Levels Of Trophic Levels
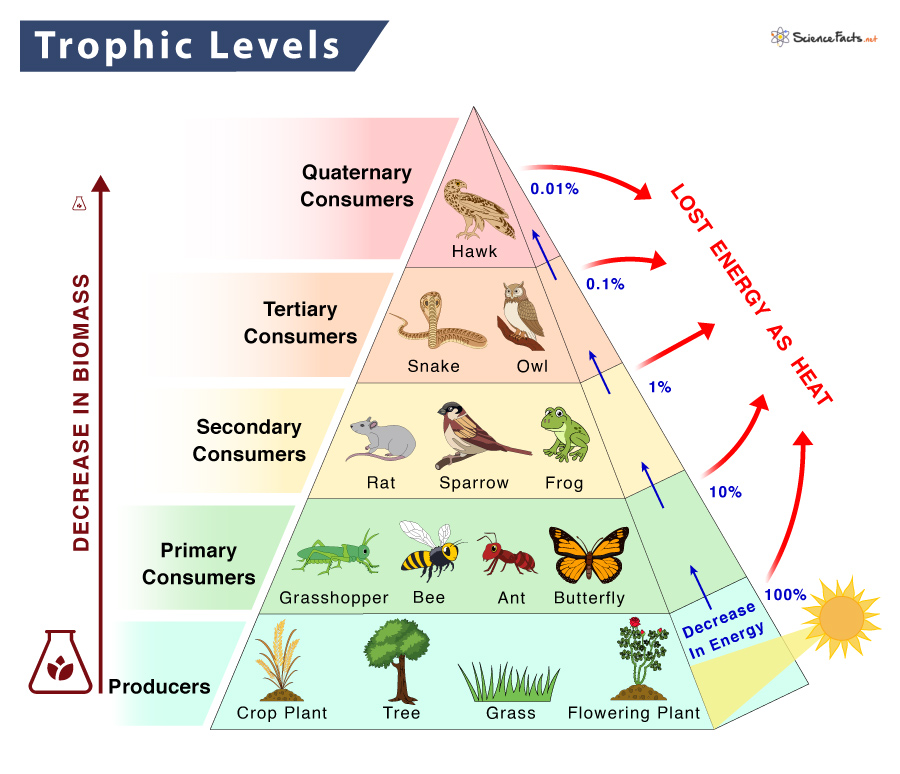
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differs in its nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea. The trophic levels refer to the position of a group of organisms in the food chain, food web, or ecological pyramid based on their feeding pattern. they are shown in a series or a succession to represent energy flow from one tropic level to another. the position of the trophic level depends upon the number of steps the organism takes from the.
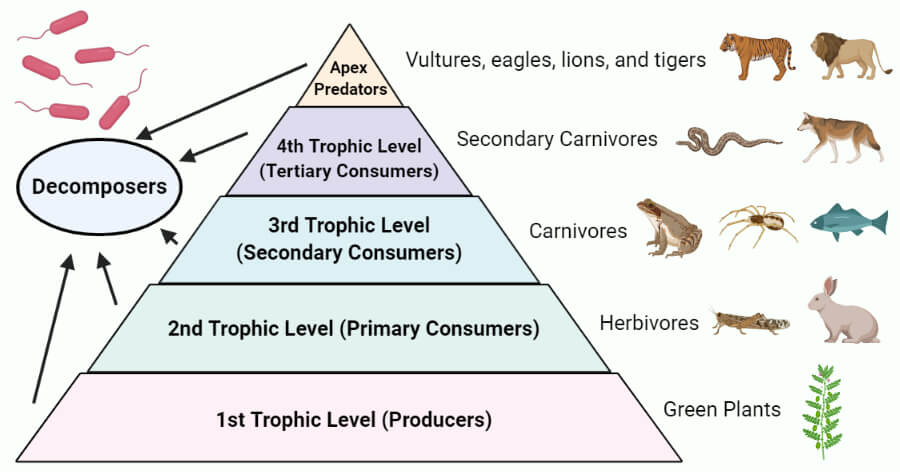
Trophic Level Food Chain Food Web Pyramid Examples Trophic level, any step in a nutritive series, or food chain, of an ecosystem. organisms are classified into levels on the basis of their feeding behavior. the lowest level contains the producers, green plants, which are consumed by second level organisms, herbivores, which, in turn, are consumed by carnivores. The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. the trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. a food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary. Trophic levels and biomass. with less energy at higher trophic levels, there are usually fewer organisms as well. organisms tend to be larger in size at higher trophic levels, but their smaller numbers result in less biomass. biomass is the total mass of organisms at a trophic level. Trophic pyramid, the basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain. the base of the pyramid is composed of species called autotrophs, the primary producers of the ecosystem. all other organisms in the ecosystem are.

Trophic Pyramid Definition Examples Britannica Trophic levels and biomass. with less energy at higher trophic levels, there are usually fewer organisms as well. organisms tend to be larger in size at higher trophic levels, but their smaller numbers result in less biomass. biomass is the total mass of organisms at a trophic level. Trophic pyramid, the basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain. the base of the pyramid is composed of species called autotrophs, the primary producers of the ecosystem. all other organisms in the ecosystem are. Most of the food energy that enters a trophic level is “lost” as heat when it is used by organisms to power the normal activities of life. thus, the higher the trophic level on the pyramid, the lower the amount of available energy. together, the autotrophs and heterotrophs form various trophic (feeding) levels in the ecosystem: the producer. A trophic level refers to a level or a position in a food chain, a food web, or an ecological pyramid. it is occupied by a group of organisms that have a similar feeding mode. in an ecological pyramid, the various trophic levels are primary producers (at the base), consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.), and predators (apex).

Trophic Level Definition Examples Energy Transfer Teachoo Most of the food energy that enters a trophic level is “lost” as heat when it is used by organisms to power the normal activities of life. thus, the higher the trophic level on the pyramid, the lower the amount of available energy. together, the autotrophs and heterotrophs form various trophic (feeding) levels in the ecosystem: the producer. A trophic level refers to a level or a position in a food chain, a food web, or an ecological pyramid. it is occupied by a group of organisms that have a similar feeding mode. in an ecological pyramid, the various trophic levels are primary producers (at the base), consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.), and predators (apex).
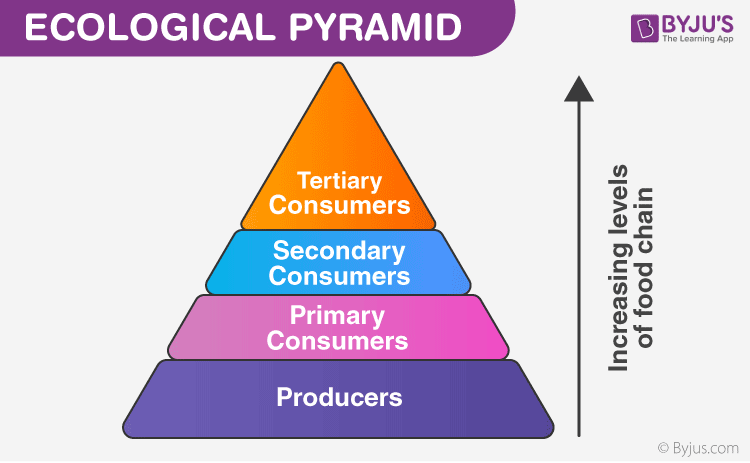
Trophic Level Diagram Ecological Pyramids

Comments are closed.