If Free Trade Is Allowed Consumer Surplus Is The Area
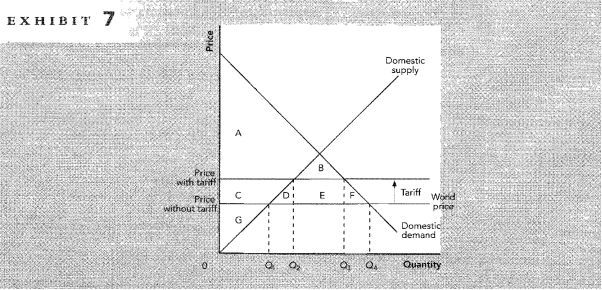
Solved 1 If Free Trade Is Allowed Consumer Surplus Is The Area A Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like if a tariff is placed on this good, consumer surplus is the area ., if free trade is allowed, consumer surplus is the area ., which of the following is not employed as an argument in support of trade restrictions? and more. A b. use exhibit to answer questions, if free trade is allowed, consumer surplus is the area. a. use exhibit to answer questions, if trade is not allowed, producer surplus is the area. c. use exhibit to answer questions, if free trade is allowed, producer surplus is the area. b c d.

Solved Use Exhibit 6 To Answer Questions 5 Through 9 If Free Trad Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. question: a. if free trade is allowed, consumer surplus is the area a. a b. a. if free trade is allowed, consumer surplus is the area. a. B. $72. c. $24. d. $144. a. $96. scenario 9 1 the before trade domestic price of peaches in the united states is $40 per bushel. the world price of peaches is $52 per bushel. the u.s. is a price taker in the market for peaches. refer to scenario 9 1. if trade in peaches is allowed, u.s. producers of peaches. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. The \(cs\) area is a triangle, and equal to the level of consumer surplus in the market (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)). similarly, the intuition of producer surplus is a good place to start. if a wheat producer can produce a bushel of wheat for four dollars, and she receives six dollars per bushel when she sells her wheat, then her level of.

Draw The Supply And Demand Diagram For An Importing Country Identify Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. The \(cs\) area is a triangle, and equal to the level of consumer surplus in the market (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)). similarly, the intuition of producer surplus is a good place to start. if a wheat producer can produce a bushel of wheat for four dollars, and she receives six dollars per bushel when she sells her wheat, then her level of. How free trade affects consumer and producer surplus. free trade means a reduction in tariffs. it leads to lower prices for consumers and an increase in consumer surplus. if tariffs are cut, then we can import at s eu (p1) – a lower price than p2. imports increase from (q3 q2) to (q4 q1) however, domestic producers see a decline in producer. Refer to table 9.17 "welfare effects of free trade area formation: trade creation case" and figure 9.12 "trade creation" to see how the magnitude of the change in consumer surplus is represented. free trade area effects on country a’s producers. producers in the importing country suffer losses as a result of the free trade area.

Ppt International Trade Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id How free trade affects consumer and producer surplus. free trade means a reduction in tariffs. it leads to lower prices for consumers and an increase in consumer surplus. if tariffs are cut, then we can import at s eu (p1) – a lower price than p2. imports increase from (q3 q2) to (q4 q1) however, domestic producers see a decline in producer. Refer to table 9.17 "welfare effects of free trade area formation: trade creation case" and figure 9.12 "trade creation" to see how the magnitude of the change in consumer surplus is represented. free trade area effects on country a’s producers. producers in the importing country suffer losses as a result of the free trade area.

Comments are closed.