Mental Health And Substance Use Considerations Among Children During
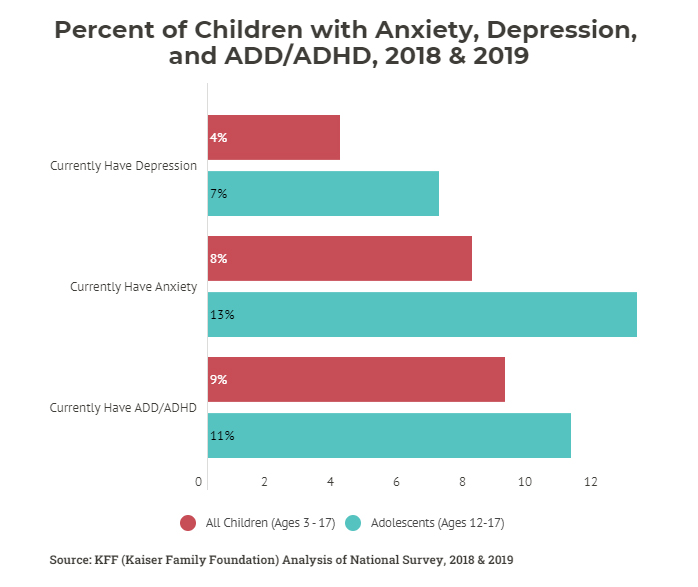
Mental Health And Substance Use Considerations Among Children During On average, in the years 2018 and 2019, among children ages 3 17, 8% (5.2 million) had anxiety disorder, 4% (2.3 million) had depressive disorder, and 9% (5.3 million) had attention deficit. The pandemic, many children in the united states were living with mental health disorders. on average, in the years 2018 and 2019, among children ages 3 17, 8% (5.2 million) had anxiety disorder, 4% (2.3 million) had depressive disorder, and 9% (5.3 million) had at. ention deficit disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (add adhd.
