Ppt Continuous Cooling Transformation Cct Diagrams Powerpoint
Ppt Continuous Cooling Transformation Cct Diagrams Powerpoint Cct diagrams measure the extent of transformation as a function of cooling time at continuously decreasing temperatures. the main difference from ttt diagrams is that continuous cooling does not allow for bainite formation and always results in pearlite. properties like hardness and strength depend on the formed microstructure constituents like. Cct diagram depends on composition of steel, nature of cooling, austenite grain size, extent of austenite homogenising, as well as austenitising temperature and time. 2. similar to ttt diagrams there are different regions for different transformation (i.e. cementite ferrite, pearlite, bainite and martensite).
Ppt Continuous Cooling Transformation Cct Diagrams Powerpoint Continuous cooling transformation (cct) diagrams r. manna assistant professor centre of advanced study department of metallurgical engineering institute of technology – a free powerpoint ppt presentation (displayed as an html5 slide show) on powershow id: 3fd0b1 ntizz. M. muneebrehman66. 1) continuous cooling transformation (cct) diagrams show transformation start, fraction of transformation, and finish temperatures for different transformations under continuous cooling conditions. 2) cct diagrams are determined through dilatometric measurements during continuous cooling, where sample dilation is measured to. Ttt diagrams apply to isothermal heat treatments where temperature is held constant, while cct diagrams apply to continuous cooling processes. the document outlines various microstructures including pearlite, bainite, martensite, and spheroidite and how they form on these diagrams. it also discusses how alloying elements can shift the. Chapter 10: phase transformations classes: 1. simple diffusion dependent transformation: no change in the number or composition of phases 2. diffusion dependent with changes in compositions and or number of phases (e.g., eutectic reaction) 3. diffusionless transformation – produces metastable phase • impediments to pt: • time dependent.

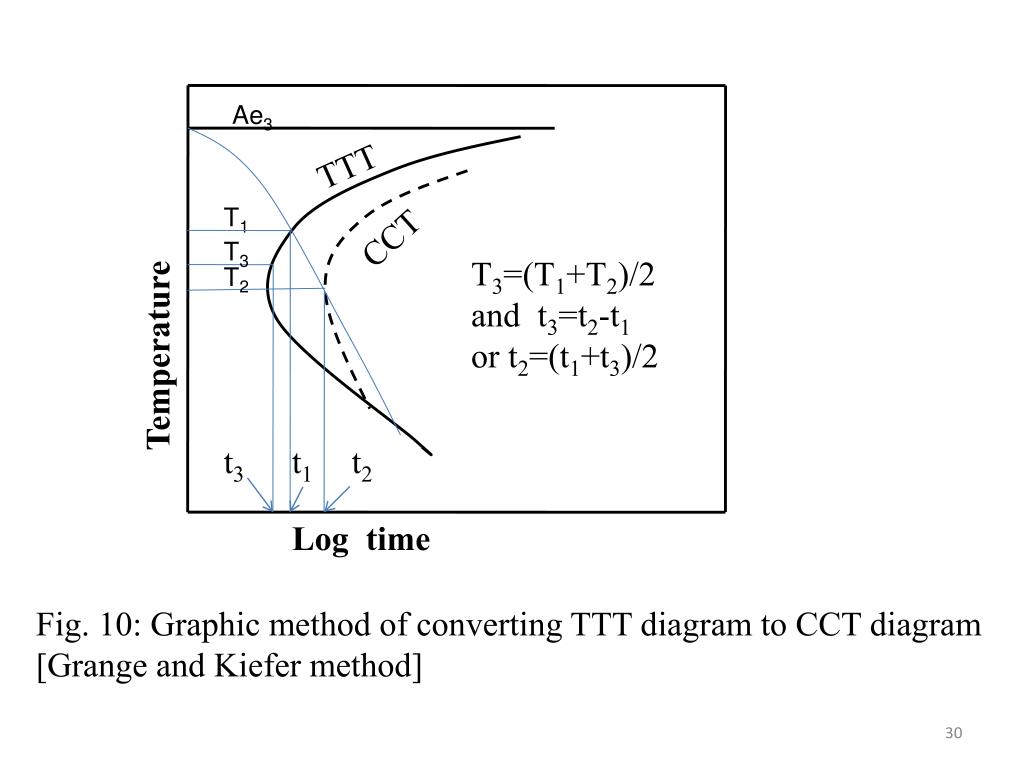
Ppt Chapter 10 Phase Transformations Powerpoint Presentation Free Ttt diagrams apply to isothermal heat treatments where temperature is held constant, while cct diagrams apply to continuous cooling processes. the document outlines various microstructures including pearlite, bainite, martensite, and spheroidite and how they form on these diagrams. it also discusses how alloying elements can shift the. Chapter 10: phase transformations classes: 1. simple diffusion dependent transformation: no change in the number or composition of phases 2. diffusion dependent with changes in compositions and or number of phases (e.g., eutectic reaction) 3. diffusionless transformation – produces metastable phase • impediments to pt: • time dependent. Continuous cooling transformation (cct) diagram definition: stability of phases during continuous cooling of austenite there are two types of cct diagrams i) plot of (for each type of transformation) transformation start, specific fraction of transformation and transformation finish temperature against transformation time on each cooling curve ii) plot of (for each type of transformation. • most heat treatments for steels involve the continuous cooling of a specimen to room temperature. • ttt diagram (dashed curve) is modified for a cct diagram (solid curve). • for continuous cooling, the time required for a reaction to begin and end is delayed. • the isothermal curves are shifted to longer times and lower temperatures.

Comments are closed.