Multiplication Rule Of Probability Probability Theory Intersection Of Two Events
Multiplication Rule For Probability Examples Solutions Lessons What is the multiplication rule of probability? how do we find the probability of the intersection of two events? that’s what we’ll go over in today’s probab. The addition rule. if a and b are defined on a sample space, then: p (a or b) = p (a) p (b) − p (a and b) if a and b are mutually exclusive, then. p(a and b) = 0. and equation 4.3.2 becomes. p (a or b) = p (a) p (b). example 4.3.1. klaus is trying to choose where to go on vacation.

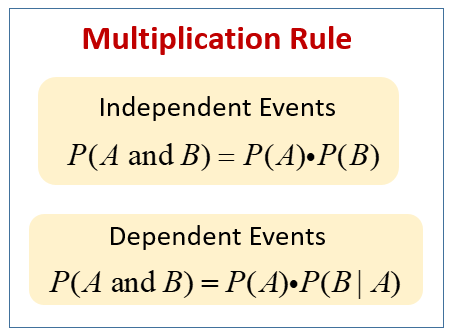
Multiplication Rule Of Probability Probability Theory Intersection Answer: identify the relevant probabilities. there are three methods to check whether two events are independent. method 1: checking. calculate the probability that a student lives on campus given that they have a private bathroom. use the formula. compare this to the probability that a student lives on campus. Stat 414 introduction to probability theory multiplication rule. the probability that two events or more events. in the case of three events, the rule looks. Multiplication rule of probability states that whenever an event is the intersection of two other events, that is, events a and b need to occur simultaneously. then, p(a and b)=p(a)⋅p(b). the set a∩b denotes the simultaneous occurrence of events a and b, that is the set in which both events a and event b have occurred. We finally developed a complete set of probability rules that we can use to find the probabilities of the complement of an event, and the union and intersection of any two events. 4.5: conditional probability and multiplication rules is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts.

Using A Venn Diagram To Understand The Multiplication Rule For Multiplication rule of probability states that whenever an event is the intersection of two other events, that is, events a and b need to occur simultaneously. then, p(a and b)=p(a)⋅p(b). the set a∩b denotes the simultaneous occurrence of events a and b, that is the set in which both events a and event b have occurred. We finally developed a complete set of probability rules that we can use to find the probabilities of the complement of an event, and the union and intersection of any two events. 4.5: conditional probability and multiplication rules is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. To use this rule, multiply the probabilities for the independent events. with independent events, the occurrence of event a does not affect the likelihood of event b. this rule is not valid for dependent events. using probability notation, the specific multiplication rule is the following: p (a ∩ b) = p (a) * p (b) or, the joint probability. We have already learned the multiplication rules we follow in probability, such as; p (a∩b) = p (a)×p (b|a) ; if p (a) ≠ 0. p (a∩b) = p (b)×p (a|b) ; if p (b) ≠ 0. let us learn here the multiplication theorems for independent events a and b. if a and b are two independent events for a random experiment, then the probability of.

Probability Rule Of Addition And Multiplication Quality Gurus To use this rule, multiply the probabilities for the independent events. with independent events, the occurrence of event a does not affect the likelihood of event b. this rule is not valid for dependent events. using probability notation, the specific multiplication rule is the following: p (a ∩ b) = p (a) * p (b) or, the joint probability. We have already learned the multiplication rules we follow in probability, such as; p (a∩b) = p (a)×p (b|a) ; if p (a) ≠ 0. p (a∩b) = p (b)×p (a|b) ; if p (b) ≠ 0. let us learn here the multiplication theorems for independent events a and b. if a and b are two independent events for a random experiment, then the probability of.

Multiplication Addition Rule Probability Mutually Exclusive

Probability Rules Cheat Sheet Basic Probability Rules With Examples

Comments are closed.