Marine Food Web вђ Science Learning Hub
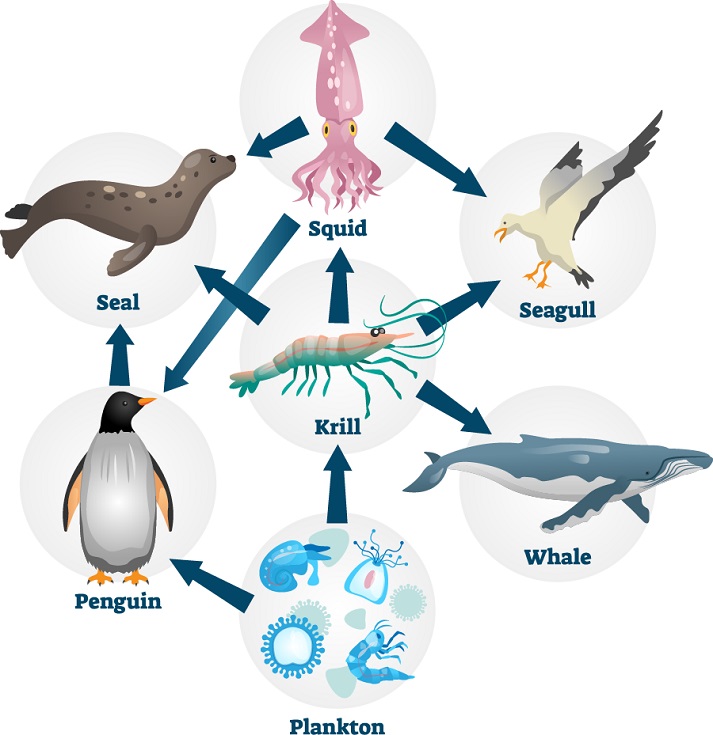
Marine Food Chain Diagram Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. Making a food web is a practical way for students to understand the complexity of food webs. marine ecosystem this interactive diagram explores food webs and other aspects of life in the sea. beach visits – habitats and food webs involves students in researching and then observing a range of organisms to understand the interconnected nature.

