Oxygen Molecule Model
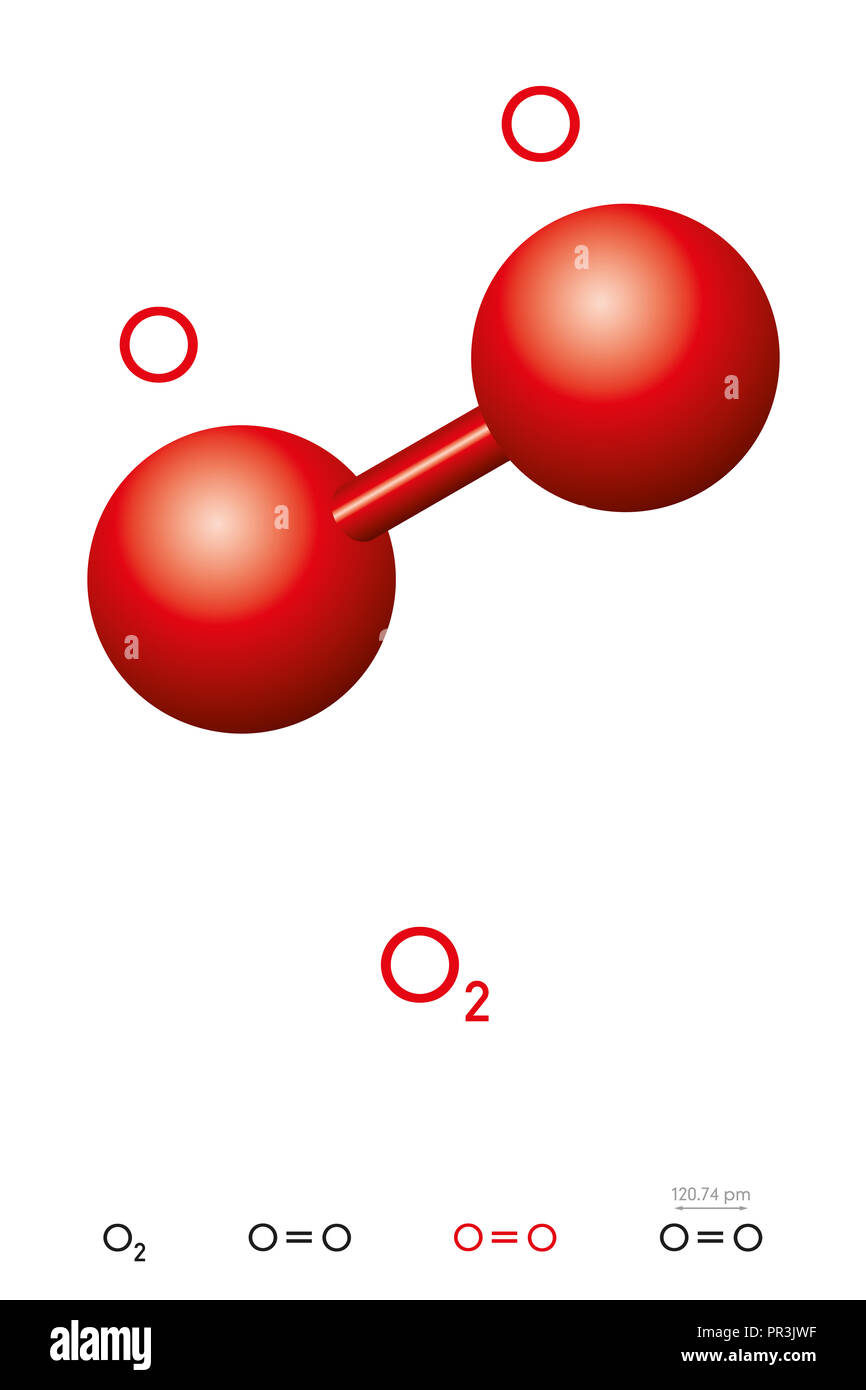
Oxygen Molecule Model Stock Photos Oxygen Molecule Model Stock Images Steps of drawing lewis diagram. find total valence electrons: it is two for each oxygen atom. find how many electrons are needed: it is four for one o2 molecule. look for the total number of bonds forming: double covalent bonds are forming in an o2 molecule. choose a central atom: both the atoms will be central. Oxygen. cubic (cp16) oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol o and atomic number 8. it is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds.
