Introduction To Weather Fronts Pressure Systems And Synoptic Charts

Introduction To Weather Fronts Pressure Systems And Synoptic Charts Get to grips with weather fronts, pressure systems (high and low pressure) and how to interpret a synoptic chart. this is the second in our free online weath. Occlusion (or occluded front) occlusions form when the cold front of a depression catches up with the warm front, lifting the warm air between the fronts into a narrow wedge above the surface. on a synoptic chart an occluded front appears as a purple line with a combination of triangles and semi circles. the direction in which the symbols point.

Conceptual Diagram Of Four Types Of Synoptic Scale Weather Systems That Troughs. a trough appears on the weather map as a dashed blue line on the chart. it is an elongated area where atmospheric pressure is low relative to its immediate surroundings. like cold fronts, troughs separate two different air masses (usually more moist air on one side and drier air on the other). The following diagram summarises the appearance on a weather chart of the main types of pressure systems. cold fronts and warm fronts. cold fronts can be identified on weather charts as bold lines with triangles. these are blue when displayed on colour charts. the points of the triangle indicate the direction in which the front is moving. Cold fronts and warm fronts. also on a synoptic chart are the lines, triangles and semi circles representing 'fronts'. with the atmosphere trying to balance temperature, pressure and wind there are different sorts of air, known as air masses, circulating around the earth. the differences are mostly between how warm, cold, dry and moist the air. Swing low. the dartboards of a weather chart are cyclones or areas of low pressure with isobars drawn in tightly packed circles. here the winds move in an anticlockwise direction, and air is rising. as it rises and cools, water vapour condenses to form clouds and rain. known to bring unsettled, wet and windy weather, these depressions are aptly.
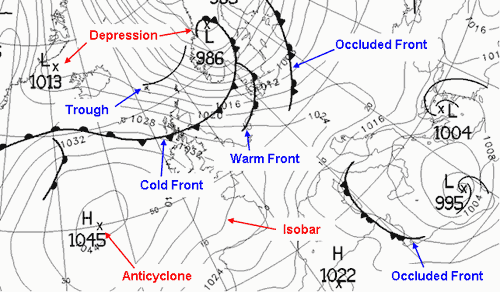
Metlink Royal Meteorological Society Weather Symbols And Synoptic Cold fronts and warm fronts. also on a synoptic chart are the lines, triangles and semi circles representing 'fronts'. with the atmosphere trying to balance temperature, pressure and wind there are different sorts of air, known as air masses, circulating around the earth. the differences are mostly between how warm, cold, dry and moist the air. Swing low. the dartboards of a weather chart are cyclones or areas of low pressure with isobars drawn in tightly packed circles. here the winds move in an anticlockwise direction, and air is rising. as it rises and cools, water vapour condenses to form clouds and rain. known to bring unsettled, wet and windy weather, these depressions are aptly. Join skipper chris as we look at weather fronts, pressure systems and synoptic charts get to grips with weather fronts, pressure systems (high and low pressu. The current surface synoptic weather map. it shows the positions of high and low pressure systems, surface weather plots, and locations of fronts. in order for meteorologists to understand any relevant information from a map like the one above, one of the primary things they must check is the time these weather elements were observed.
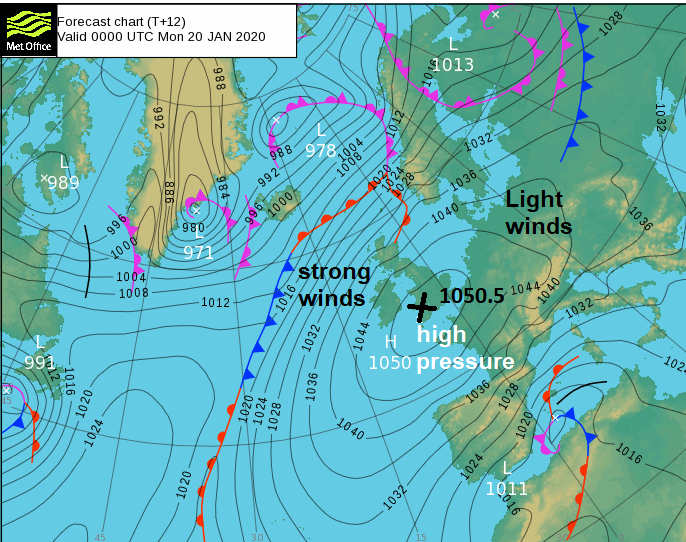
Learn About Synoptic Weather Charts From Fronts To Isobars Join skipper chris as we look at weather fronts, pressure systems and synoptic charts get to grips with weather fronts, pressure systems (high and low pressu. The current surface synoptic weather map. it shows the positions of high and low pressure systems, surface weather plots, and locations of fronts. in order for meteorologists to understand any relevant information from a map like the one above, one of the primary things they must check is the time these weather elements were observed.

Comments are closed.