Marine Food Web Science Learning Hub In build a marine food web students build their own food web using images of organisms from the marine ecosystem. the activity can be completed indoors or outside. marine ecosystem – this interactive diagram explores food webs and other aspects of life in the sea. beach visits – habitats and food webs involves students in researching and. About the science learning hub and introducing the speaker. 1–7. 00:00. introducing candy hart. 8–9. 00:58. candy using slh resources – life in the sea. 10. 02:03. using a food web image on an interactive whiteboard. 11–12. 02:35. learning about the food web through the marine ecosystem interactive. 13–14. 04:15. science information. Particular area. all food webs are made up of producers, consumers and decomposers. however, the number and type of species that make up web vary greatly between different areas and different ecosystems. this worksheet offers a suggested pathway through science learning hub education resources and. Directions. 1. define the role of marine microbes. explain to students that, in a single drop of salt water, thousands of microbes (tiny organisms), including bacteria and phytoplankton (tiny floating plants), are interacting to form the base of the food web for the entire ocean.
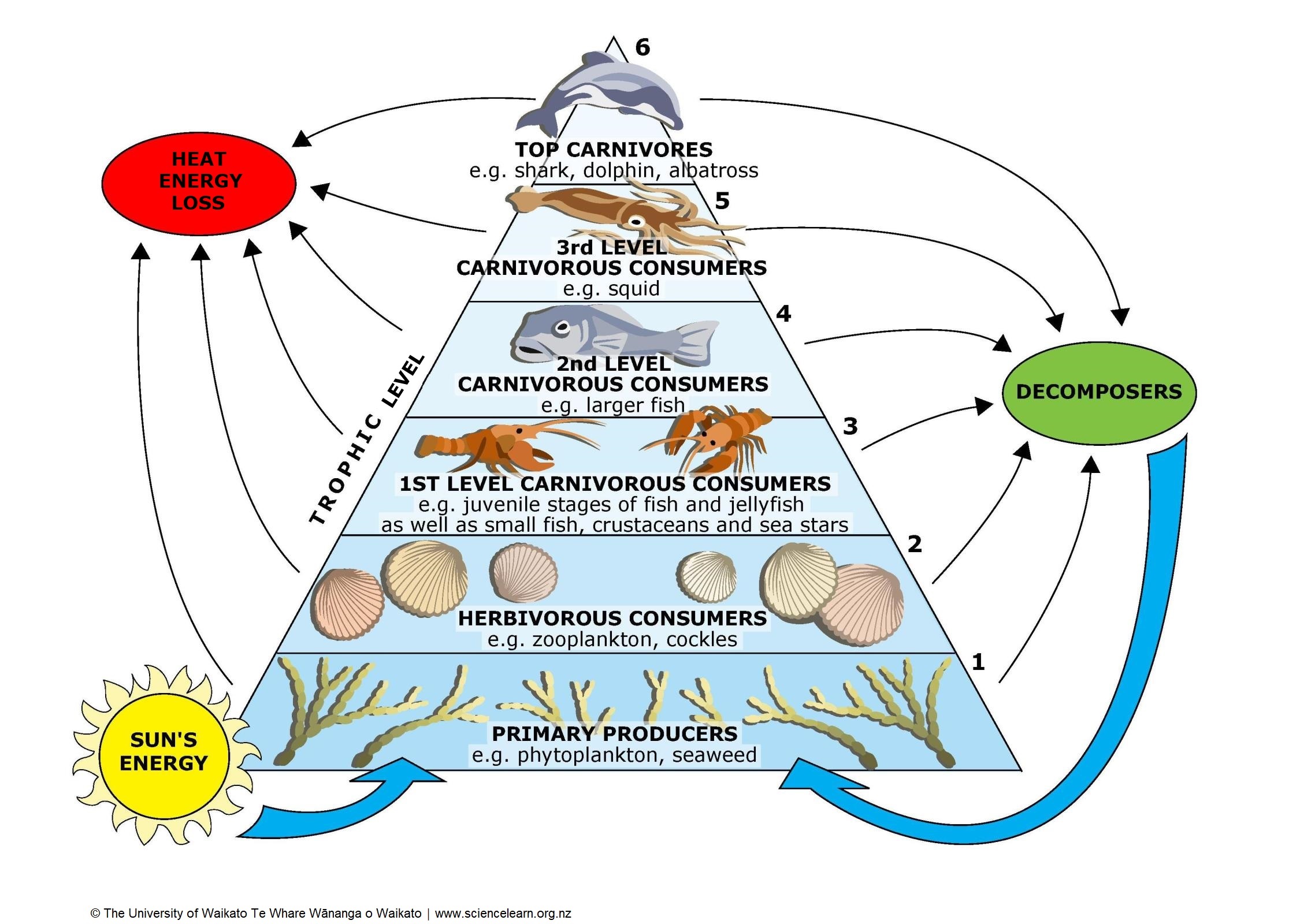
Marine Food Webs Science Learning Hub Particular area. all food webs are made up of producers, consumers and decomposers. however, the number and type of species that make up web vary greatly between different areas and different ecosystems. this worksheet offers a suggested pathway through science learning hub education resources and. Directions. 1. define the role of marine microbes. explain to students that, in a single drop of salt water, thousands of microbes (tiny organisms), including bacteria and phytoplankton (tiny floating plants), are interacting to form the base of the food web for the entire ocean. Learning objectives. students will conduct research about a specific marine species, including what it eats and what preys upon it and communicate their findings to the class. students will construct a food web diagram, as a whole class “jigsaw” activity, by combining data about individual species that each student researched. Phytoplankton are important primary producers in the marine food web. they are microscopic, single celled organisms that float freely in the ocean. they rely on energy from the sun for photosynthesis and are therefore most commonly found less than 100 metres below the surface. phytoplankton are eaten by zooplankton.
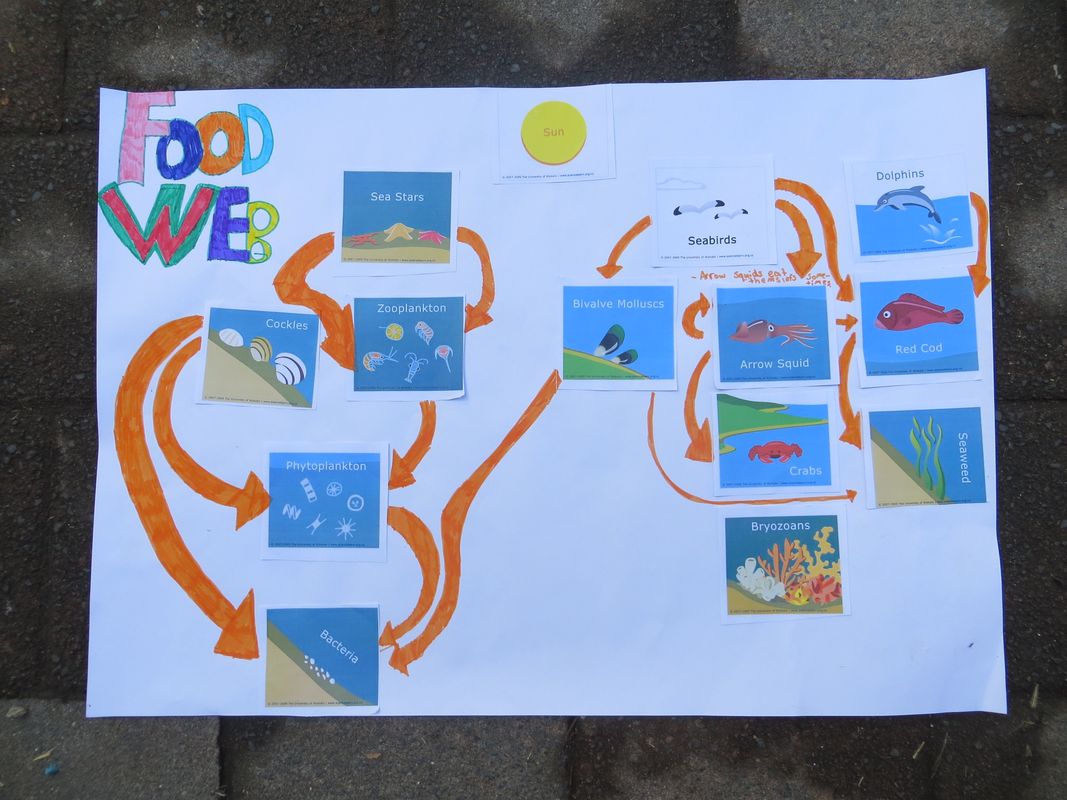
Build A Marine Food Web Activity Science Learning Hub Learning objectives. students will conduct research about a specific marine species, including what it eats and what preys upon it and communicate their findings to the class. students will construct a food web diagram, as a whole class “jigsaw” activity, by combining data about individual species that each student researched. Phytoplankton are important primary producers in the marine food web. they are microscopic, single celled organisms that float freely in the ocean. they rely on energy from the sun for photosynthesis and are therefore most commonly found less than 100 metres below the surface. phytoplankton are eaten by zooplankton.

Food Web Marine Life

Comments are closed.