Motor Neuron Cell

Motor Neuron Function Types And Structure A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. when these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. this is characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy) and loss of motor function. motor neuron. The structure of a motor neuron is characterized by three components: the soma, the axon, and the dendrites. motor neurons have a large cell body, or soma, and long projections used in transmitting information away from the soma. these projections are referred to as axons and dendrites. axons send impulses away from the soma and dendrites carry.
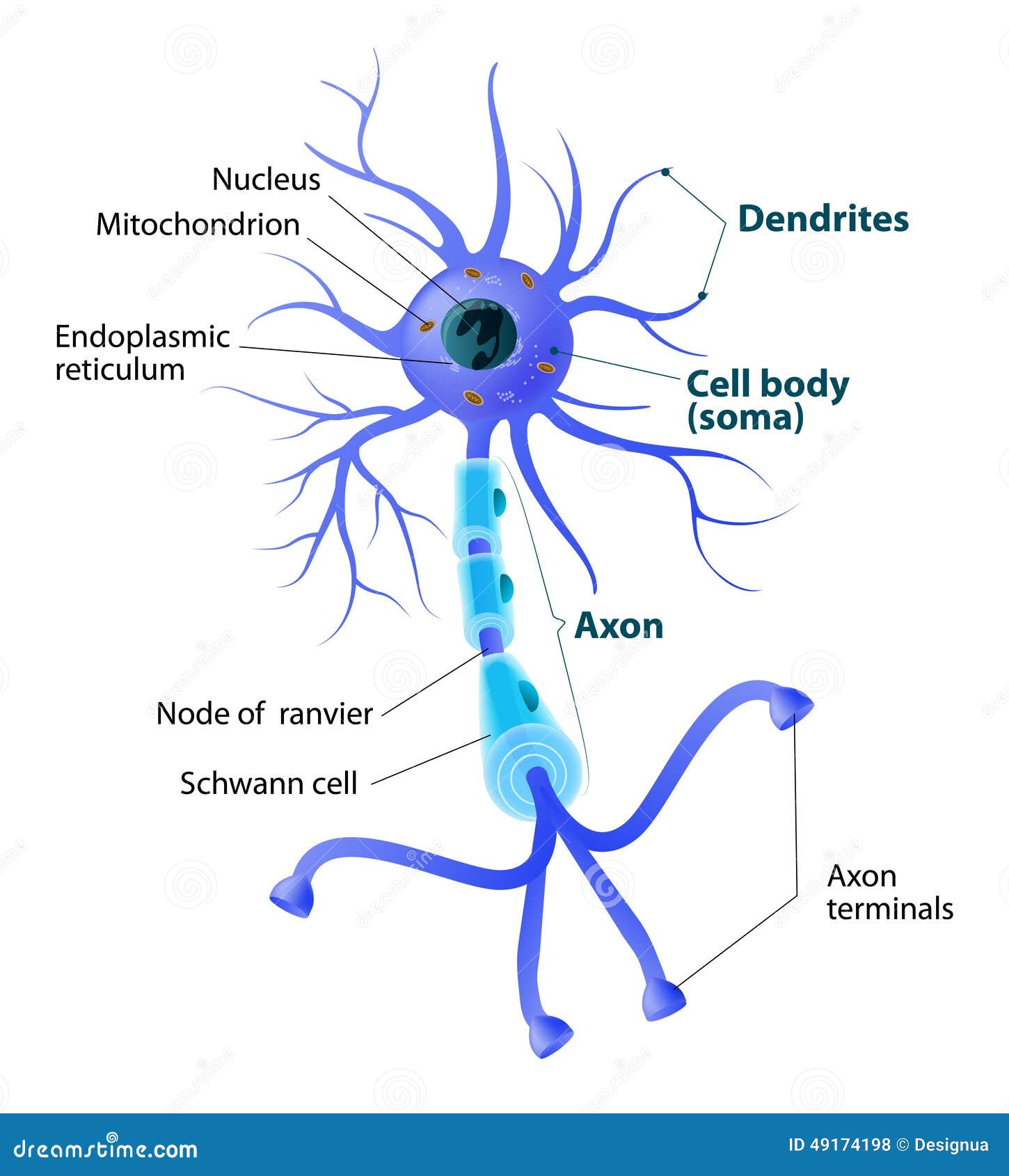
Structure Of A Motor Neuron Stock Vector Illustration Of Care Body Damage. motor neurons (also referred to as efferent neurons) are the nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system towards muscles to cause movement. they release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to muscle movement. these movements can be voluntary, such as reaching out to pick up an item, or. The large alpha motor neuron cell body can be either in the brainstem or spinal cord. in the spinal cord, the cell bodies are found in the anterior horn and thus are called anterior horn cells. from the anterior horn cell, a single axon goes on to innervate many muscle fibers within a single muscle. A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron[1]) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. [2] there are two types of motor neuron. Learn about motor neurons, the nerve cells that carry movement instructions from the brain and spinal cord to muscles. find out how they work, where they are located, and what can go wrong with them.

Myelinated Motor Neurons Function Location Types A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron[1]) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. [2] there are two types of motor neuron. Learn about motor neurons, the nerve cells that carry movement instructions from the brain and spinal cord to muscles. find out how they work, where they are located, and what can go wrong with them. The large alpha motor neuron cell body can be either in the brainstem or spinal cord. in the spinal cord, the cell bodies are found in the anterior horn and thus are called anterior horn cells. from the anterior horn cell, a single axon goes on to innervate many muscle fibers within a single muscle. Motor neuron disease. motor neurons have cell bodies in the spinal cord and brain, so they are technically part of the cns. however, they are the motor side of the peripheral nervous system, so some motor neuron diseases are briefly discussed here. a more comprehensive discussion is in chapter 5.5.

Comments are closed.