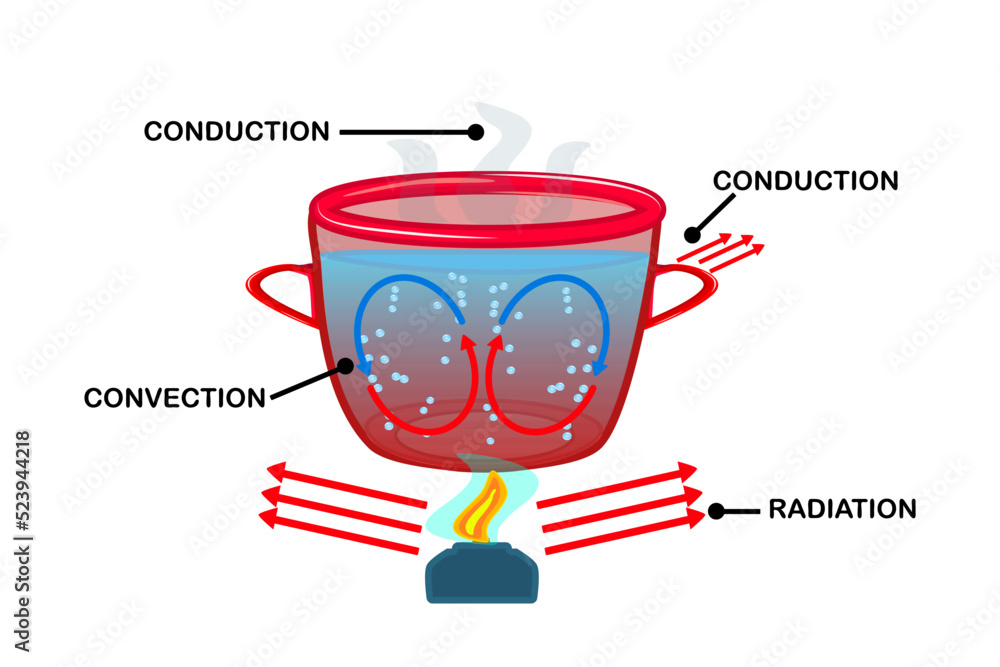
Liquid Cooling Convection Diagram

Convection Definition Examples Types Facts Britannica −heat convection, which is primarily governed by the heat transfer coefficient h. − "=𝒉𝑻 −𝑻 •air cooling is limited by specific heat. to dissipate large amounts of power, a large mass flow rate is needed. −higher flow speed, larger noise. •liquid cooling is able to achieve better heat transfer at much lower mass flow rates. The liquid cooling unit can be either in a separate unit outside of the pc case, or integrated within the pc case. in our diagram, the water cooling unit is external. the heat is transferred from.
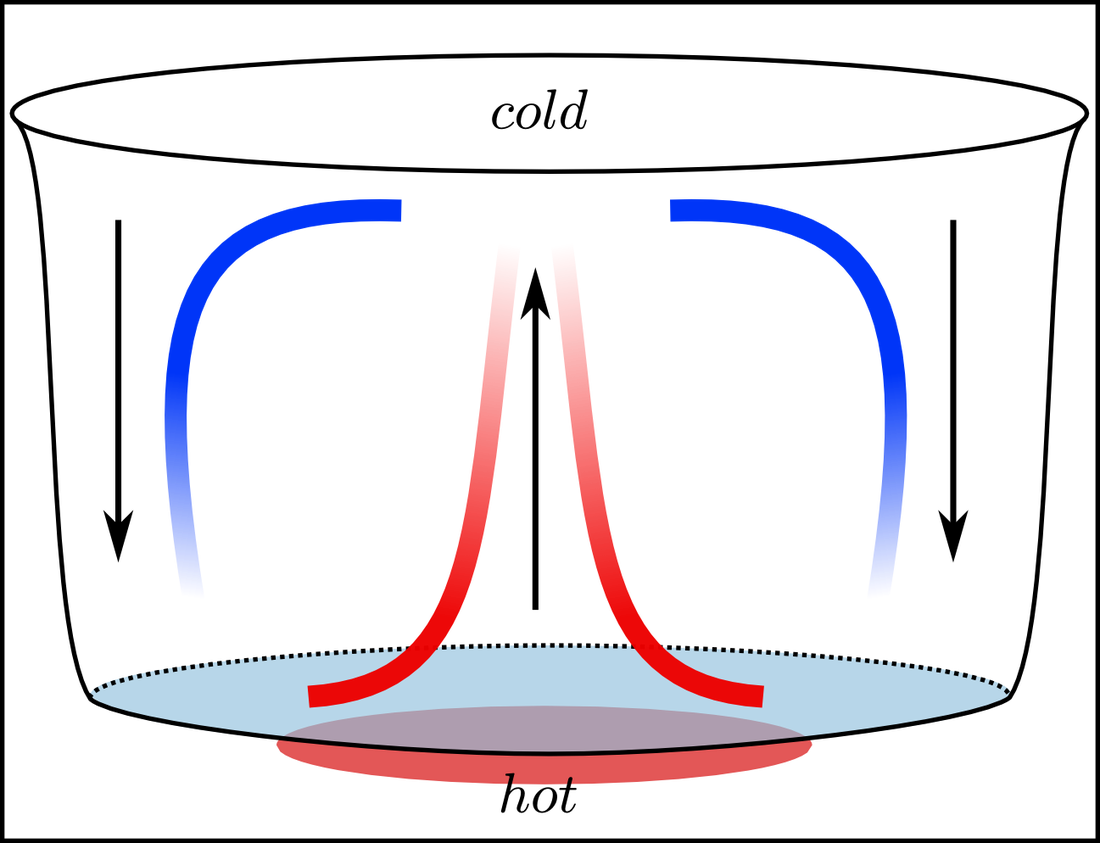
Heat Transfer Convection Currents Labeled Diagram Warm And Cool Convective heat transfer coefficient for air. the convective heat transfer coefficient for air flow can be approximated to. hc = 10.45 v 10 v1 2 (2) where. hc = heat transfer coefficient (kcal m2h°c) v = relative speed between object surface and air (m s) since. 1 kcal m2h°c = 1.16 w m2°c. Operates like a normal liquid cooling loop. the water is pumped through a cold plate with a mechanical pump. from the cold plate, the heated water is cooled with a figure 4. intel’s integrated cold plate and liquid pump assembly [3]. figure 5. intel integrated liquid cooling loop [3]. pass or reject load unit alignment motor test load unit. Liquid cooled pcs operate similar to how car radiators work. a coolant sits in a circuit of tubes and the coolant is warmed by the heat of the engine (or the computer). the radiator (just a big reservoir filled with liquid) may or may not physically touch the parts that need to be cooled, but heat can be transferred from the engine chips to. 15–3 cooling load of electronic equipment 15 9 15–4 thermal environment 15 10 15–5 electronics cooling in different applications 15 11 15–6 conduction cooling 15 13 15–7 air cooling: natural convection and radiation 15 28 15–8 air cooling: forced convection 15 36 15–9 liquid cooling 15 49 15–10 immersion cooling 15 52 summary 15 57.