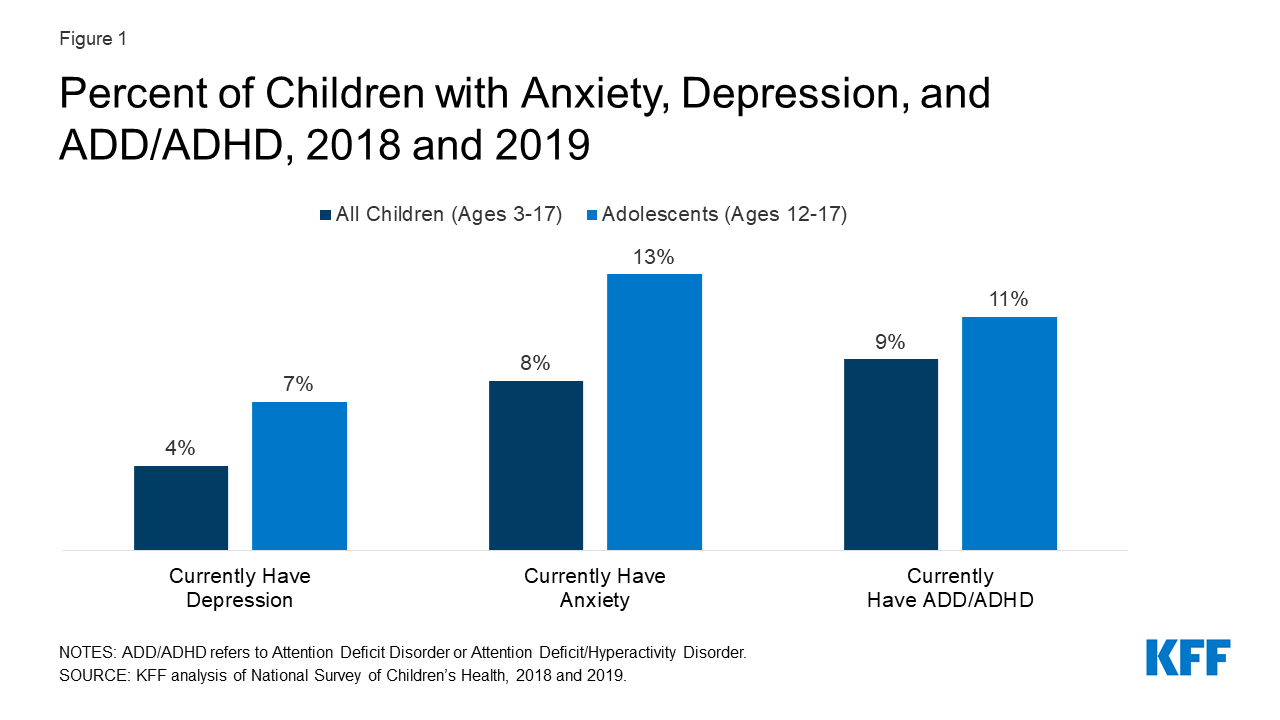
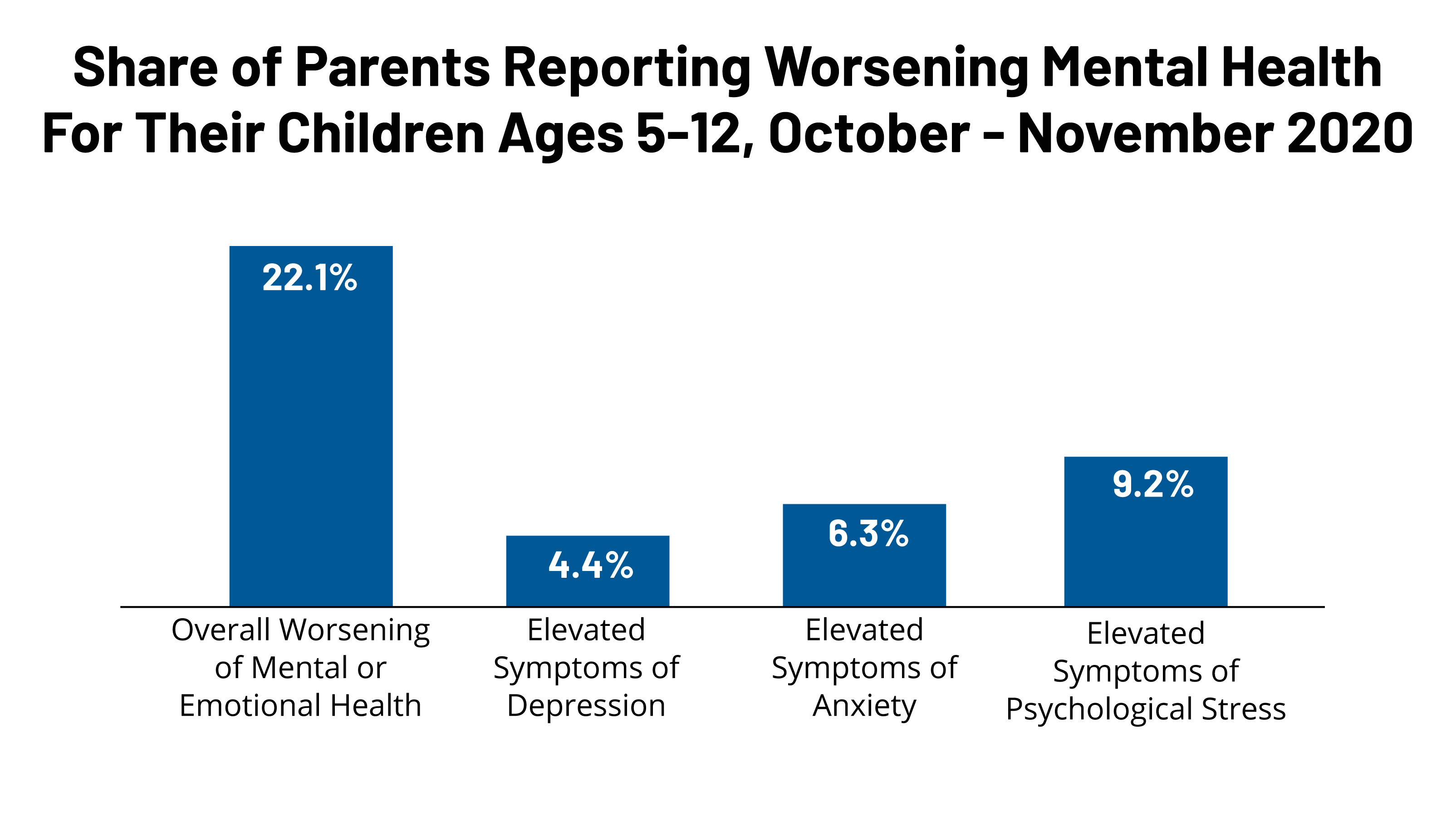
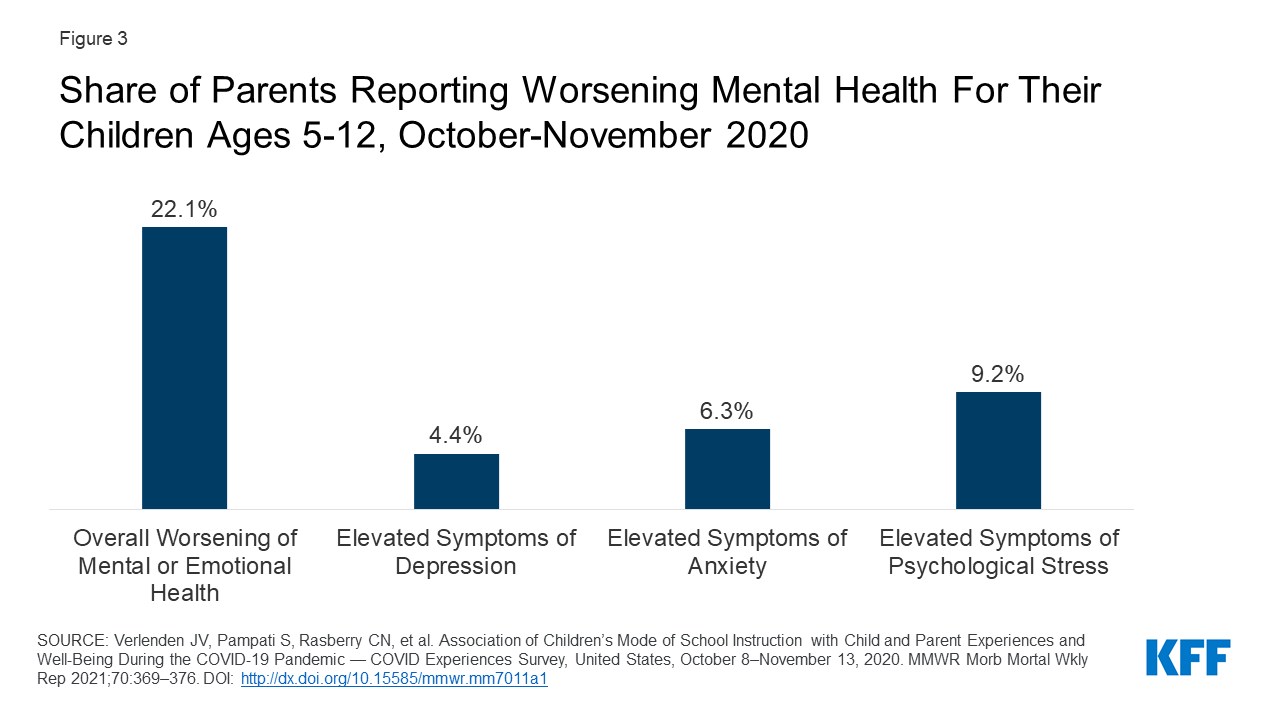
Mental Health And Substance Use Considerations Among Children During This brief identifies factors contributing to poor mental health and substance use outcomes among children during the covid 19 pandemic, focusing on groups of children who are particularly at risk and barriers to accessing mental health care. By nirmita panchal, rabah kamal, cynthia cox, et al., kaiser family foundation, may 26, 2021 introduction during the covid 19 pandemic, children have experienced major disruptions as a result of public health safety measures, including school closures, social isolation, financial hardships, and gaps in health care access. many parents have reported poor mental health outcomes in their children. Stress related to the disruption of daily life and routines, illness anxiety, and social isolation were all cited as factors that triggered or exacerbated mental illness. while 12 to 17 year olds accounted for the highest proportion of mental health related visits, young children were in no way exempt from the effects of stress and anxiety. The brief examines factors contributing to worsening mental health and substance use outcomes among children and adolescents during the pandemic, looking closely at those who are at higher risk.
