Pharmacologic Treatment Of Pulmonary Hypertension
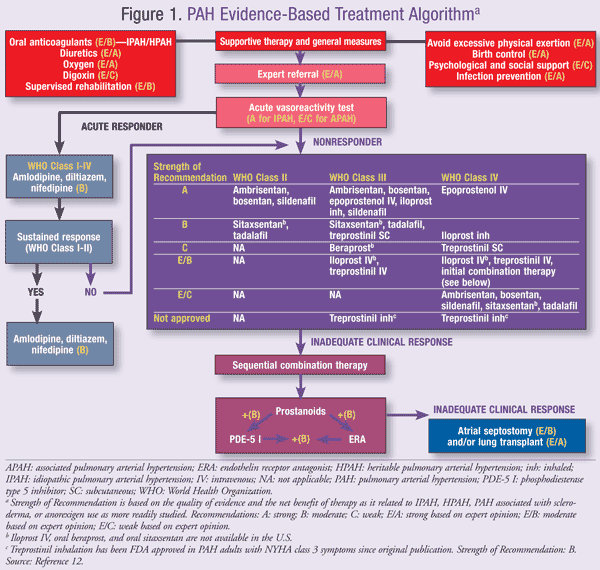
Pharmacologic Treatment Of Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) carries a poor prognosis if not promptly diagnosed and appropriately treated. the development and approval of 14 medications over the last several decades have led to a rapidly evolving approach to therapy, and have necessitated periodic updating of evidence based treatment guidelines. this guideline statement, which now includes a visual algorithm to. Choices of pharmacologic therapies for pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) are ideally guided by high level evidence. the objective of this guideline is to provide clinicians advice regarding pharmacologic therapy for adult patients with pah as informed by available evidence.

Pharmacologic Agents Approved For Use In Pulmonary Arterial 1 – 3. in patients with pulmonary hypertension due to lung disease or left heart disease, treatment should focus on optimizing comorbid conditions. c. 3, 9 – 11. in patients with pulmonary. A sleep study measures brain activity, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels and other things as you sleep. the test can help diagnose sleep apnea, which can cause pulmonary hypertension. ventilation perfusion (v q) scan. in this test, a radioactive tracer is given through a vein (iv). the tracer shows blood flow. Abstract. pulmonary arterial hypertension is a rare and devastating disease characterized by an abnormal chronic increase in pulmonary arterial pressure above 20 mmhg at rest, with a poor prognosis if not treated. currently, there is not a single fully effective therapy, even though a dozen of drugs have been developed in the last decades. Abstract. pulmonary hypertension (ph) is a disease with multiple etiologies and is categorized into five broad groups. of these groups, pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is the most studied and, therefore, all of the currently available drug classes (prostacyclin analogs, endothelin receptor antagonists and phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors) were developed to treat pah.
Pharmacologic Treatment Of Pulmonary Hypertension Abstract. pulmonary arterial hypertension is a rare and devastating disease characterized by an abnormal chronic increase in pulmonary arterial pressure above 20 mmhg at rest, with a poor prognosis if not treated. currently, there is not a single fully effective therapy, even though a dozen of drugs have been developed in the last decades. Abstract. pulmonary hypertension (ph) is a disease with multiple etiologies and is categorized into five broad groups. of these groups, pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is the most studied and, therefore, all of the currently available drug classes (prostacyclin analogs, endothelin receptor antagonists and phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors) were developed to treat pah. Pulmonary hypertension (ph), defined as a mean pulmonary arterial pressure greater than 25 mm hg at rest or greater than 30 mm hg during exercise, is often characterized by a progressive and sustained increase in pulmonary vascular resistance that eventually may lead to right ventricular (rv) failure. Purpose of review: pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a disease that carries a significant mortality left untreated. this article aims to review pharmacotherapeutics for pah. recent findings: pah specific therapies have evolved over the last three decades and have expanded from one therapy in the 1990s to 14 fda approved medications.

What Can Be Expected From Current Treatments For Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension (ph), defined as a mean pulmonary arterial pressure greater than 25 mm hg at rest or greater than 30 mm hg during exercise, is often characterized by a progressive and sustained increase in pulmonary vascular resistance that eventually may lead to right ventricular (rv) failure. Purpose of review: pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a disease that carries a significant mortality left untreated. this article aims to review pharmacotherapeutics for pah. recent findings: pah specific therapies have evolved over the last three decades and have expanded from one therapy in the 1990s to 14 fda approved medications.

Pulmonary Hypertension Lupon Gov Ph

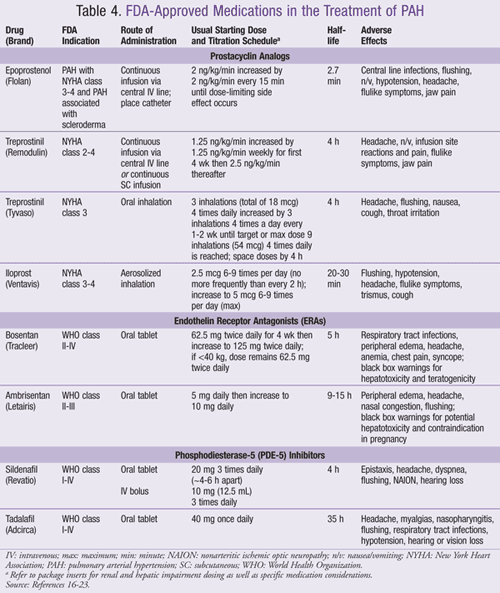
Pharmacologic Agents Approved For Use In Pulmonary Arterial

Comments are closed.