Primary Consumer Science Definition

Definition Of Primary Consumers Definitionjulb Primary consumer definition. a primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food. Primary consumers can range from microscopic organisms like zooplankton to large creatures like elephants. here are some examples. 1. ruminants like giraffes and cows. primary herbivorous consumers such as cows, goats, zebras, giraffes are primary consumers. they consume plant material such as grass, branches, and roots.
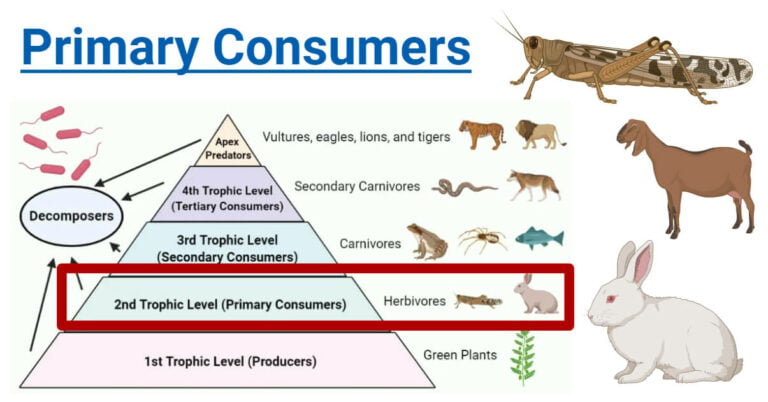
Primary Consumers Definition Food Chain Examples Roles Primary consumers are groups of organisms in the ecosystem that are categorized in the second trophic level of the food chain that feed on producers such as plants. they play an important role in transferring energy from plants to upper trophic levels. without them, the energy flow through the food chain would be disrupted, affecting the entire. Primary consumers are predominantly herbivores, feeding directly on the producers. they include a wide array of organisms such as caterpillars, insects, grasshoppers, termites, and some bird species like hummingbirds. all these organisms share a common dietary trait – they consume only autotrophs (plants or algae). The primary consumer definition is an organism that eats plants and provides the energy needed for other types of consumers to use. primary consumers differ from other consumers because they are. Primary consumers are those members of a food chain that eat producers or plants. secondary and higher consumers may eat primary consumers as well as plants or lower level consumers. a food chain has at least three elements: a producer, a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. an example of a marine food chain is algae as producer plants.

Primary Consumers Lesson For Kids Definition Examples Lesson The primary consumer definition is an organism that eats plants and provides the energy needed for other types of consumers to use. primary consumers differ from other consumers because they are. Primary consumers are those members of a food chain that eat producers or plants. secondary and higher consumers may eat primary consumers as well as plants or lower level consumers. a food chain has at least three elements: a producer, a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. an example of a marine food chain is algae as producer plants. Primary consumers feed exclusively on autotrophs. any organism that must eat in order to produce energy is both a heterotroph and a consumer. rather confusingly, primary consumers are located in the second trophic level of the ecosystem. a trophic level is the position any organism occupies within any food chain. Primary consumers are typically herbivores. they play a crucial role in transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels. examples of primary consumers include deer, rabbits, and zooplankton. the efficiency of energy transfer from producers to primary consumers is usually around 10%.

Primary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Primary consumers feed exclusively on autotrophs. any organism that must eat in order to produce energy is both a heterotroph and a consumer. rather confusingly, primary consumers are located in the second trophic level of the ecosystem. a trophic level is the position any organism occupies within any food chain. Primary consumers are typically herbivores. they play a crucial role in transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels. examples of primary consumers include deer, rabbits, and zooplankton. the efficiency of energy transfer from producers to primary consumers is usually around 10%.

Comments are closed.