Introduction To Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Introduction To Differential Scanning Calorimetry Youtube A practical introduction to differential scanning calorimetry paul gabbott contents 1.1 introduction 2 1.2 principles of dsc and types of measurements made 2 1.2.1 a definition of dsc 2 1.2.2 heat flow measurements 3 1.2.3 specific heat (c p)3 1.2.4 enthalpy 5 1.2.5 derivative curves 5 1.3 practical issues 6 1.3.1 encapsulation 6 1.3.2. 3. differential scanning calorimetry 3.1 introduction differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is an experimental technique for measuring the energy necessary to establish a nearly zero temperature difference between a test substance s (and or its reaction products) and an inert reference material r, while the.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Introduction Basic Principles A beginner’s guide. this booklet provides an introduction to the concepts of differential scanning calorimetry (dsc). it is written for the materials scientist unfamiliar with dsc. dsc family. the differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) is a fundamental tool in thermal analysis. The output yielded by differential scanning calorimetry is called a differential thermogram, which plots the required heat flow against temperature. data analysis is highly dependent on the assumption that both the reference and sample cells are constantly and accurately maintained at equal temperatures. this graph indicates the change in power. Dielectric thermal analysis. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. [1] both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. in this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely programmed temperature change. dsc is very similar to dta and gives much the same sort of information but dsc is more often used for quantitative measurement.
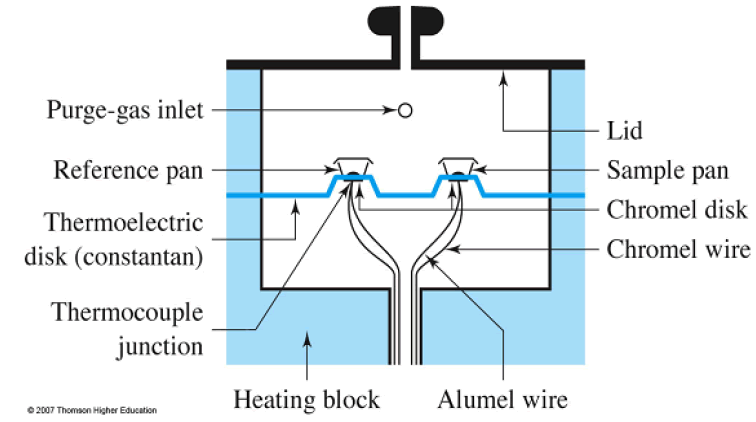
Easy Read Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc In 2021 Ampersand Dielectric thermal analysis. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. [1] both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. in this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely programmed temperature change. dsc is very similar to dta and gives much the same sort of information but dsc is more often used for quantitative measurement. In this updated and fully revised second edition, the authors provide the newcomer and the experienced practitioner with a balanced and comprehensive insight into all important methods and aspects of differential scanning calorimetry (dsc), including a sound presentation of the theoretical basis of dsc thermal analysis and temperature modulated dsc (tmdcs). Figure 31.2.2 31.2. 2: components of instrument for a differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) experiment. the sample and the reference material are (a) placed in small aluminum pans, each with a separate lid, and then (b) the lid and the pan are crimped together. the sample chamber in (c) allows for applying heat to the sample and the reference.

Differential Thermal Analysis Differential Scanning Calorimetry Ppt In this updated and fully revised second edition, the authors provide the newcomer and the experienced practitioner with a balanced and comprehensive insight into all important methods and aspects of differential scanning calorimetry (dsc), including a sound presentation of the theoretical basis of dsc thermal analysis and temperature modulated dsc (tmdcs). Figure 31.2.2 31.2. 2: components of instrument for a differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) experiment. the sample and the reference material are (a) placed in small aluminum pans, each with a separate lid, and then (b) the lid and the pan are crimped together. the sample chamber in (c) allows for applying heat to the sample and the reference.

A Schematic Differential Scanning Calorimetry Measurement Download

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Introduction And Instrumentation

Comments are closed.