Ppt Showing Covalent Bonding Using Dot Cross Diagrams Powerpoint
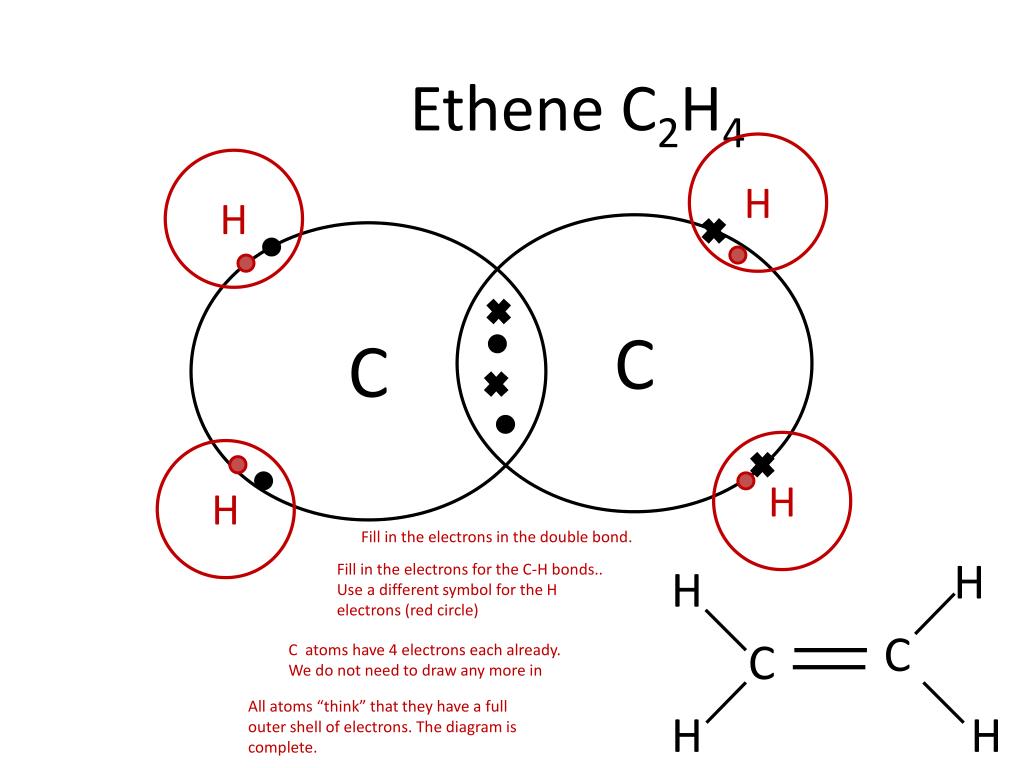
Ppt Showing Covalent Bonding Using Dot Cross Diagrams Powerpoint If you work through this powerpoint you should be able to draw a dot cross diagram for any covalent molecule provided you are given the displayed formula of the molecule. (displayed formula atoms shown as letters and covalent bonds shown as sticks) methane ch4 using the stick model as a guide, draw the atoms as circles. Download ppt "showing covalent bonding using dot cross diagrams". if you work through this powerpoint you should be able to draw a dot cross diagram for any covalent molecule provided you are given the displayed formula of the molecule. (displayed formula atoms shown as letters and covalent bonds shown as sticks).

Ppt Showing Covalent Bonding Using Dot Cross Diagrams Powerpoint Drawing dot cross diagrams. the document discusses the formation of ionic and covalent bonds, including how to determine the charge of ions, represent ionic compounds using dot cross diagrams, and represent covalent molecules using dot cross diagrams, structural formulas, and lewis structures to show how atoms share electrons to achieve stable. Single covalent bond: 2 electrons shared in a bond (called the bonding pair), represented by two dots, or a vertical line for the bond. examples with dot structures: h 2, h 2 o, nh 3, ch 4. on your own, draw the dot structures for: ph 3, h 2 s, hcl, ccl 4, sih 4, hf. single covalent bonds are also called sigma bonds. The document summarizes key concepts about covalent bonding from a chemistry textbook chapter: 1) covalent bonds form when two nonmetal atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a noble gas configuration, forming molecules like h2, o2, and co2. 2) molecular compounds formed by covalent bonds tend to have lower melting and boiling. 1.32 understand covalent bonding as a strong attraction between the bonding pair of electrons and the nuclei of the atoms involved in the bond. 1.33 explain, using dot and cross diagrams, the formation of covalent compounds by electron sharing for the following substances:.
