Images And Name Sof Best Vascular Plants For Kids
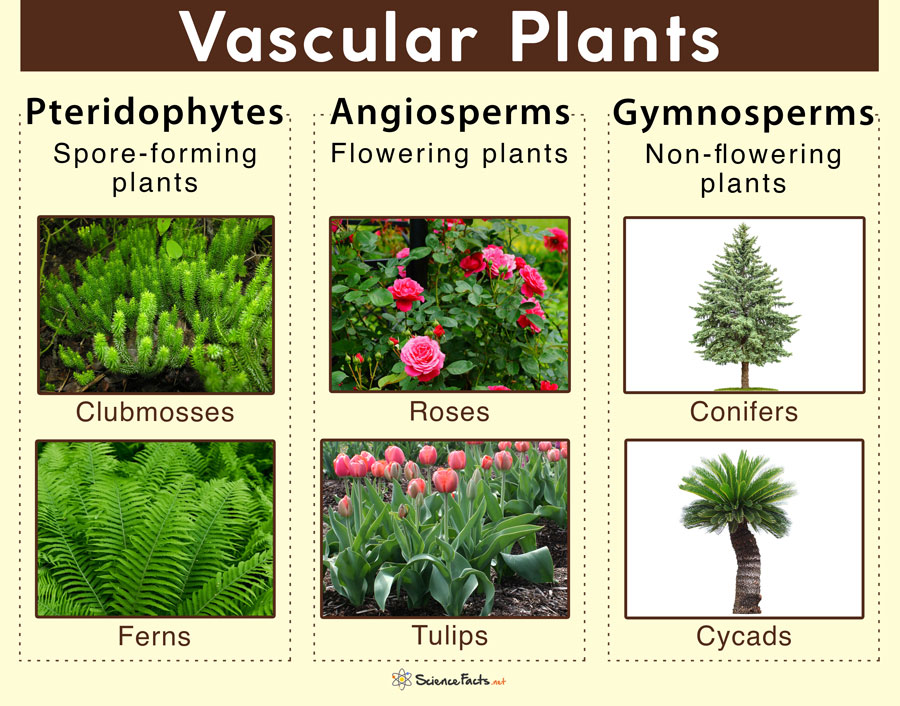
Vascular Plants вђ Definition Characteristics Examples Diagram The vascular plants, or tracheophytes, are plants that have specialized tissues for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. they include the ferns, clubmosses, horsetails, flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms. they are often called the higher plants. the vascular plants are set apart in two main. Vascular plants. vascular plants (from latin word ‘vasculum’ meaning duct), also known as tracheophytes (from greek word ‘trachea’, a duct or tube), are land plants containing specialized vascular conducting tissues. they are found almost everywhere on earth. common examples of vascular plants include trees, shrubs, grasses, flowering.

Vascular Plants Click Learn Botany For Kids Vascular Plant The lilies, maple trees, elm and sunflower. most of the vascular plants examples start by making of fruit that has the seeds and also includes the peanuts, cones of pines and the apple with peppers kind of trees. there are very less trees that are said to be without seed and make spore for generation. Evolution of vascular plants. the first vascular plants evolved about 420 million years ago. they probably evolved from moss like bryophyte ancestors, but they had a life cycle dominated by the diploid sporophyte generation. as they continued to evolve, early vascular plants became more plant like in other ways as well. vascular plants evolved. Vascular plant definition. a vascular plant is any one of a number of plants with specialized vascular tissue. the two types of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, are responsible for moving water, minerals, and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. as opposed to a non vascular plant, a vascular plant can grow much larger. Definition. fern. vascular seedless plant with large divided leaves called fronds; more plant like than the clubmosses; have stems, leaves, and roots. horsetail. vascular seedless plant with hollow, ribbed stems; it is often found in marshes. vascular seedless plant. plant with vascular tissue but no seeds or flowers.

Vascular Plants For Kids Vascular plant definition. a vascular plant is any one of a number of plants with specialized vascular tissue. the two types of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, are responsible for moving water, minerals, and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. as opposed to a non vascular plant, a vascular plant can grow much larger. Definition. fern. vascular seedless plant with large divided leaves called fronds; more plant like than the clubmosses; have stems, leaves, and roots. horsetail. vascular seedless plant with hollow, ribbed stems; it is often found in marshes. vascular seedless plant. plant with vascular tissue but no seeds or flowers. Vascular plants evolved true roots made of vascular tissues. compared with rhizoids, roots can absorb more water and minerals from the soil. they also anchor plants securely in the ground, so plants can grow larger without toppling over. vascular plants evolved stems made of vascular tissues and lignin. because of lignin, stems are stiff, so. Vascular plant facts. the vascular plants, or tracheophytes, are plants that have specialized tissues for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. they include the ferns, clubmosses, horsetails, flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms.[1] they are often called the higher plants.[2][3][4][5].

Comments are closed.