Kinetics Initial Rates And Integrated Rate Laws

Integrated Rate Laws Zero First Second Order Reactions Chemical Who likes math! oh, you don't? maybe skip this one on kinetics. unless you have to answer this stuff for class. then yeah, watch this.watch the whole general. Example 12.5.3: the integrated rate law for a second order reaction. the reaction of butadiene gas (c 4 h 6) with itself produces c 8 h 12 gas as follows: 2c 4h 6(g) c 8h 12(g) the reaction is second order with a rate constant equal to 5.76 × 10 −2 l mol min under certain conditions.
Kinetics Either the differential rate law or the integrated rate law can be used to determine the reaction order from experimental data. often, the exponents in the rate law are the positive integers: 1 and 2 or even 0. thus the reactions are zeroth, first, or second order in each reactant. the common patterns used to identify the reaction order are. 12.2 factors affecting reaction rates; 12.3 rate laws; 12.4 integrated 0 is the initial the integrated rate law for zero order kinetics describes a. Kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical processes. the rate of a reaction is defined at the change in concentration over time: rate expressions describe reactions in terms of the change in reactant or product concentrations over the change in time. the rate of a reaction can be expressed by any one of the reactants or products in the. Example 12.4.3: the integrated rate law for a second order reaction. the reaction of butadiene gas (c 4 h 6) to yield c 8 h 12 gas is described by the equation: 2c4h6(g) c8h12(g) this “dimerization” reaction is second order with a rate constant equal to 5.76 10 −2 l mol −1 min −1 under certain conditions.
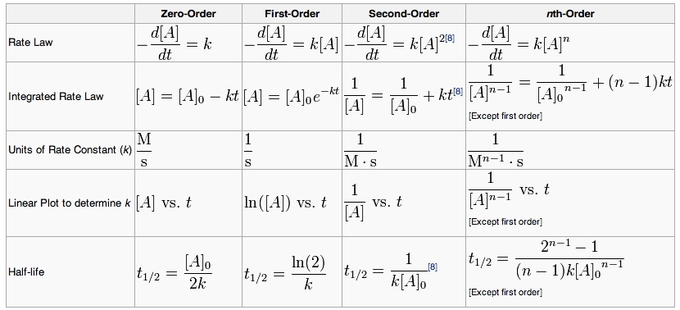
The Integrated Rate Law Introduction To Chemistry Course Hero Kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical processes. the rate of a reaction is defined at the change in concentration over time: rate expressions describe reactions in terms of the change in reactant or product concentrations over the change in time. the rate of a reaction can be expressed by any one of the reactants or products in the. Example 12.4.3: the integrated rate law for a second order reaction. the reaction of butadiene gas (c 4 h 6) to yield c 8 h 12 gas is described by the equation: 2c4h6(g) c8h12(g) this “dimerization” reaction is second order with a rate constant equal to 5.76 10 −2 l mol −1 min −1 under certain conditions. The integrated rate law is widely used in chemical kinetics studies and allows us to determine important parameters such as the half life of a reaction, the initial concentration of a species, and the overall reaction rate. it also helps us compare and analyze different reaction mechanisms and understand the factors that influence reaction rates. Rate laws in chemical kinetics are studied in this chapter: reaction rates, rate laws and reaction orders, the method of initial rates, integrated rate laws, half life, first order, second order, and zeroth order reactions, radioactive decay.

Comments are closed.