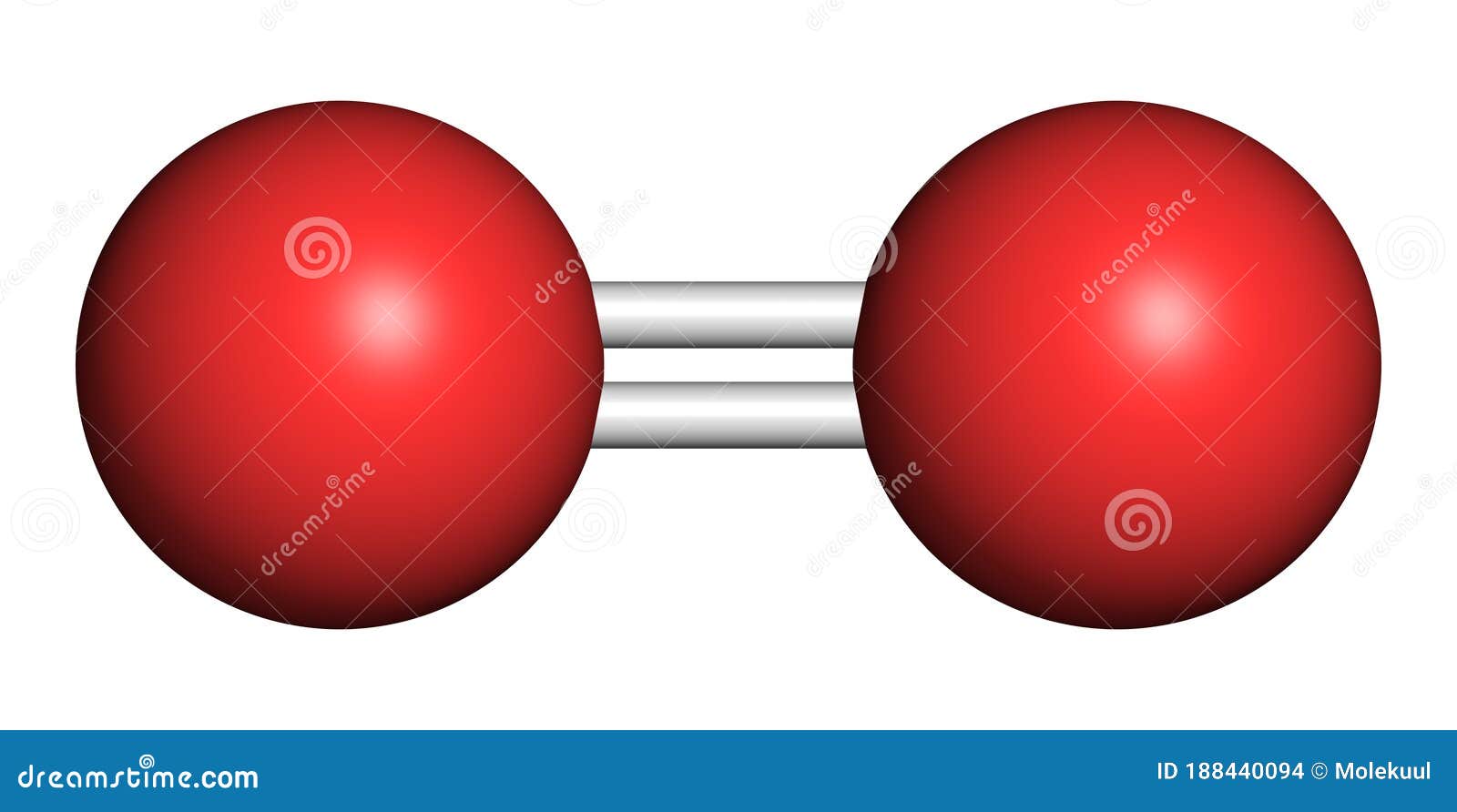
Elemental Oxygen O2 Molecule Skeletal Formula Cartoon Vector Model of molecular or diatomic oxygen, composed of two oxygen atoms bonded together. [1] molecular oxygen (o 2) is a diatomic molecule that is composed of two oxygen atoms held together by a covalent bond. molecular oxygen is essential for life, as it is used for respiration by many organisms. it's also essential for fossil fuel combustion. Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3d! how does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? find out by adding single, double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom. then, compare the model to real molecules!. Molecular oxygen (o2) is key to all life on earth, as it is constantly cycled via photosynthesis and cellular respiration. substantial scientific effort has been devoted to understanding every part of this cycle. classical molecular dynamics (md) simulations have been used to study some of the key processes involved in cellular respiration: o2 permeation through alveolar monolayers and. Structural formula. o 2. oxygen molecular model.

Diagram Representation Of The Element Oxygen Vector Image Molecular oxygen (o2) is key to all life on earth, as it is constantly cycled via photosynthesis and cellular respiration. substantial scientific effort has been devoted to understanding every part of this cycle. classical molecular dynamics (md) simulations have been used to study some of the key processes involved in cellular respiration: o2 permeation through alveolar monolayers and. Structural formula. o 2. oxygen molecular model. Dioxygen is a diatomic oxygen, a gas molecular entity and an elemental molecule. it has a role as an anti inflammatory drug, a reagent, a nutrient, a micronutrient, an oxidising agent, a human metabolite, a member of food packaging gas and a saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite. it is a conjugate base of a hydridodioxygen(1 ). The intense reactivity of ozone is sometimes explained by suggesting that one of the three oxygen atoms is in an “atomic” state; on reacting, this atom is dissociated from the o 3 molecule, leaving molecular oxygen. the molecular species, o 2, is not especially reactive at normal (ambient) temperatures and pressures. the atomic species, o.
