Practicing Manual Proning As A Proactive Measure Against Ards

Practicing Manual Proning As A Proactive Measure Against Ards Youtube At ruhs, we are training nurses physicians and other clinical staff on the procedures for manual proning. this allows our teams the ability to extend proning. Background. manual prone positioning has been shown to reduce mortality among patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome, but it is associated with a high incidence of pressure injuries and unplanned extubations. this study investigated the feasibility of safely implementing a manual prone positioning protocol that uses a dedicated device.review of evidence. a search.
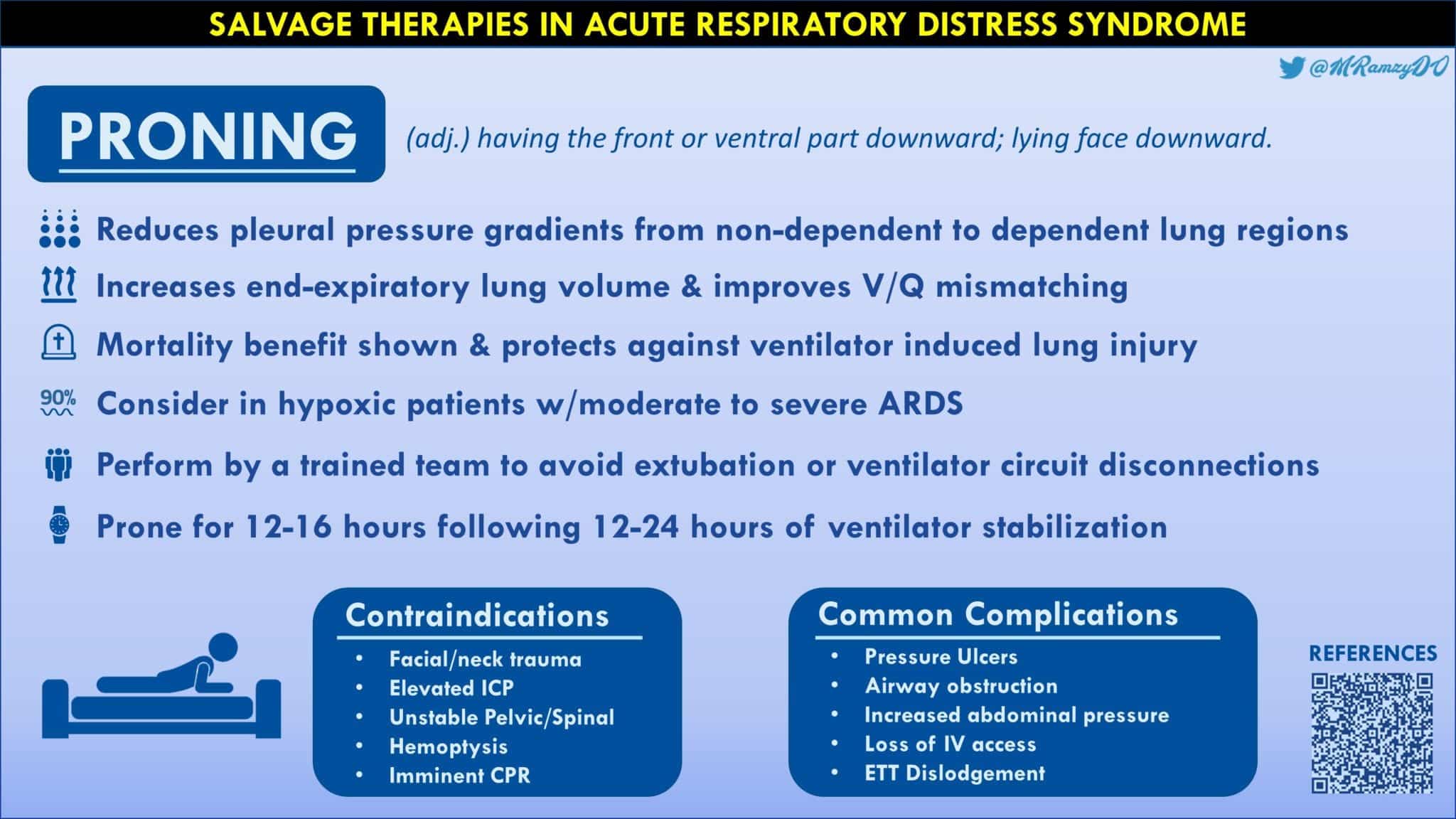
Ards Proning Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog To perfusion (v q) mismatch. proning for 16 or more hours day may reduce mortality. ii. clinical practice guidelines 1. indications for manual proning a. one or more of the following: moderate to severe ards with peep >10, fio2 >0.6, inability to maintain pao2 fio2 ratio >150mmhg 2. absolute contraindications to manual proning a. Prone positioning is an important non pharmacologic strategy that should be considered for all invasively ventilated patients with moderate to severe ards (including those with covid 19). prone positioning offers several physiologic and clinical benefits, including improving hypoxemia, matching ventilation with perfusion, reducing regional. Safely and effectively positioning the patient prone reduces risks of morbidity and mortality for the patient while reducing the risk of injury for the nurse and other caregivers. this practice alert addresses reducing the risk of harm to intubated adult ards patients undergoing manual prone positioning for at least 12 to 16 hours per day. To perfusion (v q) mismatch. proning for 16 or more hours day may reduce mortality. ii. clinical practice guidelines 1. indications for manual proning a. one or more of the following: moderate to severe ards with peep >10, fio2 >0.6, inability to maintain pao2 fio2 ratio >150mmhg 2. absolute contraindications to manual proning a.

Manual Prone Positioning For Patients With Ards Youtube Safely and effectively positioning the patient prone reduces risks of morbidity and mortality for the patient while reducing the risk of injury for the nurse and other caregivers. this practice alert addresses reducing the risk of harm to intubated adult ards patients undergoing manual prone positioning for at least 12 to 16 hours per day. To perfusion (v q) mismatch. proning for 16 or more hours day may reduce mortality. ii. clinical practice guidelines 1. indications for manual proning a. one or more of the following: moderate to severe ards with peep >10, fio2 >0.6, inability to maintain pao2 fio2 ratio >150mmhg 2. absolute contraindications to manual proning a. Ween 12 to 20 consecutive hours per day nursing care of patients in the prone position is challenging, as is the physical act of. turning the patient from supine to prone. prone positioning should be approached with ad. ng, teamwork and coordinationrationale turning the patient with ards from a supine to a prone position can increase pulm. Background. prone positioning is a standard treatment for moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), but the outcomes associated with manual versus automatic prone positioning have not been evaluated.objective. to retrospectively evaluate outcomes associated with manual versus automatic prone positioning as part of a pronation quality improvement project implemented by a.

Comments are closed.