Plant Root System Shoot System

Plant Root System Shoot System Youtube Plant shoot system of angiosperms (a.k.a., flowering plants) are composed of stem and stem attached organs such as leaves, buds, and flowers. the stem of a plant is the primary axis that supports plant leaves and reproductive structures. furthermore, the stem provides water and minerals to above ground parts, whereas roots transport. The shoot system of the plant is an outgrowth that originates from the plumule of the seed’s embryo above the ground. the term shoot is generally interchangeable with the term stem, as it constitutes the major part of the shoot system. the morphology and physiology of the shoot system are more complex than the root system of the plant.
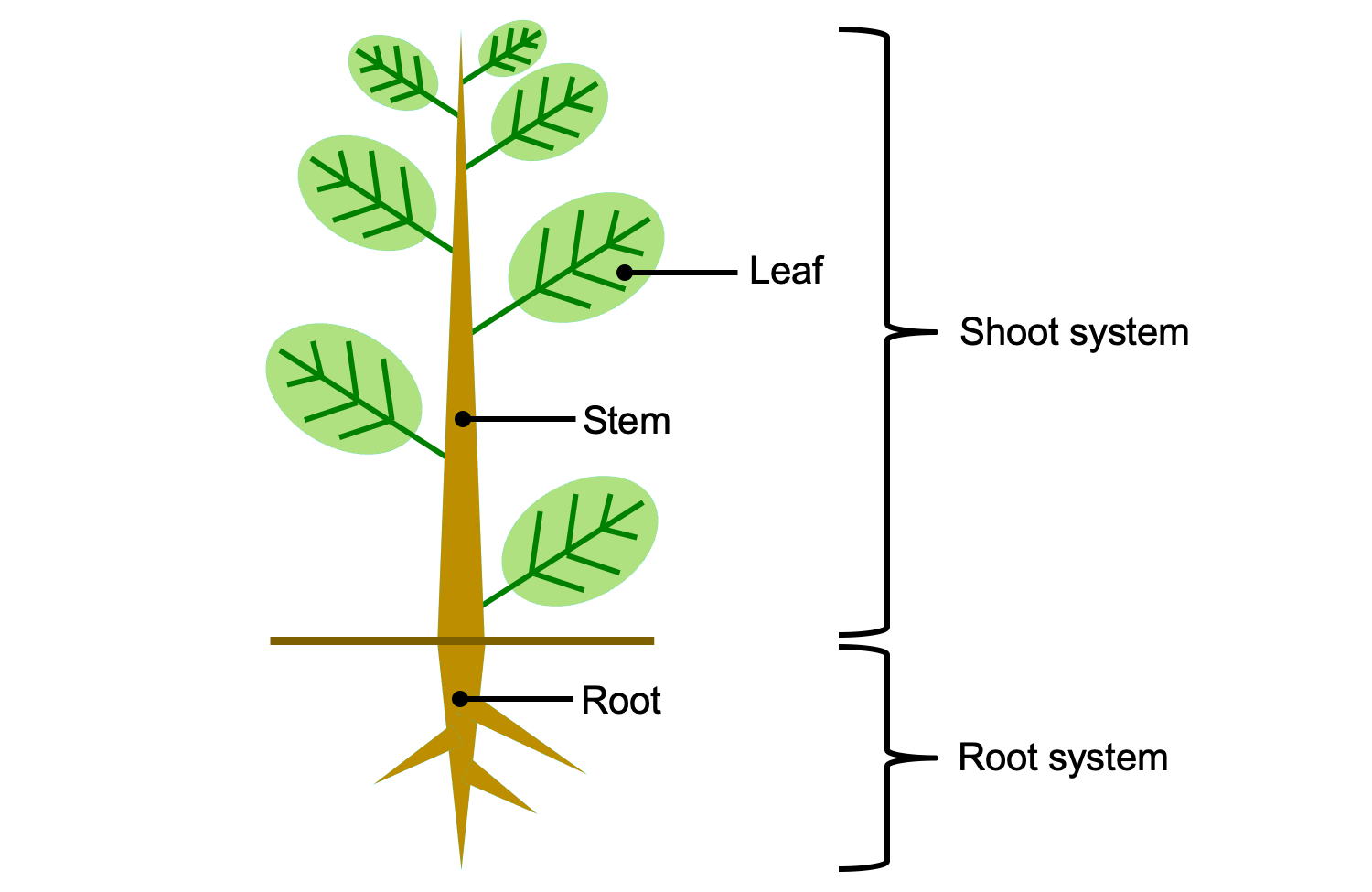
Introduction To Vascular Plant Structure Digital Atlas Of Ancient Life July 10, 2018. by lakna. 4 min read. the main difference between root system and shoot system is that the root system consists of roots, tubers, and rhizoids of the plant whereas the shoot system consists of leaves, buds, flowers, and fruits of the plant. furthermore, root system occurs in the ground while shoot system occurs on the ground. The root system refers to the ramose structures that exist subterranean or superterranean to the earth surface. a root consists of the hard root cap, primary root meristem and root hairs. the growth of the root system depends upon the soil composition, soil type, type of plant species and growth conditions. roots are complex structures whose. The root system, which supports the plants and absorbs water and minerals, is usually underground. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1 shows the organ systems of a typical plant. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1: the shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. the root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil. The root system, which anchors the plant into the ground, absorbs water and minerals, and serves as a storage site for food is usually underground. (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)) shows the organ systems of a typical plant. figure \(\pageindex{1}\): the shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. the root system anchors.
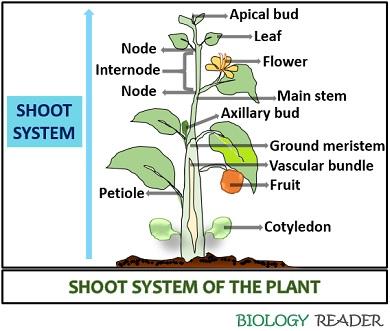
Shoot System Of Plant Definition Characteristics Functions The root system, which supports the plants and absorbs water and minerals, is usually underground. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1 shows the organ systems of a typical plant. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1: the shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. the root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil. The root system, which anchors the plant into the ground, absorbs water and minerals, and serves as a storage site for food is usually underground. (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)) shows the organ systems of a typical plant. figure \(\pageindex{1}\): the shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. the root system anchors. As we’ll see in a later chapter, the portion of the stem just above the root shoot transition zone is called the hypocotyl. adventitious roots that contribute to the fibrous root system stay close to the soil surface. fibrous root systems are excellent at holding soil in place because they are thin, extensive, and weblike. An immense fibrous root system in one growing season. a single rye plant 50 cm (20 in) tall, with 80 tillers (shoot branches), may have a root system surface area of about 210 m 2 (1890 ft2), compared to only about 5 m 2 (45 ft2) for its aboveground shoot system. plants with a large storage root, like carrot ( daucus carota), have a tap.

Comments are closed.