Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure
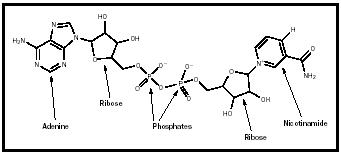
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Niacin is a component of two coenzymes: nad, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (nadp). nad (the oxidized form of the nad coenzyme) is important in catabolism and in the production of metabolic energy. Nicotinamide. nicotinamide is the most common form of the vitamin niacin. nicotinamide is found in the body as part of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad), an important cofactor of many enzymes involved in metabolism and the production of energy from sugars and fats. the structure of nicotinamide, shown in figure 1, incorporates a six atom.
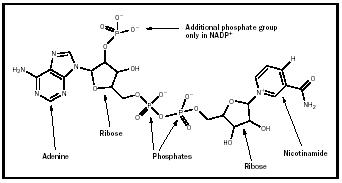
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide consists of two nucleosides joined by pyrophosphate. the nucleosides each contain a ribose ring, one with adenine attached to the first carbon atom (the 1' position) (adenosine diphosphate ribose) and the other with nicotinamide at this position. [4][5] the redox reactions of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) page id. nicotinamide is from the niacin vitamin. the nad coenzyme is involved with many types of oxidation reactions where alcohols are converted to ketones or aldehydes. it is also involved in the first enzyme complex 1 of the electron transport chain.the structure for the coenzyme, nad. As the glucose is oxidized by the glycolytic enzymes, the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad ) is converted from its oxidized to reduced form (nad to nadh). when oxygen is available (aerobic conditions), mitochondria in the cell can reoxidize to nadh to nad . Nicotinamide is from the niacin vitamin. the nad coenzyme is involved with many types of oxidation reactions where alcohols are converted to ketones or aldehydes. it is also involved in the first enzyme complex 1 of the electron transport chain.the structure for the coenzyme, nad , nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is shown in figure \(\pageindex{1}\).
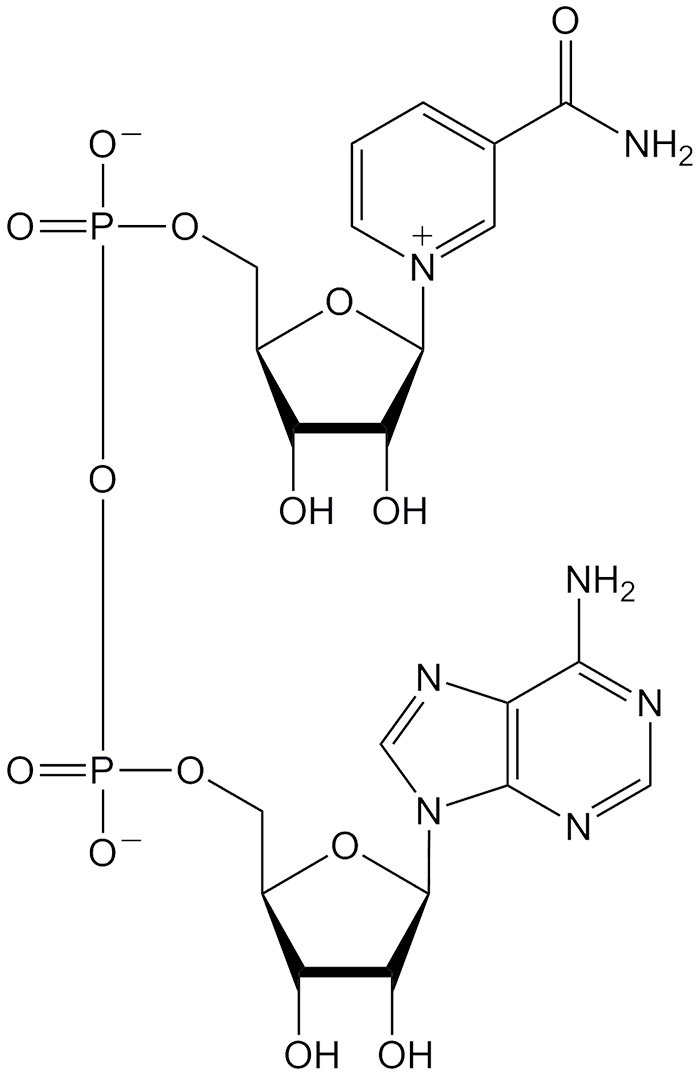
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide American Chemical Society As the glucose is oxidized by the glycolytic enzymes, the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad ) is converted from its oxidized to reduced form (nad to nadh). when oxygen is available (aerobic conditions), mitochondria in the cell can reoxidize to nadh to nad . Nicotinamide is from the niacin vitamin. the nad coenzyme is involved with many types of oxidation reactions where alcohols are converted to ketones or aldehydes. it is also involved in the first enzyme complex 1 of the electron transport chain.the structure for the coenzyme, nad , nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is shown in figure \(\pageindex{1}\). Nad is a dinucleotide composed of two mononucleotides (adenosine 5′ monophosphate, amp, and nicotinamide mononucleotide, nmn), which are joined through their 5′ phosphate groups (fig. 1). the molecule is present in all living cells and reversibly converted between its oxidized (nad ) and reduced (nadh) forms acting as a coenzyme in many. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) is an important coenzyme that regulates various metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, β oxidation, and oxidative phosphorylation. additionally, nad.
