Lipid Metabolism In Vivo Dietary Fatty Acids Fa Are Absorbed From

Lipid Metabolism In Vivo Dietary Fatty Acids Fa Are Absorbed From Abstract. the perception that intracellular lipolysis is a straightforward process that releases fatty acids from fat stores in adipose tissue to generate energy has experienced major revisions. The objective is either to reduce lipid absorption for overweighed, hyperlipidemics or metabolic syndrome subjects (armand, 2013) or to reduce the fat and food intake by increasing the satiety. as recently reviewed, the structure of dietary lipids can affect fa bioavailability and lipid metabolism (michalski et al., 2013).

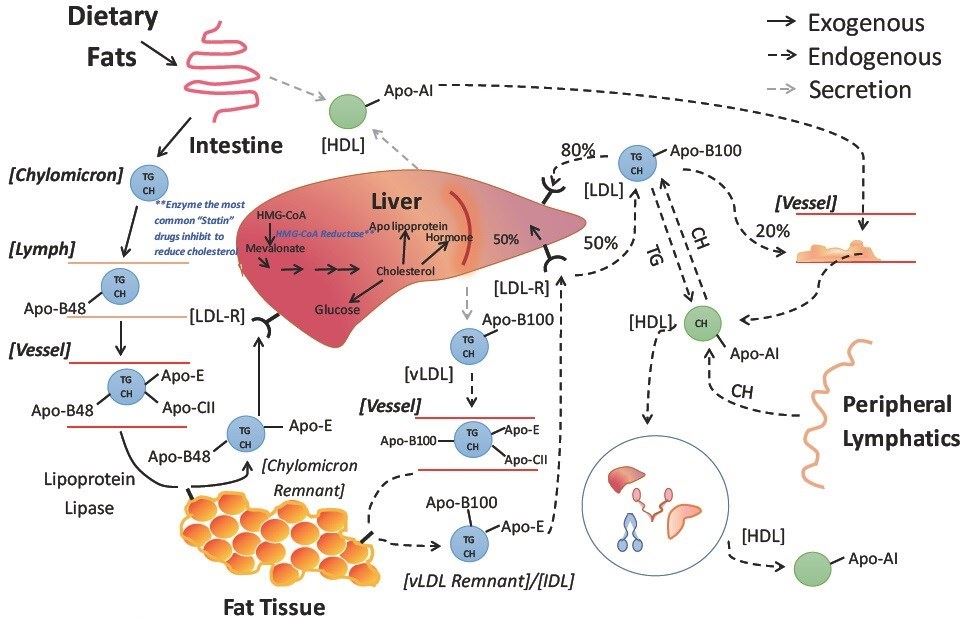
Lipid Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Download scientific diagram | lipid metabolism in vivo. dietary fatty acids (fa) are absorbed from the gut and converted to triglycerides to be incorporated into chylomicrons in the intestinal. In summary, the fate of fa absorption and metabolism in vivo is summarized as follows (figure 1): free fa and some simple conjugated forms are often directly absorbed in the stomach or small intestine, avoiding degradation by microflora. however, fa conjugated with polymers cannot be absorbed by the stomach and small intestine but is degraded. Abstract. dietary fat is an energy dense nutrient that provides essential fatty acids (fas) and aids in fat soluble vitamin absorption. when dietary fat absorption becomes dysregulated, it contributes to altered blood lipid levels and metabolic disease risk. triacylglycerol (tag), the major form of dietary fat, is efficiently absorbed (>95%). This role might be important in enterocytes, given the large amounts of fatty acid flux into the cell during active fat absorption. in addition, as lipids and fatty acids can serve as signalling.

Digestion And Absorption Of Dietary Lipids Fa Fatty Acids Pls Abstract. dietary fat is an energy dense nutrient that provides essential fatty acids (fas) and aids in fat soluble vitamin absorption. when dietary fat absorption becomes dysregulated, it contributes to altered blood lipid levels and metabolic disease risk. triacylglycerol (tag), the major form of dietary fat, is efficiently absorbed (>95%). This role might be important in enterocytes, given the large amounts of fatty acid flux into the cell during active fat absorption. in addition, as lipids and fatty acids can serve as signalling. In biological responses, fatty acids (fa) are absorbed and metabolized in the form of substrates for energy production. the molecular structures (number of double bonds and chain length) and composition of dietary fa impact digestion, absorption and metabolism, and the biological roles of fa. recently, increasing evidence indicates that fa are. Lipid absorption from epithelial cells (enterocytes) and chylomicron secretion in lymphatic vessels (lacteals). (a) during absorption of dietary lipids, the fa and mags are released from micelles in the lumen (indicated by 1, top panel) and both enter at the apical side of intestinal epithelial cells, also called enterocytes that line the luminal side of the small intestine.
Lipid Metabolism The Mobilization Of Fatty Acids Fa From Their In biological responses, fatty acids (fa) are absorbed and metabolized in the form of substrates for energy production. the molecular structures (number of double bonds and chain length) and composition of dietary fa impact digestion, absorption and metabolism, and the biological roles of fa. recently, increasing evidence indicates that fa are. Lipid absorption from epithelial cells (enterocytes) and chylomicron secretion in lymphatic vessels (lacteals). (a) during absorption of dietary lipids, the fa and mags are released from micelles in the lumen (indicated by 1, top panel) and both enter at the apical side of intestinal epithelial cells, also called enterocytes that line the luminal side of the small intestine.
Lipid Metabolism And Enzymes Creative Diagnostics

Lipid Metabolism Pathway Diagram

Comments are closed.