Pin By M Hodge On Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystems Habitats

Pin By M Hodge On Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystems Habitats Components and constituents. ecosystem: the components of an ecosystem are both biotic (living) and abiotic (non living). this means ecosystems consider interactions between plants, animals, microorganisms, water, soil, and even the climate. habitat: the components of a habitat are primarily the specific conditions and resources an organism needs. This research in terrestrial and marine ecosystems has led to significant developments in knowledge, conservation, restoration and affiliated policy and management decisions (hutchinson et al., 2019; windsor et al., 2021). further developing our understanding of these processes in different freshwater habitats and ecosystems is therefore a.

Difference Between Ecology And Ecosystem Javatpoint An ecosystem is a system of different living organisms interacting with one another and their physical environment. habitats can be found inside of ecosystems and give home to specific living organisms. read on to learn more about ecosystem vs habitat. 1. habitats are contained within ecosystems. The ecosystems with habitat diversity levels 2 to 4 consisted of a mixture of different habitat types: 2 2 for diversity 2, 1 1 2 for diversity 3, and 1 1 1 1 for diversity 4. the cylinders containing the experimental ecosystems were placed in a greenhouse with a continuous flow of surface water pumped from an adjacent bay (fig. s9). Fig. 2: ecosystem decay drives patterns of biodiversity loss in habitat fragments. a, global map, indicating the taxon group and location of studies (n = 123) included in our analyses. b – d. Noun. area of the planet which can be classified according to the plant and animal life in it. biotic. adjective. having to do with living or once living organisms. boreal forest. noun. land covered by evergreen trees in cool, northern latitudes. also called taiga.

Les Biomes Les écosystèmes Et Les Habitats Labster Theory Fig. 2: ecosystem decay drives patterns of biodiversity loss in habitat fragments. a, global map, indicating the taxon group and location of studies (n = 123) included in our analyses. b – d. Noun. area of the planet which can be classified according to the plant and animal life in it. biotic. adjective. having to do with living or once living organisms. boreal forest. noun. land covered by evergreen trees in cool, northern latitudes. also called taiga. An ecosystem is a dynamic complex of organisms (plant, animal, and microorganism), their communities, and their physical environments (air, water, and mineral soil) interacting as a functional unit (maastik et al. 2004). the biotic and abiotic components interact through nutrient cycles and energy flows (begon et al. 2006). Context the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning (bef) has been a central topic in ecology for more than 20 years. while experimental and theoretical studies have produced much knowledge of how biodiversity affects ecosystem functioning, it remains poorly understood how habitat fragmentation affects the bef relationship. objectives to develop a framework that connects.
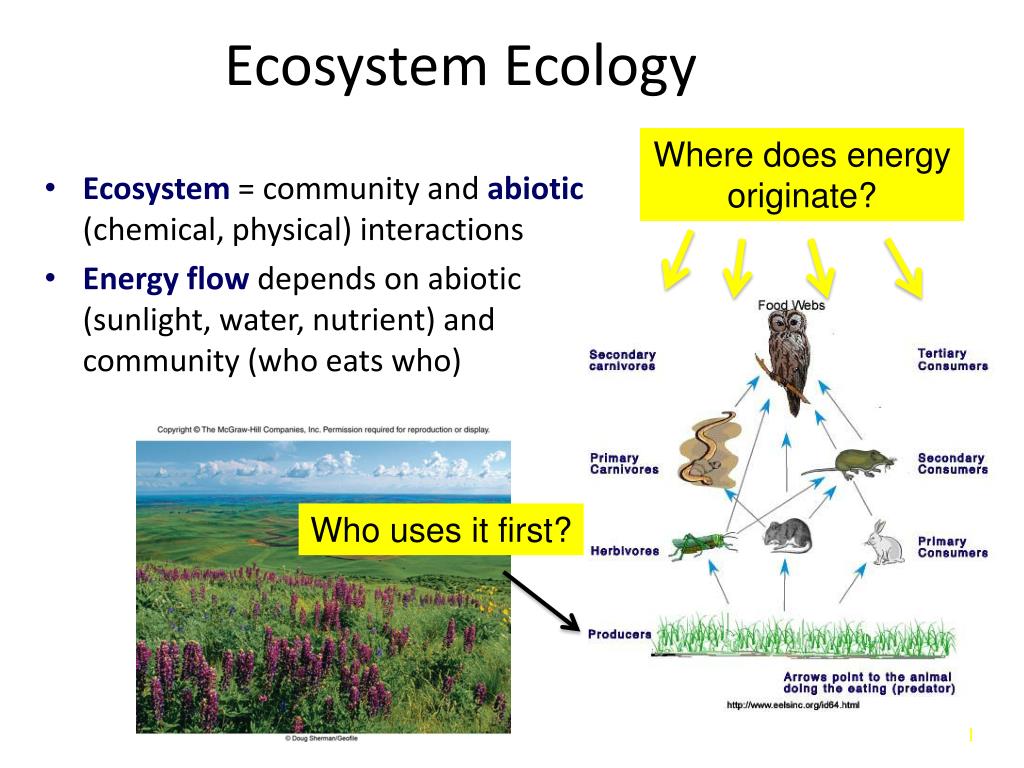
Ppt Ecosystem Ecology Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2742411 An ecosystem is a dynamic complex of organisms (plant, animal, and microorganism), their communities, and their physical environments (air, water, and mineral soil) interacting as a functional unit (maastik et al. 2004). the biotic and abiotic components interact through nutrient cycles and energy flows (begon et al. 2006). Context the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning (bef) has been a central topic in ecology for more than 20 years. while experimental and theoretical studies have produced much knowledge of how biodiversity affects ecosystem functioning, it remains poorly understood how habitat fragmentation affects the bef relationship. objectives to develop a framework that connects.

Comments are closed.