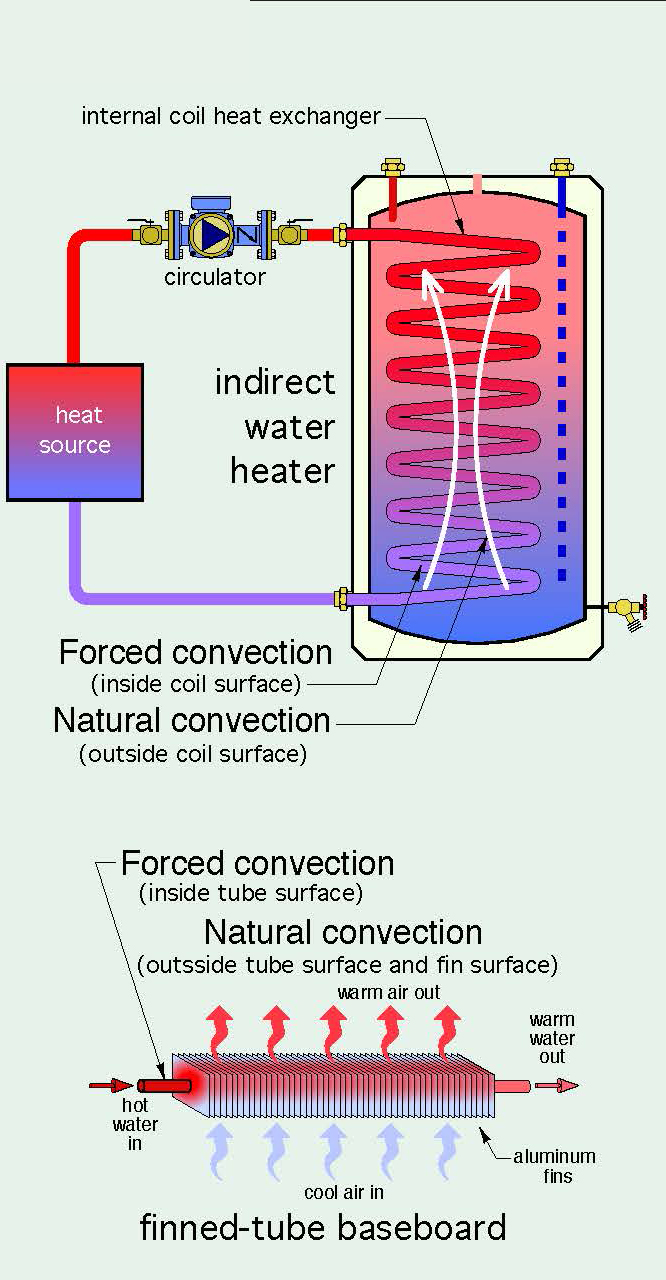
Convective Cooling Liquid cooled pcs operate similar to how car radiators work. a coolant sits in a circuit of tubes and the coolant is warmed by the heat of the engine (or the computer). the radiator (just a big reservoir filled with liquid) may or may not physically touch the parts that need to be cooled, but heat can be transferred from the engine chips to. 15–3 cooling load of electronic equipment 15 9 15–4 thermal environment 15 10 15–5 electronics cooling in different applications 15 11 15–6 conduction cooling 15 13 15–7 air cooling: natural convection and radiation 15 28 15–8 air cooling: forced convection 15 36 15–9 liquid cooling 15 49 15–10 immersion cooling 15 52 summary 15 57. Introduction to cooling water system fundamentals. cooling of process fluids, reaction vessels, turbine exhaust steam, and other applications is a critical operation at thousands of industrial facilities around the globe, such as general manufacturing plants or mining and minerals plants. cooling systems require protection from corrosion. There are 2 main categories of liquid cooling – direct to chip (sometimes called conductive or cold plate) and immersive. from these two categories come a total of five main liquid cooling methods, as the diagram in figure 1 depicts (the orange boxes). in this section, we’ll describe and illustrate each method. the green grid.
Convection In The Sun Science News Introduction to cooling water system fundamentals. cooling of process fluids, reaction vessels, turbine exhaust steam, and other applications is a critical operation at thousands of industrial facilities around the globe, such as general manufacturing plants or mining and minerals plants. cooling systems require protection from corrosion. There are 2 main categories of liquid cooling – direct to chip (sometimes called conductive or cold plate) and immersive. from these two categories come a total of five main liquid cooling methods, as the diagram in figure 1 depicts (the orange boxes). in this section, we’ll describe and illustrate each method. the green grid.
10 Convection Diagram Muaadthrocha
Mode Of Heat Transfer Convection And Radiation Lesson Science

Comments are closed.