Overview Of The Atria Ventricles Conduction System And Ecg Waveforms
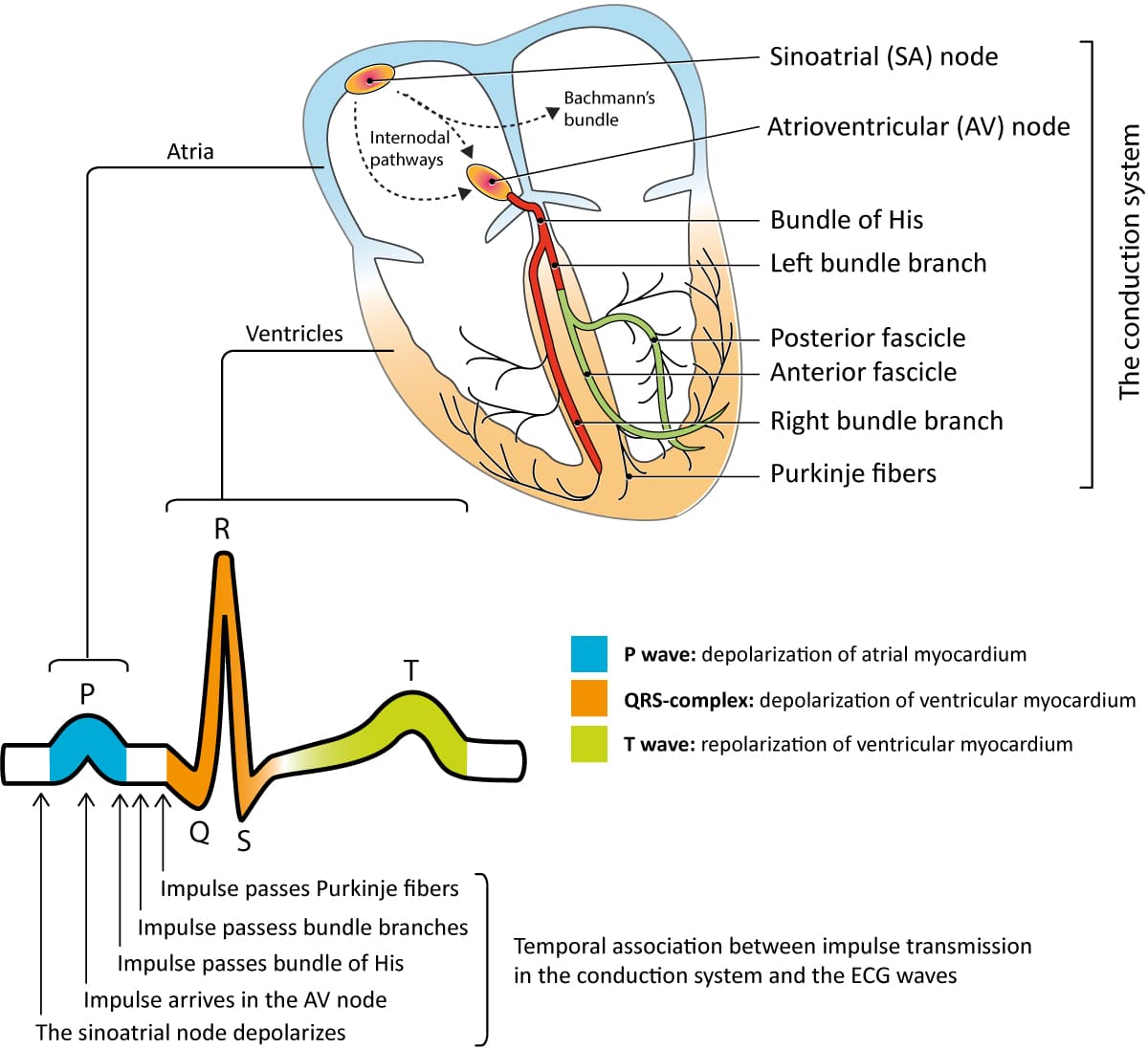
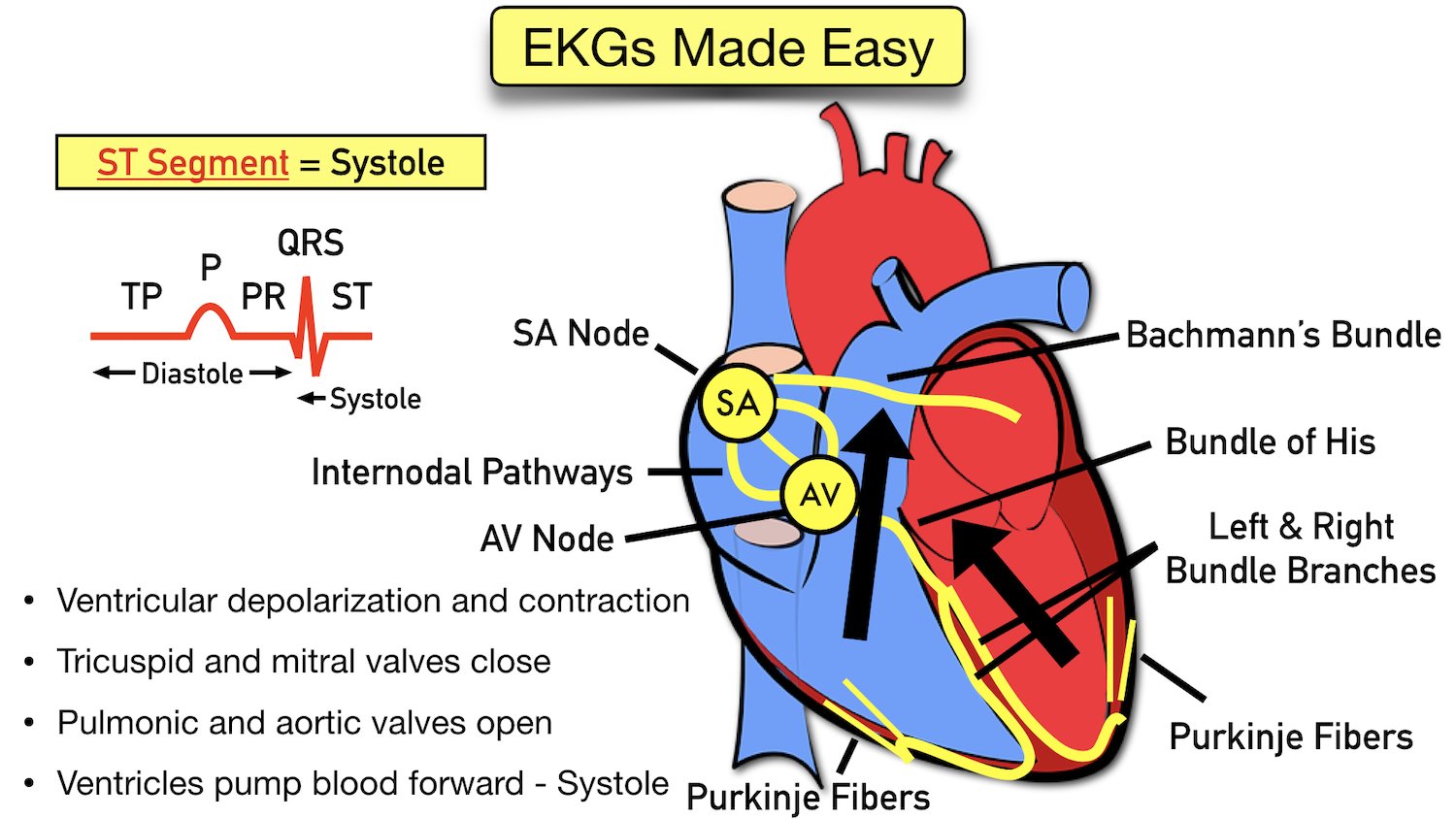
Overview Of The Atria Ventricles Conduction System And Ecg Waveforms A wiggers diagram is a standard diagram used in cardiac physiology to illustrate the association between aortic pressure, ventricular pressure, atrial pressure, volumes and ecg waveforms. learn the principles of cardiac physiology, electrocardiography and ecg interpretation. the action potential and conduction system are also discussed. The cardiac conduction system is designed for electrical impulse creation and propagation. it allows for initiation of impulses in the atrium, slowed conduction in the atrioventricular (av) node, and rapid propagation through the his purkinje system to allow synchronous contraction in the ventricles. layers of redundancy occur, so that if one.
