Inductance Of Transmission Line Two Wire Line Three Phase
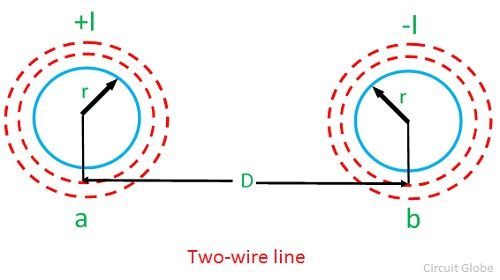
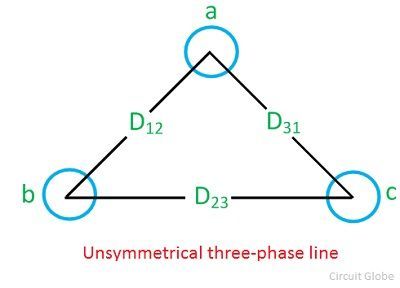
Inductance Of Transmission Line Two Wire Line Three Phase The inductance of an individual conductor is one half of the total inductance of a two wire line. inductance of symmetrical three phase line. in symmetrical three phase line, all the conductors are placed at the corners of the equilateral triangle. such an arrangement of conductors is also referred to as equilateral spacing. Two wire system inductance: the inductance in a two wire single phase system depends on the currents in both wires and their distance apart. three phase system inductance: in a three phase transmission line, the inductance is influenced by the currents in all three conductors and their mutual interactions.

Inductance Of 3 Phase Double Circuit Transmission Line With Symmetrical Inductance of the conductor. inductance is defined as l = λ i l = λ i. some lines of flux exist inside the conductor. filaments on the surface of the conductor are not linked by internal flux. flux linking the filament near the surface of the conductor is less than that of interior. cross section of a cylindrical conductor. Line inductance example: three phase double circuit, bundled conductors. each conductor is stranded, r=1.8cm and conductor spacing is 45cm. find la. gmd of the three phase double circuit 3 gmd gmd gmd gmd= =12 23 13 16.5572 4 12 12 12' 1'2 1'2' 4 10 4 10 20 10 22 10 2 15.47182 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 gmd d d d d m = = = 4 gmd d d d d m23 23 23' 2. 1 introduction. a transmission line is a pair of conductors which have a cross which remains constant with distance. for example, a coaxial cable transmission line has a cross section of a central rod and an outer concentric cylinder. similarly a twisted pair transmission line has two conducting rods or wires which slowly wind around each other. 4. electrical properties of transmission lines. series resistance. voltage drop (𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼) and real power loss (𝐼𝐼2𝐼𝐼) along the line. due to finite conductivity of the line. series inductance. series voltage drop, no real power loss. only self inductance (no mutual inductance) in balanced systems.

Inductance Of Two Wire Transmission Line Derivation Explanation And 1 introduction. a transmission line is a pair of conductors which have a cross which remains constant with distance. for example, a coaxial cable transmission line has a cross section of a central rod and an outer concentric cylinder. similarly a twisted pair transmission line has two conducting rods or wires which slowly wind around each other. 4. electrical properties of transmission lines. series resistance. voltage drop (𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼) and real power loss (𝐼𝐼2𝐼𝐼) along the line. due to finite conductivity of the line. series inductance. series voltage drop, no real power loss. only self inductance (no mutual inductance) in balanced systems. The inductance of the conductor 1 in phase a is l a1 = a1 ia=2 = 4 10 7 ln 3 p d abp d bcd ca r0d also l a2 = l a1. since there are two conductors per phase, the inductance per phase l a = l a1 2 = 2 10 7 ln 3 p d abp d bcd ca r0d h m also l a = l b = l c. the inductance per phase is l = 2 10 7 ln gmd gmr h m where gmd is the geometric mean. Electrical characteristics. transmission lines are characterized by a series resistance, inductance, and shunt capacitance per unit length. these values determine the power carrying capacity of the transmission line and the voltage drop across it at full load. the dc resistance of a conductor is expressed in terms of resistively, length and.

Inductance Of Transmission Line Bartleby The inductance of the conductor 1 in phase a is l a1 = a1 ia=2 = 4 10 7 ln 3 p d abp d bcd ca r0d also l a2 = l a1. since there are two conductors per phase, the inductance per phase l a = l a1 2 = 2 10 7 ln 3 p d abp d bcd ca r0d h m also l a = l b = l c. the inductance per phase is l = 2 10 7 ln gmd gmr h m where gmd is the geometric mean. Electrical characteristics. transmission lines are characterized by a series resistance, inductance, and shunt capacitance per unit length. these values determine the power carrying capacity of the transmission line and the voltage drop across it at full load. the dc resistance of a conductor is expressed in terms of resistively, length and.
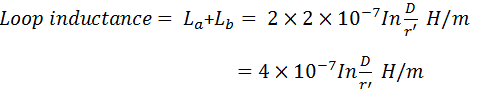
Inductance Of Transmission Line Two Wire Line Three Phase
Inductance Of Transmission Line Two Wire Line Three Phase

Comments are closed.