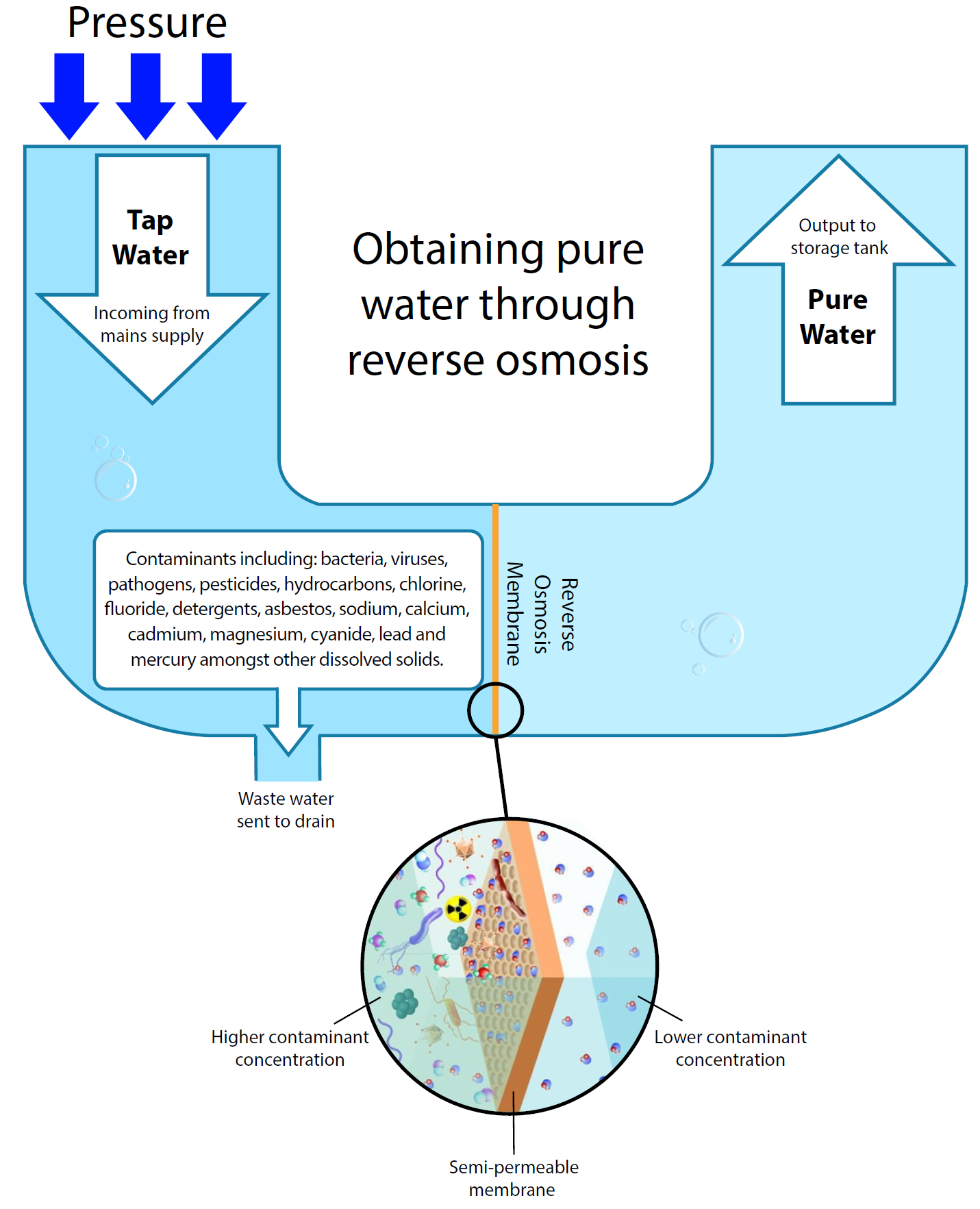
What Is Reverse Osmosis And How Does It Work There are four common stages of all reverse osmosis systems: a sediment pre filter, an activated carbon stage, the reverse osmosis membrane, and a post or polishing filter. 1. sediment pre filter. water contains a number of large sediment particles such as dust, rust, salt, and sand. Learn how reverse osmosis works opposite to osmosis by applying external pressure to separate pure water from impurities. find out the advantages and disadvantages of this technique and its uses in water purification, desalination, and more.
