Imaging Intracranial Hemorrhage Case 6 Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Caa

Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Caa Medlink Neurology Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is a cerebrovascular disorder caused by the accumulation of cerebral amyloid β (aβ) in the tunica media and adventitia of leptomeningeal and cortical vessels of the brain. the resultant vascular fragility tends to manifest in normotensive elderly patients as lobar intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is an important but underrecognized cause of cerebrovascular disorders that predominantly affect elderly patients. caa results from deposition of β amyloid protein in cortical, subcortical, and leptomeningeal vessels. this deposition is responsible for the wide spectrum of clinical symptoms and neuroimaging findings. many cases of caa are asymptomatic.

Imaging Intracranial Hemorrhage Case 6 Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy The history of how to diagnosis cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) tells the story of the disease itself. caa is defined by histopathology—deposition of β amyloid in the cerebrovasculature—and through the 1980s the disorder was only diagnosed in patients with available brain tissue from hematoma evacuation, biopsy, or most commonly postmortem examination. 1 introduction of the imaging. Abstract. cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is a cerebral small vessel disease caused by β amyloid (aβ) deposition at the leptomeningeal vessel walls. it is a common cause of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage and a frequent comorbidity in alzheimer’s disease. the high recurrent hemorrhage rate in caa makes it very important to recognize. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is a type of cerebrovascular disorder characterized by the accumulation of amyloid beta peptide within the leptomeninges and small medium sized cerebral blood vessels.[1] the amyloid deposition results in fragile vessels that may manifest in lobar intracerebral hemorrhages (ich). it may also present with cognitive impairments, incidental microbleeds. Still a syndromal diagnosis. cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is a common form of cerebral small vessel disease, due to progressive amyloid β deposition in the walls of small leptomeningeal and cortical arteries and cortical capillaries. 1 the main clinical manifestations of caa are lobar intracerebral hemorrhage (ich) and cognitive impairment.
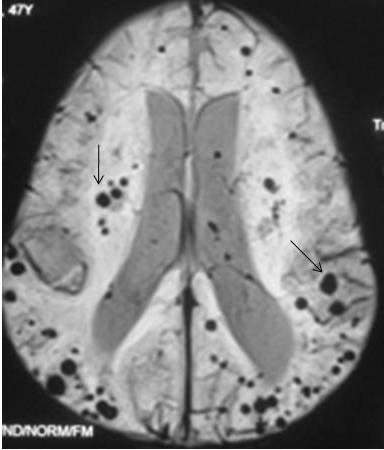
Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Mri Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is a type of cerebrovascular disorder characterized by the accumulation of amyloid beta peptide within the leptomeninges and small medium sized cerebral blood vessels.[1] the amyloid deposition results in fragile vessels that may manifest in lobar intracerebral hemorrhages (ich). it may also present with cognitive impairments, incidental microbleeds. Still a syndromal diagnosis. cerebral amyloid angiopathy (caa) is a common form of cerebral small vessel disease, due to progressive amyloid β deposition in the walls of small leptomeningeal and cortical arteries and cortical capillaries. 1 the main clinical manifestations of caa are lobar intracerebral hemorrhage (ich) and cognitive impairment. Caa is defined by histopathology—deposition of β amyloid in the cerebrovasculature—and through the 1980s the disorder was only diagnosed in patients with available brain tissue from hematoma evacuation, biopsy, or most commonly postmortem examination.1 introduction of the imaging based boston crite ria for diagnosis of caa in the 1990s2,3. Imaging intracranial hemorrhage – case 6 – cerebral amyloid angiopathy – caa in patients over 70, amyloid angiopathy can be a cause of intracranial hemorrhage. this condition is caused by pathologic accumulation of amyloid in vessel walls, and is characterized by multiple chronic areas of hemorrhage in a peripheral location.

Comments are closed.