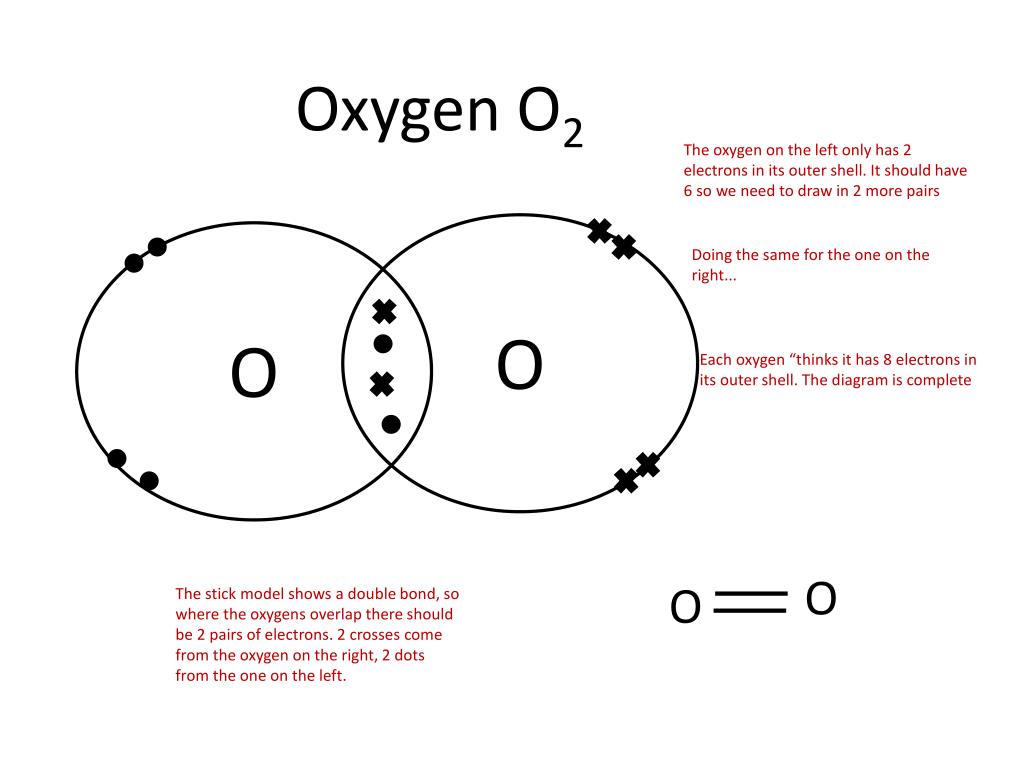
Ppt Showing Covalent Bonding Using Dot Cross Diagrams Powerpoint The document summarizes key concepts about covalent bonding from a chemistry textbook chapter: 1) covalent bonds form when two nonmetal atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a noble gas configuration, forming molecules like h2, o2, and co2. 2) molecular compounds formed by covalent bonds tend to have lower melting and boiling. 1.32 understand covalent bonding as a strong attraction between the bonding pair of electrons and the nuclei of the atoms involved in the bond. 1.33 explain, using dot and cross diagrams, the formation of covalent compounds by electron sharing for the following substances:. Presentation transcript. lewis structures • lewis structures: electron dot diagrams show how electrons are arranged in molecules (aka covalent compounds) • diagrams show only valence electrons. • dashes represent “bonding pairs” • dots represent “lone pairs” or “nonbonding pairs”. • brackets and charge signify polyatomic ions. Specification point 1.44 know that a covalent bond is formed between atoms by the sharing of a pair of electrons. specification point 1.45 understand covalent bonds in terms of electrostatic attractions. specification point 1.46 understand how to use dot and cross diagrams to represent covalent bonds in a variety of molecules.
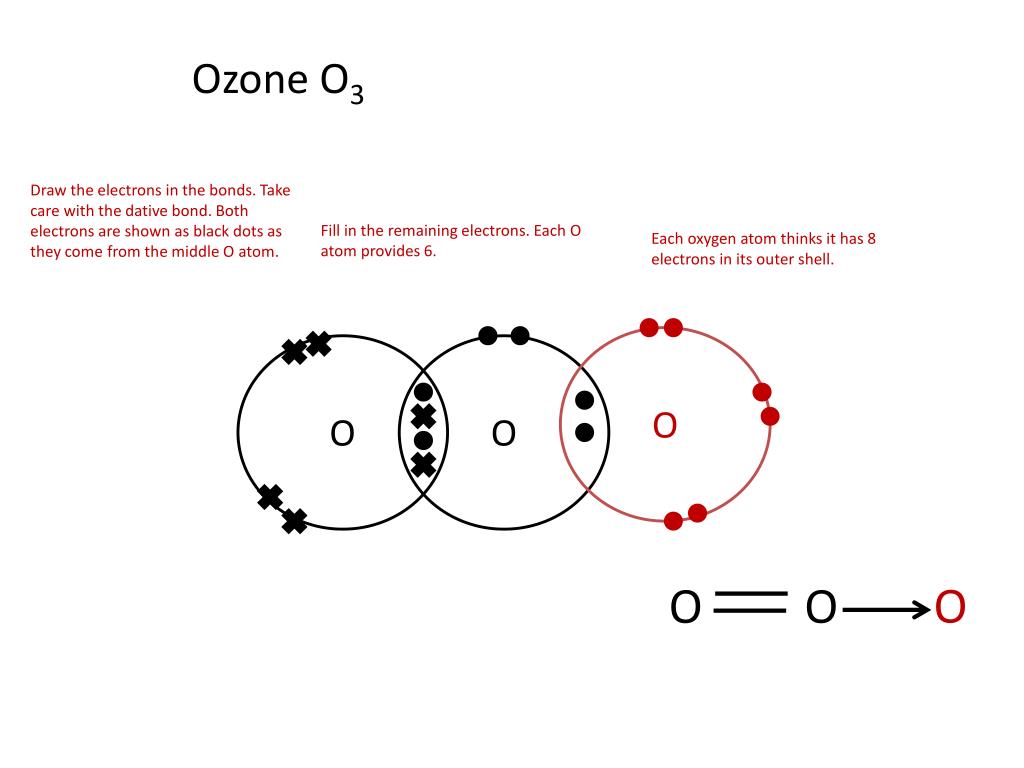
Ppt Showing Covalent Bonding Using Dot Cross Diagrams Powerpoint Presentation transcript. lewis structures • lewis structures: electron dot diagrams show how electrons are arranged in molecules (aka covalent compounds) • diagrams show only valence electrons. • dashes represent “bonding pairs” • dots represent “lone pairs” or “nonbonding pairs”. • brackets and charge signify polyatomic ions. Specification point 1.44 know that a covalent bond is formed between atoms by the sharing of a pair of electrons. specification point 1.45 understand covalent bonds in terms of electrostatic attractions. specification point 1.46 understand how to use dot and cross diagrams to represent covalent bonds in a variety of molecules.

Comments are closed.