How To Determine The Reaction Order Chemistry Steps

Determine A → products. rate = k[a]n. where k is the rate constant and n is the reaction order. our objective is to determine the reaction order by calculating the n from a set of experiments. keep in mind that: if n = 0, the reaction is zero order, and the rate is independent of the concentration of a. if n = 1, the reaction is first order, and the. Using equation 14.22 and the data from any row in table 14.3, we can calculate the rate constant. substituting values at time 10 min, for example, gives the following: rate = k[a]2 8.0 × 10 − 5 m min = k(4.4 × 10 − 3 m)2 4.1 m − 1 ⋅ min − 1 = k. we can also determine the reaction order using the integrated rate law.
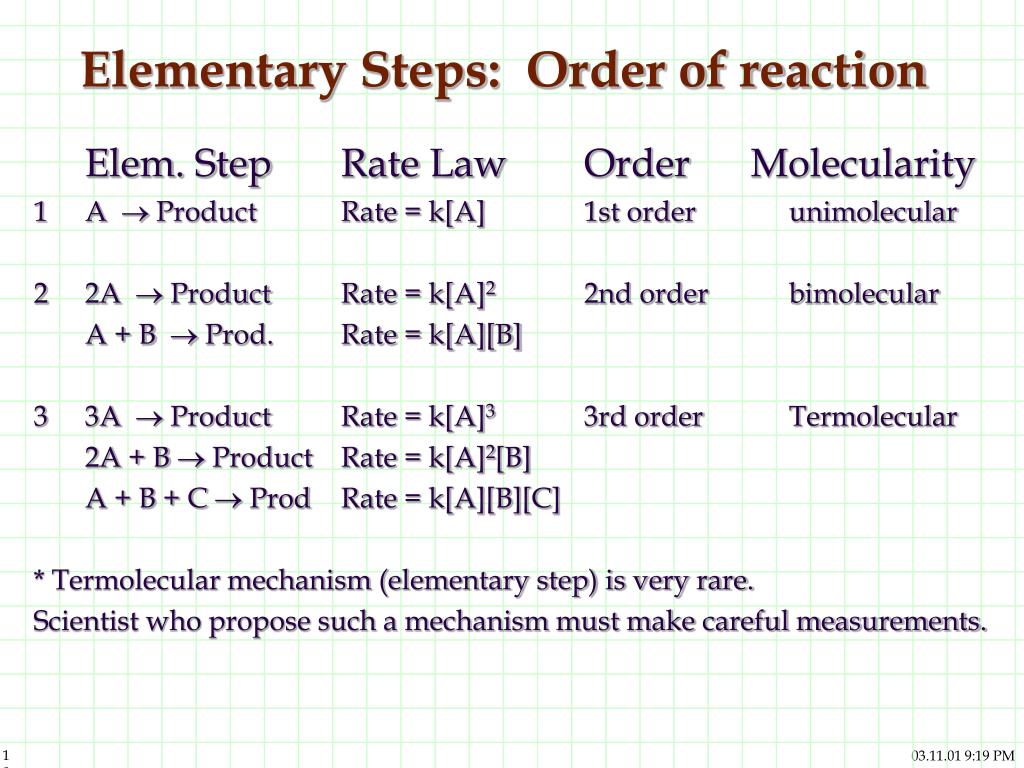
Ppt Reaction Mechanisms Steps Of A Reaction Powerpoint Presentation Given the rate law equation: rate = k[a]1[b]2. 2. determine: a) the reaction order with respect to a, b) the reaction order with respect to b, and c) the total reaction order for the equation. 3. assuming the reaction occurs in one elementary step, propose a chemical equation using p as the symbol for your product. For a simple reaction with one reactant, the rate law could be written as: a → products. rate = k[a]n. where k is the rate constant and n is the reaction order. the rate constant is the proportionality constant between the reaction rate and the concentration of reactant (s). the value of n is the reaction order, and it determines how the rate. The reaction is zero order in c, and the rate does not depend on its concentration. the reason is that c is present in such a vast amount that its concentration change does not affect the reaction rate. how to determine the reaction order. in the case of an elementary (single step) reaction, the reaction order is easy to determine. it is the. Determine the order of a reaction. the order of a reaction is simply the sum of the exponents on the. rate = k[a]x[b]y reaction order = x y. a]1[b]0 = k [a]is 1st order in [a]and 0th order in. [b] and 1st order for the reaction.example 2: rate = k [a]3[b]0.5 is 3rd order in [a], half. eed to know the order of a reactionbecause it tells us the.
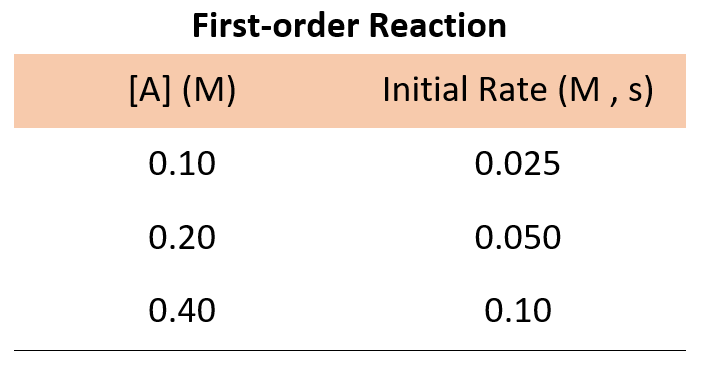
How To Determine The Reaction Order Chemistry Steps The reaction is zero order in c, and the rate does not depend on its concentration. the reason is that c is present in such a vast amount that its concentration change does not affect the reaction rate. how to determine the reaction order. in the case of an elementary (single step) reaction, the reaction order is easy to determine. it is the. Determine the order of a reaction. the order of a reaction is simply the sum of the exponents on the. rate = k[a]x[b]y reaction order = x y. a]1[b]0 = k [a]is 1st order in [a]and 0th order in. [b] and 1st order for the reaction.example 2: rate = k [a]3[b]0.5 is 3rd order in [a], half. eed to know the order of a reactionbecause it tells us the. That means that that particular term disappears from the rate equation. the overall order of the reaction is found by adding up the individual orders. for example, if the reaction is first order with respect to both a and b (a = 1 and b = 1), the overall order is 2. we call this an overall second order reaction. Mechanism 2. remember that in simple cases, where the slow step is the first step of the mechanism, the orders tell you what is taking part in the slow step. in this case, the reaction is first order with respect to both a and b, so one molecule of each must be taking part in the slow step. that means that mechanism 2 is possible.

3 Ways To Determine Order Of Reaction Wikihow That means that that particular term disappears from the rate equation. the overall order of the reaction is found by adding up the individual orders. for example, if the reaction is first order with respect to both a and b (a = 1 and b = 1), the overall order is 2. we call this an overall second order reaction. Mechanism 2. remember that in simple cases, where the slow step is the first step of the mechanism, the orders tell you what is taking part in the slow step. in this case, the reaction is first order with respect to both a and b, so one molecule of each must be taking part in the slow step. that means that mechanism 2 is possible.

How To Determine Reaction Order

How To Determine The Order Of Reaction By Comparing Initial Rates Of

Comments are closed.