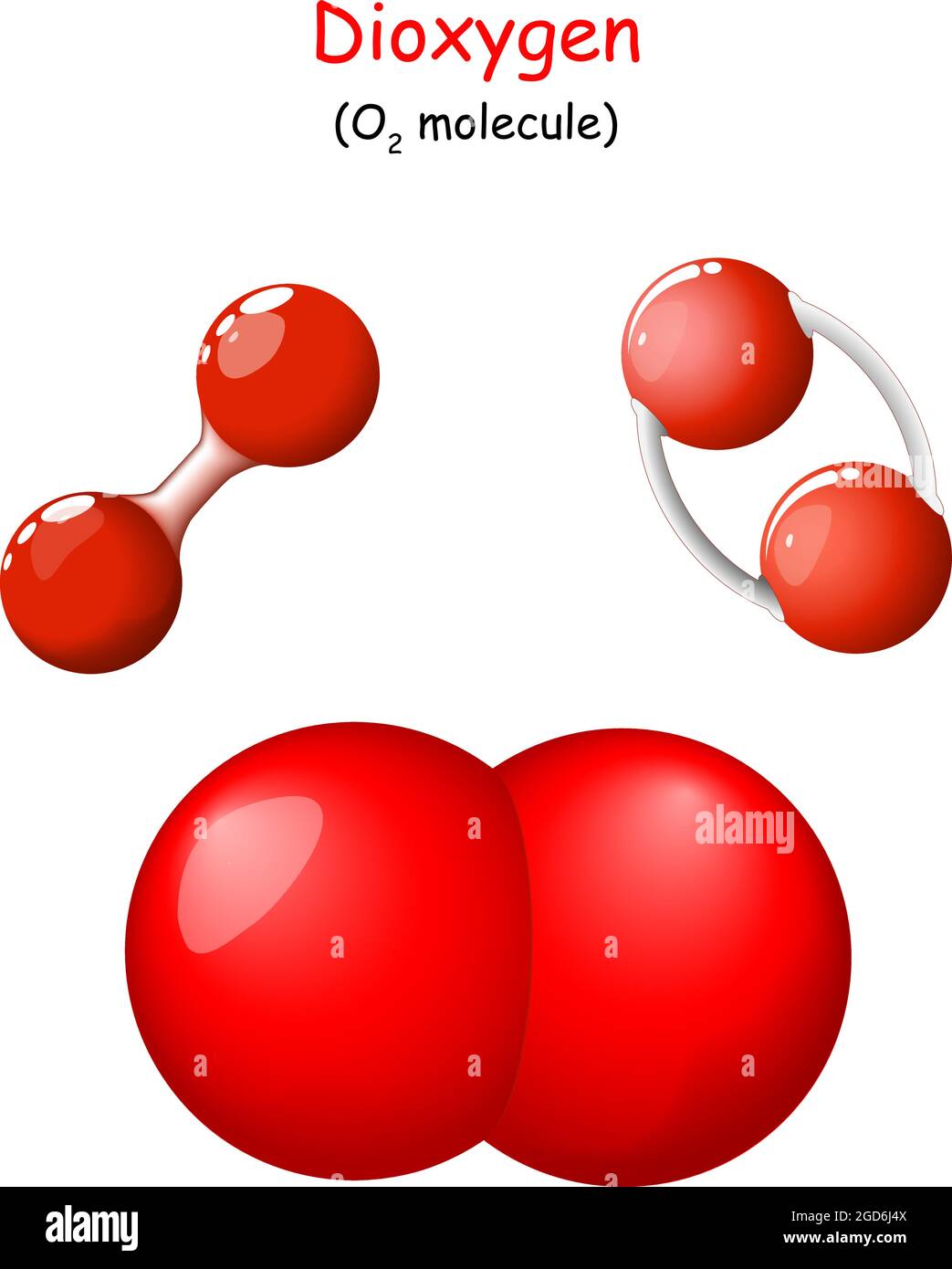
Oxygen Molecule Dioxygen is a diatomic oxygen, a gas molecular entity and an elemental molecule. it has a role as an anti inflammatory drug, a reagent, a nutrient, a micronutrient, an oxidising agent, a human metabolite, a member of food packaging gas and a saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite. it is a conjugate base of a hydridodioxygen(1 ). The intense reactivity of ozone is sometimes explained by suggesting that one of the three oxygen atoms is in an “atomic” state; on reacting, this atom is dissociated from the o 3 molecule, leaving molecular oxygen. the molecular species, o 2, is not especially reactive at normal (ambient) temperatures and pressures. the atomic species, o.

Comments are closed.