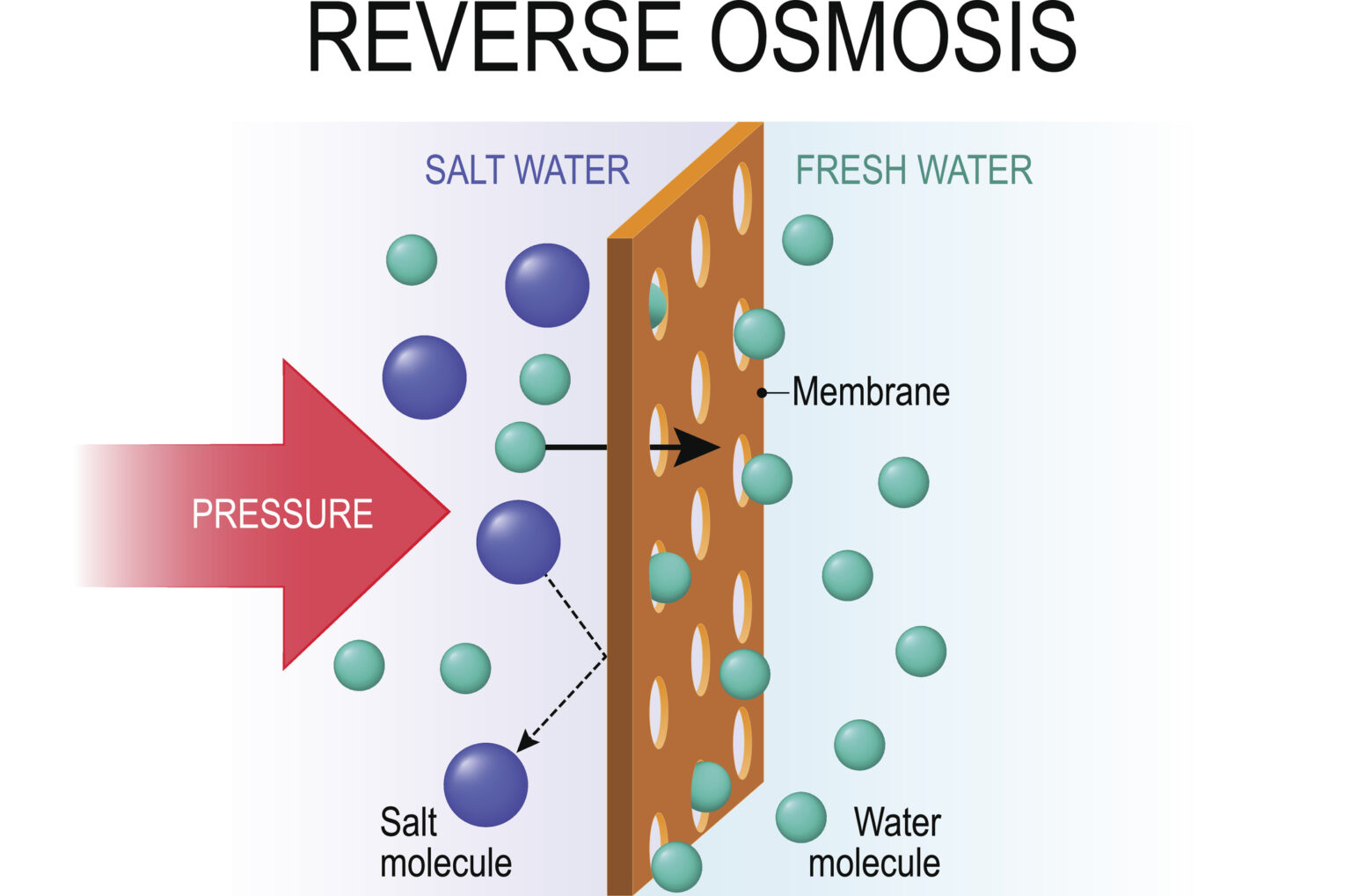
What Is Reverse Osmosis And How Is It Used For Industrial Applications

How Does Home Reverse Osmosis System Work At Monique Slezak Blog

Comments are closed.