Overview Of Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Fcs Overview Of

Overview Of Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Fcs Overview Of By time correlation of the fluorescence fluctuations induced by molecules diffusing through a focused light, fcs can quantitatively evaluate the concentration, diffusion coefficient, and interaction of the molecules in vitro or in vivo. in this review, the basic principle and implementation of fcs are introduced. 2.5 fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (fcs) is a powerful technique, using a confocal microscope to analyse fluorescence signals only in a small sub volume of the sample. the diffusion of molecules in this sub femtoliter volume is observed by measuring the time dependent fluctuation of fluorescence.

Overview Of Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Fcs Overview Of Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (fcs) is a single molecule sensitive tool for the quantitative measurement of biomolecular dynamics and interactions. an overview of the versatility of. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (fcs) is a single molecule detection technique that measures the fluorescence fluctuations of molecules diffusing through a well defined volume. introduced over 40 years ago by magde, elson, and webb (1972) , one of the initial applications of fcs was to analyze the interaction of ethidium bromide with dna. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (fcs) is a statistical analysis, via time correlation, of stationary fluctuations of the fluorescence intensity. its theoretical underpinning originated from l. onsager's regression hypothesis. the analysis provides kinetic parameters of the physical processes. Essential information about processes governing molecular dynamics can thus be derived from the temporal pattern by which fluorescence fluctuations arise and decay. at its first introduction by madge, elson and webb in 1972, fcs was applied to measure diffusion and chemical dynamics of dna drug intercalation.
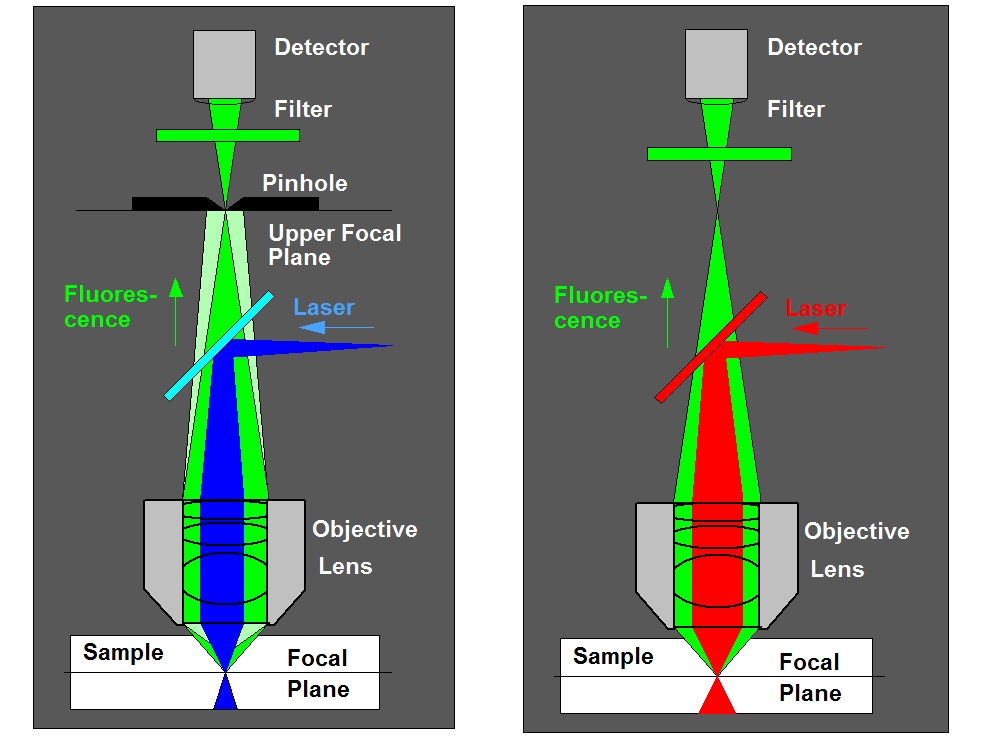
Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Fcs Becker Hickl Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (fcs) is a statistical analysis, via time correlation, of stationary fluctuations of the fluorescence intensity. its theoretical underpinning originated from l. onsager's regression hypothesis. the analysis provides kinetic parameters of the physical processes. Essential information about processes governing molecular dynamics can thus be derived from the temporal pattern by which fluorescence fluctuations arise and decay. at its first introduction by madge, elson and webb in 1972, fcs was applied to measure diffusion and chemical dynamics of dna drug intercalation. 1.5.2 the year of the invention. mew had to struggle for a few years before the experiments and the theory fell in place. it was not an easy experiment to perform half a century ago. the detectors were insensitive, the laser had just been invented, and the data processor (the ‘correlator card) was slow. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (fcs) is a powerful technique for quanti fi cation of. molecular dynamics, and it has been widely applied in diverse fields, e.g., biomedicine, biophysics.

Comments are closed.