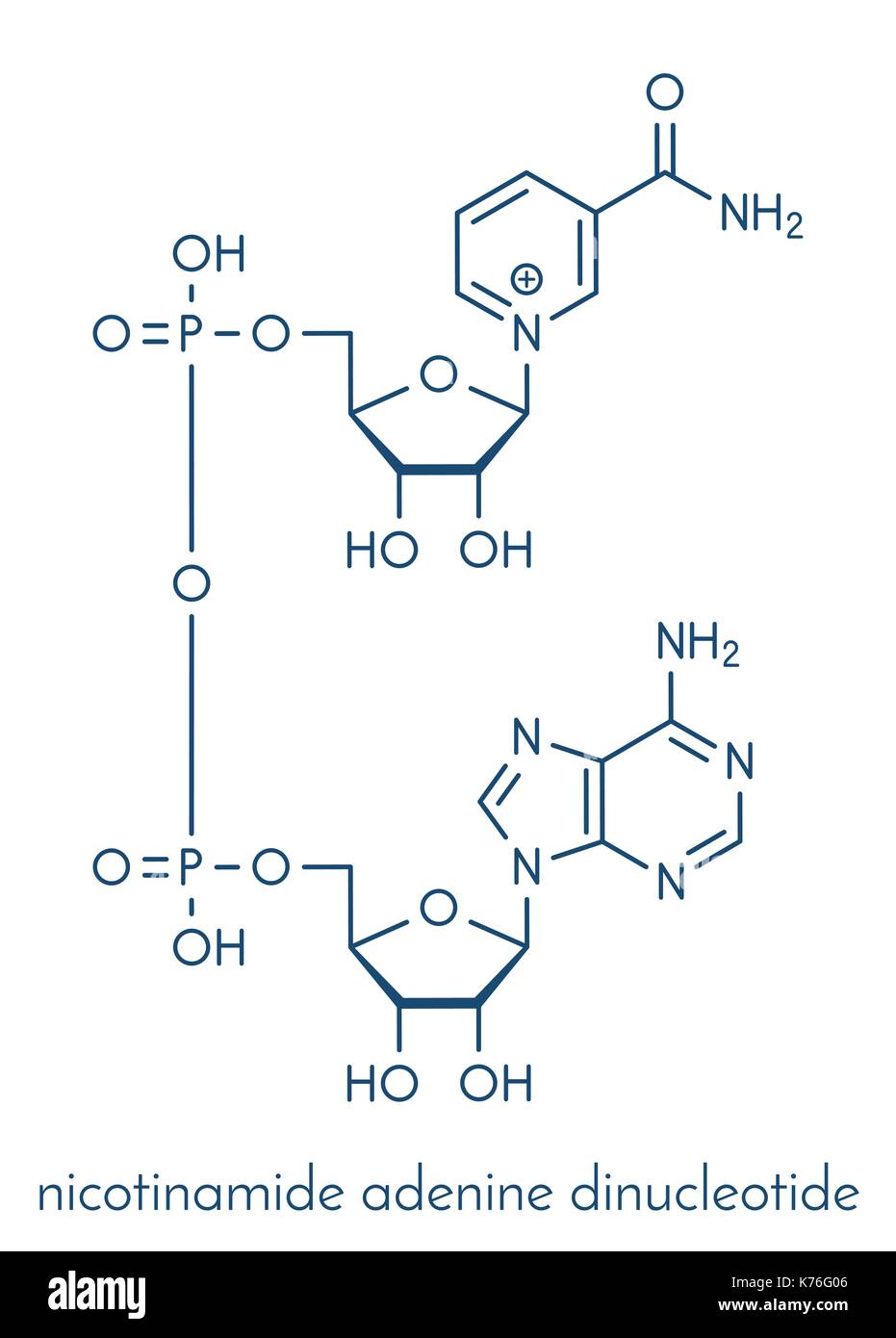
Le Nicotinamide Adénine Dinucléotide Nad Molécule Coenzyme Nad is a dinucleotide composed of two mononucleotides (adenosine 5′ monophosphate, amp, and nicotinamide mononucleotide, nmn), which are joined through their 5′ phosphate groups (fig. 1). the molecule is present in all living cells and reversibly converted between its oxidized (nad ) and reduced (nadh) forms acting as a coenzyme in many. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) is an important coenzyme that regulates various metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, β oxidation, and oxidative phosphorylation. additionally, nad.

Comments are closed.