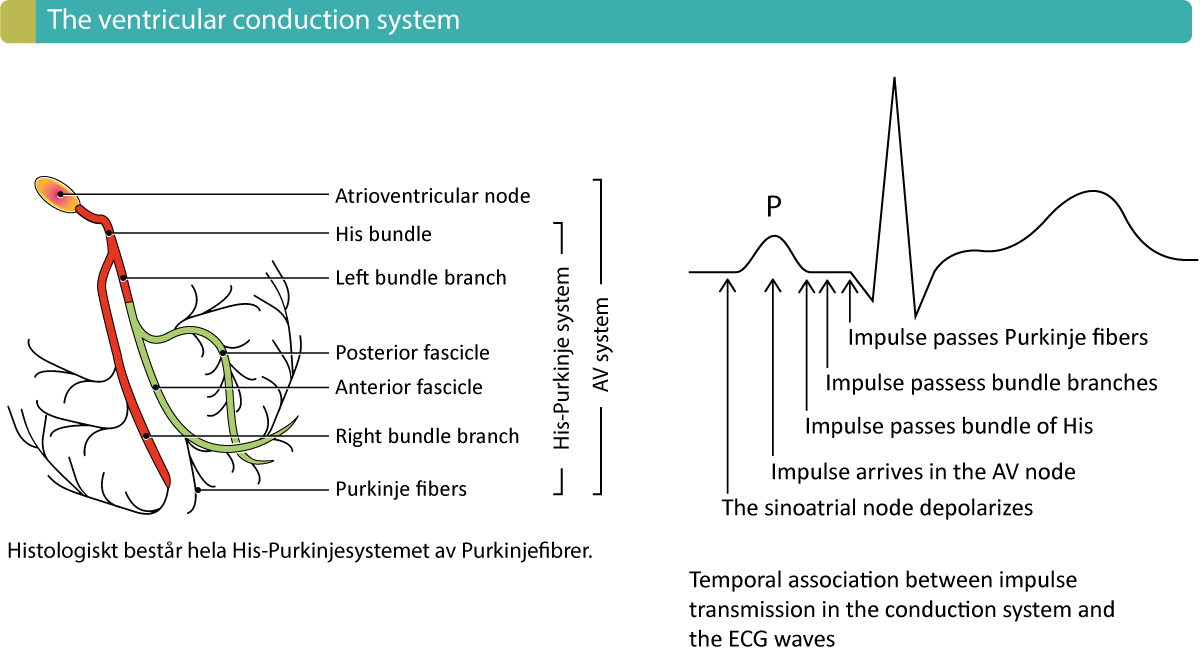
Overview Of Atrioventricular Av Blocks Ecg Learning The pr interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles is normal. the flat line between the end of the p wave and the onset of the qrs complex is called the pr segment and it reflects the slow impulse conduction through the atrioventricular node. There are five prominent components (points) on the ecg: the p wave, the qrs complex, and the t wave. the small p wave represents the depolarization of the atria. the atria begin contracting approximately 25 ms after the start of the p wave. the large qrs complex represents the depolarization of the ventricles, which requires a much stronger. The recorded tracing is called an electrocardiogram (ecg, or ekg). a typical ecg tracing is shown to the right. the different waves that comprise the ecg represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles. the ecg is recorded at a speed of 25 mm sec (5 large squares sec), and the voltages are calibrated so. Figure 19.3.2 – relationship between the cardiac cycle and ecg: initially, both the atria and ventricles are relaxed (diastole). the p wave represents depolarization of the atria and is followed by atrial contraction (systole). atrial systole extends until the qrs complex, at which point, the atria relax.

Vectors And Waveforms Ecg Learning The recorded tracing is called an electrocardiogram (ecg, or ekg). a typical ecg tracing is shown to the right. the different waves that comprise the ecg represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles. the ecg is recorded at a speed of 25 mm sec (5 large squares sec), and the voltages are calibrated so. Figure 19.3.2 – relationship between the cardiac cycle and ecg: initially, both the atria and ventricles are relaxed (diastole). the p wave represents depolarization of the atria and is followed by atrial contraction (systole). atrial systole extends until the qrs complex, at which point, the atria relax. Ecg interpretation starts with assessment of the p wave and pr interval. the p wave is generated by depolarization (activation, contraction) of the atria. the pr interval is the interval between the start of the p wave and the start of the qrs complex. the pr interval determines whether impulse transmission from atria to ventricles is normal. The p wave is created by depolarisation of the atria, the qrs by depolarisation of the ventricles, and the t wave by repolarisation of the ventricles (hampton, 2008). in most people, these waveforms occur in a repeating rhythm called sinus rhythm, so called because it originates in the sinus node.

Ekg And Conduction System Diagram Quizlet Ecg interpretation starts with assessment of the p wave and pr interval. the p wave is generated by depolarization (activation, contraction) of the atria. the pr interval is the interval between the start of the p wave and the start of the qrs complex. the pr interval determines whether impulse transmission from atria to ventricles is normal. The p wave is created by depolarisation of the atria, the qrs by depolarisation of the ventricles, and the t wave by repolarisation of the ventricles (hampton, 2008). in most people, these waveforms occur in a repeating rhythm called sinus rhythm, so called because it originates in the sinus node.

Cardiac Cycle Anatomy And Physiology
Ecg Waveform Explained Ekg Labeled Diagrams And Components Ezmed

Comments are closed.