Mental Health And Substance Use Considerations Among Children During Stress related to the disruption of daily life and routines, illness anxiety, and social isolation were all cited as factors that triggered or exacerbated mental illness. while 12 to 17 year olds accounted for the highest proportion of mental health related visits, young children were in no way exempt from the effects of stress and anxiety. The brief examines factors contributing to worsening mental health and substance use outcomes among children and adolescents during the pandemic, looking closely at those who are at higher risk. This study aimed to address this gap by reviewing changes in youth (age ≤ 25) mental health, psychological wellbeing, substance use, and the use or delivery of relevant services during the pandemic. pubmed and embase were searched in may 2021 to conduct a rapid review of the literature. Increasingly, research confirms the negative effects of covid 19 safety measures on the mental health of children and adolescents. 1 5 saunders and colleagues 6 call for an urgent response to the increasing sustained demand for mental health services inclusive of substance use and developmental disorders. the authors’ population based cross.
Mental Health And Substance Use Considerations Among Children During This study aimed to address this gap by reviewing changes in youth (age ≤ 25) mental health, psychological wellbeing, substance use, and the use or delivery of relevant services during the pandemic. pubmed and embase were searched in may 2021 to conduct a rapid review of the literature. Increasingly, research confirms the negative effects of covid 19 safety measures on the mental health of children and adolescents. 1 5 saunders and colleagues 6 call for an urgent response to the increasing sustained demand for mental health services inclusive of substance use and developmental disorders. the authors’ population based cross.
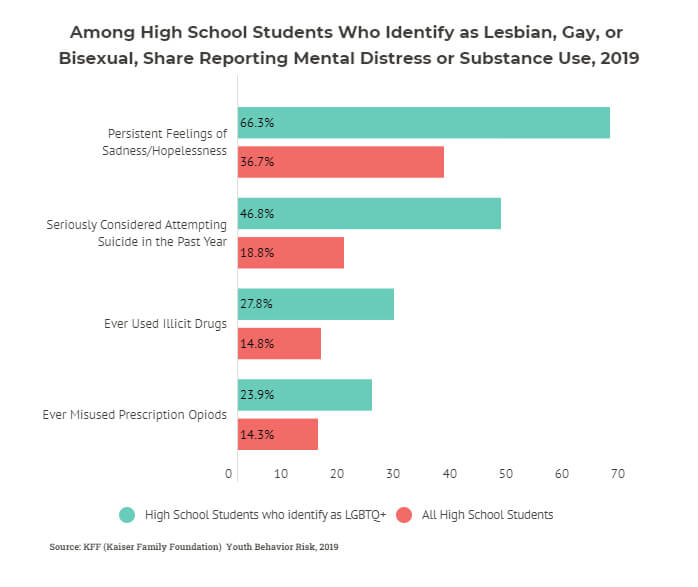
Mental Health And Substance Use Considerations Among Children During

Comments are closed.