Intro To Rate Laws Rate Constants Reaction Order Chemistry Tutorial

Intro To Rate Laws Rate Constants Reaction Order Chemistry Tutorial This video gives an overview of what a rate law is, what a rate constant is, what appropriate units for the rate constant should be, and how to determine the. A rate law shows how the rate of a chemical reaction depends on reactant concentration. for a reaction such as aa → products, the rate law generally has the form rate = k[a]ⁿ, where k is a proportionality constant called the rate constant and n is the order of the reaction with respect to a. the value of n is not related to the reaction stoichiometry and must be determined by experiment.

Intro To Rate Laws Rate Constants Reaction Order Chemistry Tutorial Chad provides a comprehensive lesson on rate laws and how to calculate a rate law from a table of kinetic data. the lesson begins with an introduction to wh. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into reaction mechanisms within a chemical kinetics setting. it explains how to write the rate l. The rate law for this reaction is written as: rate = k[a]m[b]n rate = k [a] m [b] n. in which [a] and [b] represent the molar concentrations of reactants, and k is the rate constant, which is specific for a particular reaction at a particular temperature. the exponents m and n are the reaction orders and are typically positive integers, though. The exponent to which a concentration is raised in a rate law indicates the reaction order, the degree to which the reaction rate depends on the concentration of a particular reactant. 15.2 rate laws: an introduction is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts.
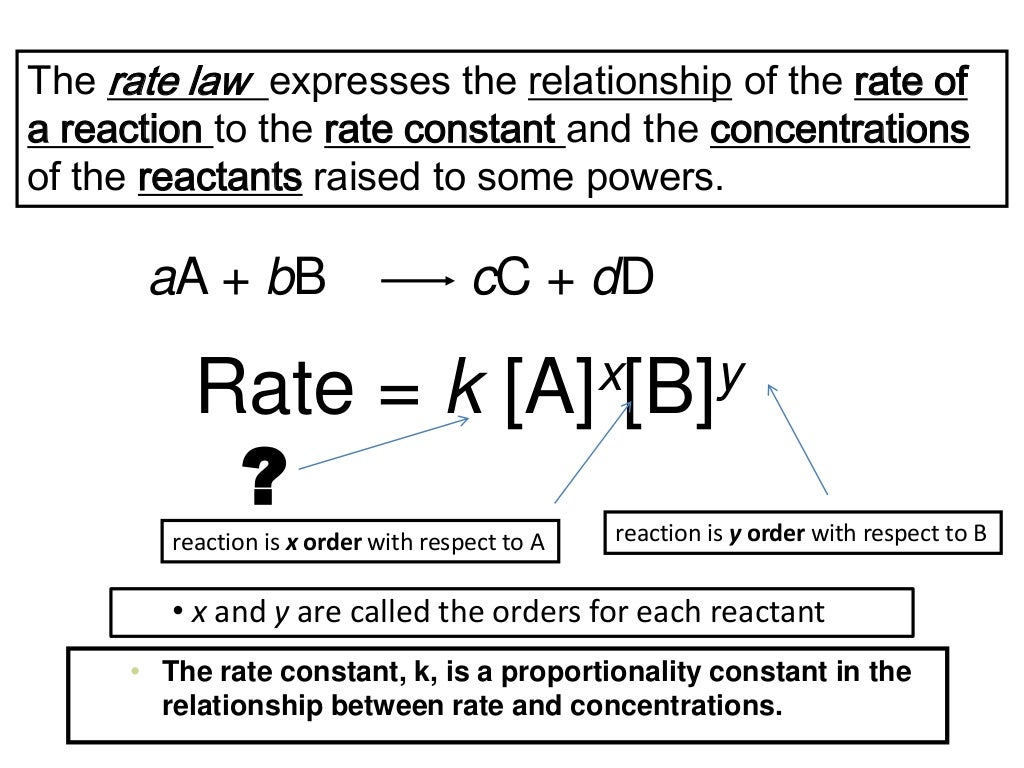
Reaction Order And Rate Law Expression Worksheet Printable Calendars The rate law for this reaction is written as: rate = k[a]m[b]n rate = k [a] m [b] n. in which [a] and [b] represent the molar concentrations of reactants, and k is the rate constant, which is specific for a particular reaction at a particular temperature. the exponents m and n are the reaction orders and are typically positive integers, though. The exponent to which a concentration is raised in a rate law indicates the reaction order, the degree to which the reaction rate depends on the concentration of a particular reactant. 15.2 rate laws: an introduction is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. If m = 1 and n = 1, the overall order of the reaction is second order (m n = 1 1 = 2). the rate law: rate = k[h 2o 2] describes a reaction that is first order in hydrogen peroxide and first order overall. the rate law: rate = k[c 4h 6]2. describes a reaction that is second order in c 4 h 6 and second order overall. Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of its reactants. as an example, consider the reaction described by the chemical equation. where a and b are stoichiometric coefficients.

Rate Law Rate Constant Order Of A Reaction Chemical Kinetics If m = 1 and n = 1, the overall order of the reaction is second order (m n = 1 1 = 2). the rate law: rate = k[h 2o 2] describes a reaction that is first order in hydrogen peroxide and first order overall. the rate law: rate = k[c 4h 6]2. describes a reaction that is second order in c 4 h 6 and second order overall. Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of its reactants. as an example, consider the reaction described by the chemical equation. where a and b are stoichiometric coefficients.

Comments are closed.