Number System Integers

Class 7 Number System Integers And Rational Numbers Basics Problems The natural (or counting) numbers are the part of the number system that includes all the positive integers from 1 through infinity. they are used for the purpose of counting. natural numbers do not include 0, fractions, decimals, or negative numbers. the set of natural numbers is usually represented by the letter "n". Therefore, the required octal number is (25)8. example 4: convert hexadecimal 2c to decimal number. solution: we need to convert 2c16 into binary numbers first. 2c → 00101100. now convert 001011002 into a decimal number. 101100 = 1 × 25 0 × 24 1 × 23 1 × 22 0 × 2 1 0 × 2 0.
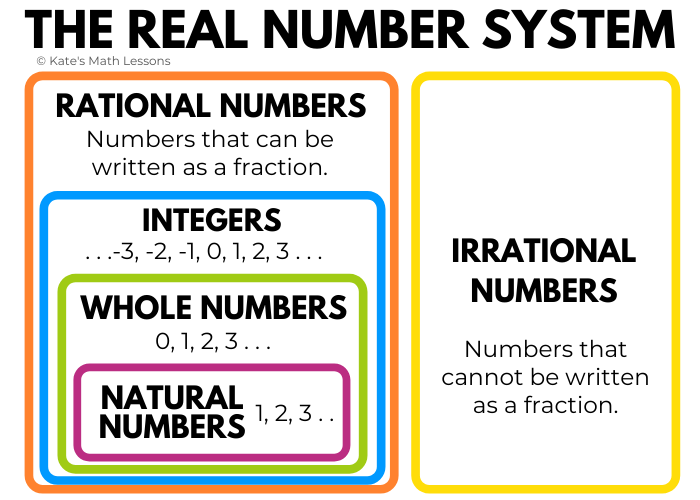
Classifying Real Numbers Kate S Math Lessons Example 3: tell if the statement is true or false. the number zero (0) is a rational number. solution: the number zero can be written as a ratio of two integers, thus it is indeed a rational number. this statement is true. example 4: name the set or sets of numbers to which each real number belongs. it belongs to the sets of natural numbers, {1. A number line (figure 3.12) helps envision the integers. this also means that an integer gives magnitude (size) and direction (positive is to the right, negative is to the left). graphing an integer on the number line means placing a solid dot at the integer on the number line. Real numbers are closed under the arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. in other words, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of two real numbers, ‘m’ and ‘n’, always give a real number. for example, 2 5 = 7. 0.9 – 0.6 = 0.3. Integers are a special set of numbers comprising zero, positive numbers, and negative numbers. so, an integer is a whole number (not a fractional number) that can be positive, negative, or zero. examples of integers are 7, 1, 3, 78, 56, and 300. examples of numbers that are not integers are 1.4, 5 2, 9.23, 0.9, 3 7.

Number Systems Integers Ppt Real numbers are closed under the arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. in other words, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of two real numbers, ‘m’ and ‘n’, always give a real number. for example, 2 5 = 7. 0.9 – 0.6 = 0.3. Integers are a special set of numbers comprising zero, positive numbers, and negative numbers. so, an integer is a whole number (not a fractional number) that can be positive, negative, or zero. examples of integers are 7, 1, 3, 78, 56, and 300. examples of numbers that are not integers are 1.4, 5 2, 9.23, 0.9, 3 7. Integers are whole numbers plus negatives they look a little bit like this 2, 1, 0, 1, and so on. last but not least, not to be outdone rational numbers are integers plus fractions like 3, 1 2, 5 8 and 14.2. all natural numbers are whole numbers all whole numbers are integers all integers are rational numbers now listen to that drummer! what. Real numbers derive from the concept of the number line: the positive numbers sitting to the right of zero, and the negative numbers sitting to the left of zero. any number that you can plot on this real line is a real number. the numbers 27, 198.3, 0, 32 9 and 5 billion are all real numbers.number line. strangely enough, you can also plot.

Integer Venn Diagram Integers are whole numbers plus negatives they look a little bit like this 2, 1, 0, 1, and so on. last but not least, not to be outdone rational numbers are integers plus fractions like 3, 1 2, 5 8 and 14.2. all natural numbers are whole numbers all whole numbers are integers all integers are rational numbers now listen to that drummer! what. Real numbers derive from the concept of the number line: the positive numbers sitting to the right of zero, and the negative numbers sitting to the left of zero. any number that you can plot on this real line is a real number. the numbers 27, 198.3, 0, 32 9 and 5 billion are all real numbers.number line. strangely enough, you can also plot.
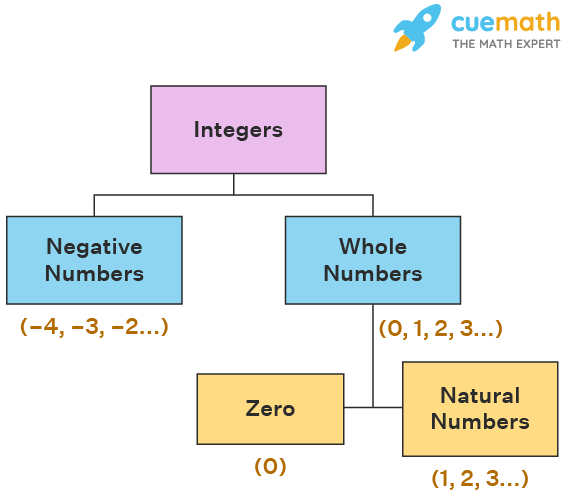
Integers Definition Properties Meaning Examples 2022

Comments are closed.