Motor Sparing Median And Ulnar Nerve Blocks At The Wrist A How To Guide

Motor Sparing Median And Ulnar Nerve Blocks At The Wrist A How To The median and ulnar nerves can be blocked close to the wrist, which will preserve motor function in the forearm flexor muscles. this is useful in minor hand. The wrist block involves anesthesia of the median, ulnar, and radial nerves, including the dorsal sensory branch of the ulnar nerve. the wrist block is simple to perform, essentially devoid of systemic complications, and highly effective for a variety of procedures on the hand and fingers. wrist blocks can be used in the office or operating room setting. as such, skill in performing a wrist.
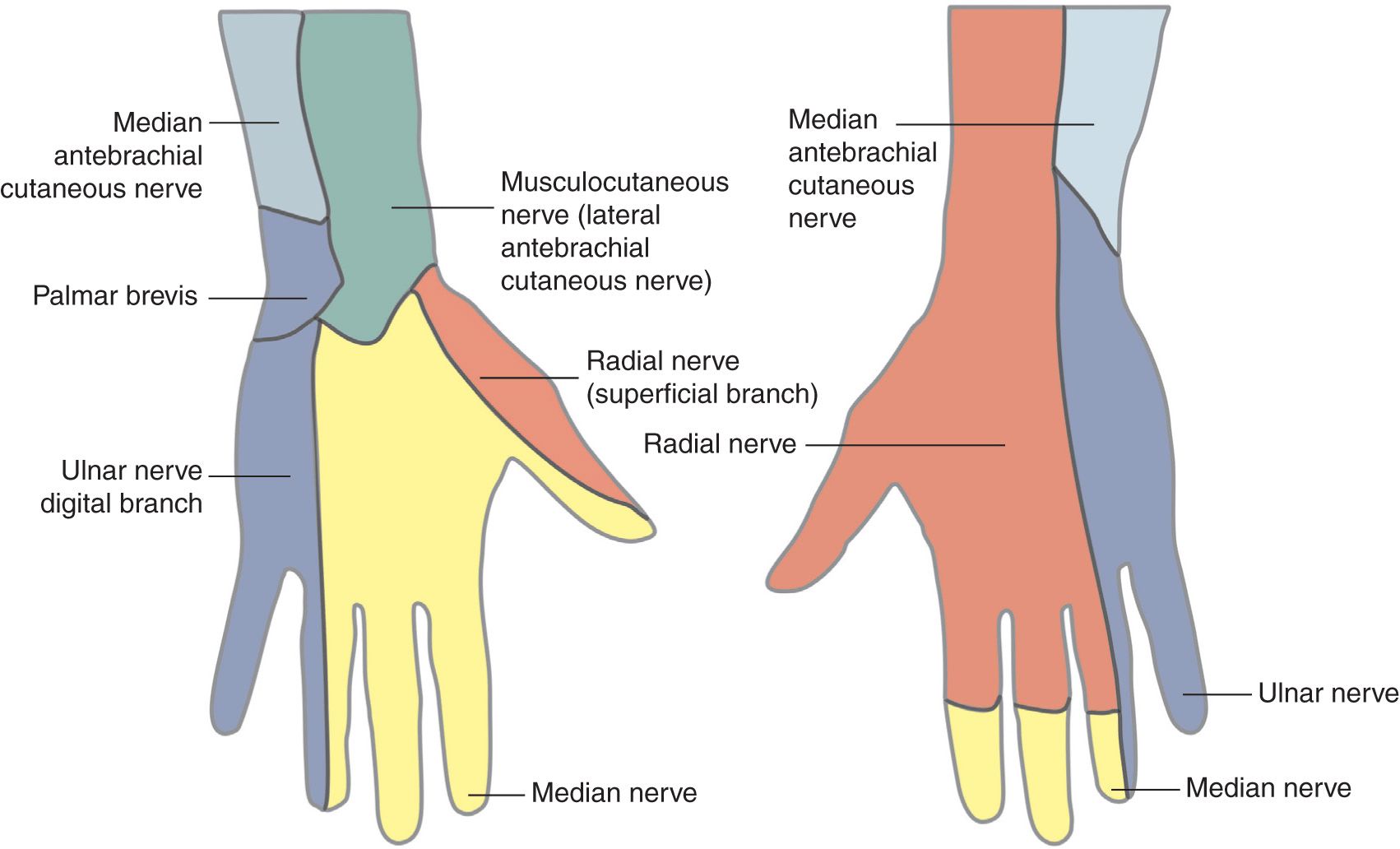
Median Nerve Wrist Anatomy Technique (figure 5) the median nerve is blocked by inserting the needle 2.5cm proximal to the wrist crease between the tendons of palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis with the forearm is supinated. the needle is inserted until it pierces the deep fascia (3 5mm). 3 to 5 ml of local anaesthetic is injected. Ulnar nerve to block the ulnar nerve, the same needle can be advanced beneath the tendon of fcu towards the radial border of the forearm, to a depth of 1–1.5 cm. the needle is redirected subcu taneously around the ulnar aspect of the wrist in order to block the dorsal cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve. this medial. Nerve blocks of the ulnar, median, and radial nerves at the wrist and elbow provide effective anesthesia for a wide range of medical procedures in the upper extremity. To make this technique more effective for carpal surgery, blocks of the posterior interosseous and anterior interosseous nerves are added. step 1: the patient is counseled about the procedure and the expected outcomes. step 2: drug allergies are checked. step 3: the maximum safe dose of the chosen local anesthetic agent is calculated using the.

