Median And Ulnar Nerve Blocks вђ Sinai Em

Median And Ulnar Nerve Blocks Sinaiem Forearm nerve blocks are relatively easy to perform and deliver excellent regional anesthesia to the hand without systemic side effects. successful utilization of nerve blocks requires an intimate understanding of anatomical relationships and motor sensory supply. nerve blocks are made easier by employing ultrasound. Feasibility of forearm ultrasonography guided nerve blocks of the radial, ulnar, and median nerves for hand procedures in the emergency department. ann emerg med 2006;48:558 62. stone mb, price dd, wang r. ultrasound guided supraclavicular block for the treatment of upper extremity fractures, dislocations, and abscesses in the emergency department.

Median Nerve Mri Wrist The median nerve should be approximately 1 cm medial to the brachial artery at this point. insert the needle approximately 1 2 cm proximal to the flexor crease and advance with negative pressure applied to the syringe. at 1 2 cm deep, aspirate prior to injection to rule out intravascular placement. inject 5 10 ml of local anesthetic. Forearm nerve blocks provide excellent anesthesia of the hand including fractures, lacerations, or deep space abscess i&ds of the hand. unfortunately, the forearm nerve blocks do not provide anesthesia to the volar forearm ( musculocutaneous nerve, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve ) or the wrist ( musculocutaneous, ain and pin are missed. Insert a 1.5 inch block needle using an in plane approach for all 3 forearm nerve blocks. to block the median nerve, enter the skin from the side most comfortable and accessible to the operator. to block the radial nerve, enter the skin from a direction radial to the probe. to block the ulnar nerve, enter the skin from a direction ulnar to the. The ulnar nerve is ulnar in relation to the ulnar artery; even still, it is important to aspirate prior to injecting anesthetic to rule out intra arterial placement. discontinue and reposition should the patient report shooting "electrical" pains or numbness prior to injection. inject approximately 5 ml of local anesthetic.
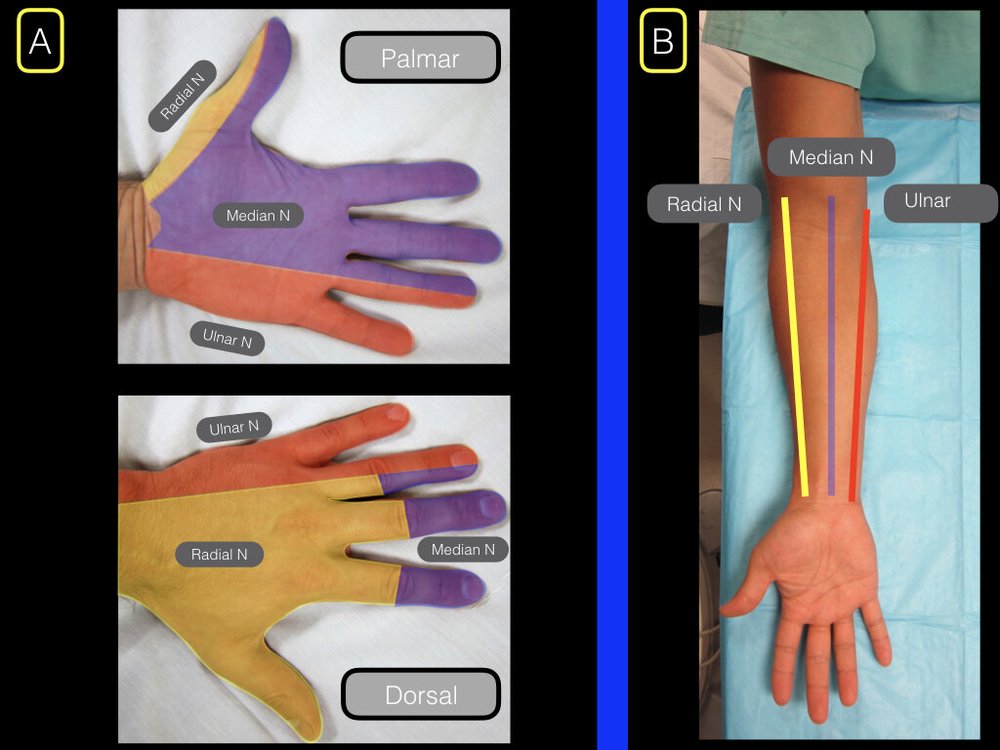
Forearm Blocks Highland Em Ultrasound Fueled Pain Management Insert a 1.5 inch block needle using an in plane approach for all 3 forearm nerve blocks. to block the median nerve, enter the skin from the side most comfortable and accessible to the operator. to block the radial nerve, enter the skin from a direction radial to the probe. to block the ulnar nerve, enter the skin from a direction ulnar to the. The ulnar nerve is ulnar in relation to the ulnar artery; even still, it is important to aspirate prior to injecting anesthetic to rule out intra arterial placement. discontinue and reposition should the patient report shooting "electrical" pains or numbness prior to injection. inject approximately 5 ml of local anesthetic. The utility of us guided nerve blocks for pain control in various clinical scenarios (laceration repair, incision and drainage, exploration for a foreign body, joint dislocation, and fracture management), it is unknown whether us guided nerve blocks are actively taught and performed in academic emergency medicine training programs.1,11,12. Indication. the ultrasound guided femoral nerve block (ugfnb) is an ideal adjunct in the emergency department (ed) treatment of femoral neck, intertrochanteric and shaft fractures. this block will also provide analgesia for large thigh lacerations, abscesses, and even some aspect of knee injuries.

Comments are closed.