Ultrasound Guided Blocks Of The Median Ulnar And Radial Nerves Youtube Nerve blocks of the ulnar, median, and radial nerves at the wrist and elbow provide effective anesthesia for a wide range of medical procedures in the upper extremity. To make this technique more effective for carpal surgery, blocks of the posterior interosseous and anterior interosseous nerves are added. step 1: the patient is counseled about the procedure and the expected outcomes. step 2: drug allergies are checked. step 3: the maximum safe dose of the chosen local anesthetic agent is calculated using the. The ulnar nerve lies along the ulnar aspect of the wrist, medial (ulnar) to the ulnar artery. the artery and the nerve are deep to the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon, which inserts on the pisiform. the dorsal cutaneous branches of the nerve wrap around the ulna to innervate the dorsum of the ulnar side of the hand. The wrist nerve block is an effective method to provide anesthesia of the hand and fingers without the arm immobility that occurs with more proximal brachial plexus nerve blocks. traditional wrist nerve block technique involves advancing needles using surface landmarks toward the three nerves that supply the hand: the median, ulnar, and radial.
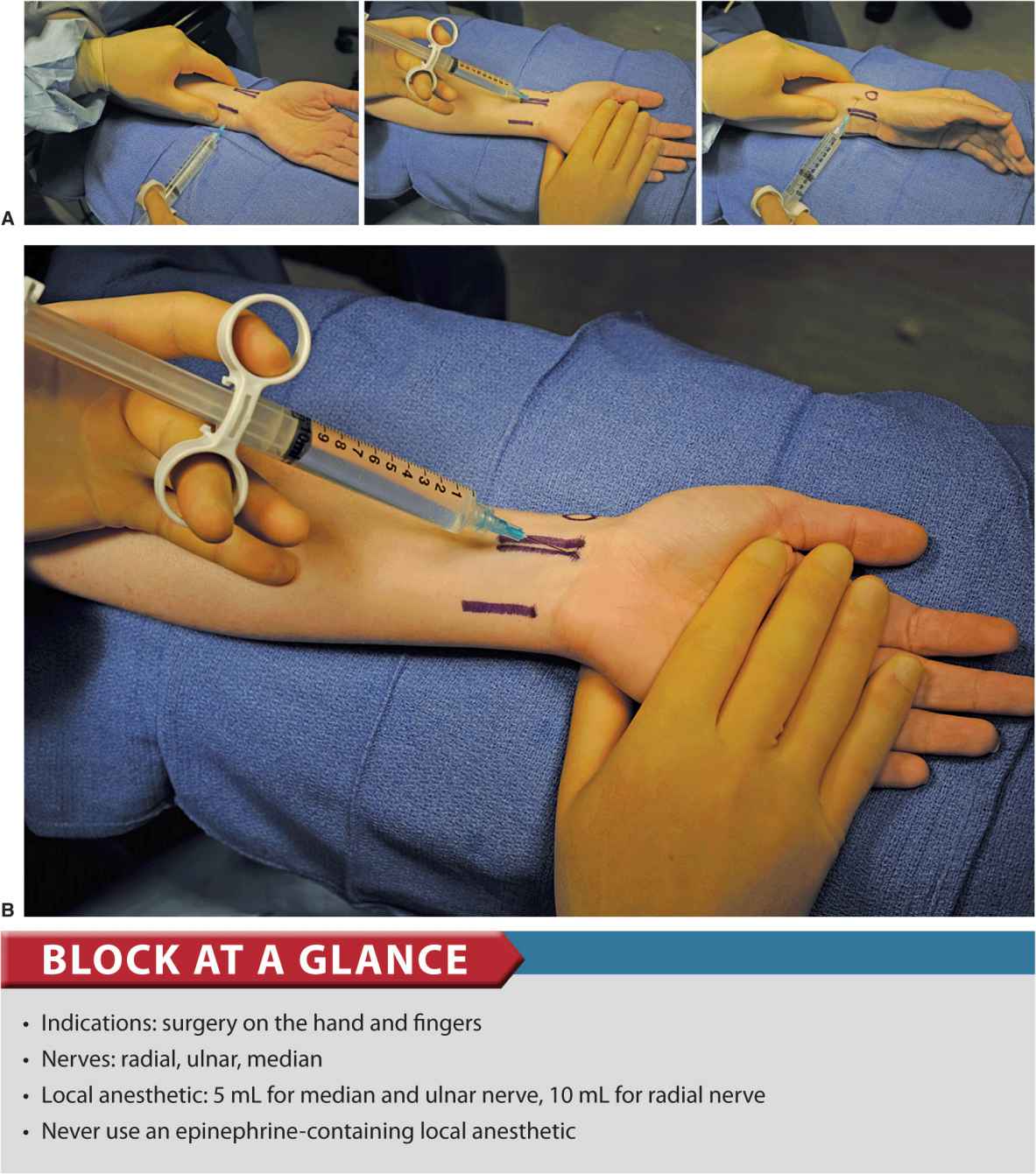
Wrist Block Anesthesia Key The ulnar nerve lies along the ulnar aspect of the wrist, medial (ulnar) to the ulnar artery. the artery and the nerve are deep to the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon, which inserts on the pisiform. the dorsal cutaneous branches of the nerve wrap around the ulna to innervate the dorsum of the ulnar side of the hand. The wrist nerve block is an effective method to provide anesthesia of the hand and fingers without the arm immobility that occurs with more proximal brachial plexus nerve blocks. traditional wrist nerve block technique involves advancing needles using surface landmarks toward the three nerves that supply the hand: the median, ulnar, and radial.

Comments are closed.