Primary Consumers Definition Food Chain Examples Roles
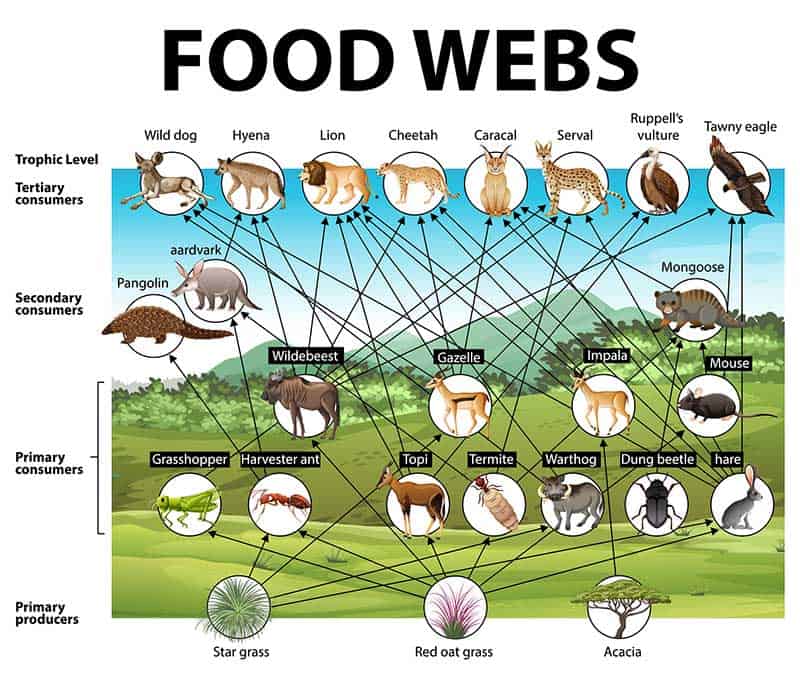
12 Examples Of Primary Consumers Pictures Diagram Wildlife Informer Primary consumers are groups of organisms in the ecosystem that are categorized in the second trophic level of the food chain that feed on producers such as plants. they play an important role in transferring energy from plants to upper trophic levels. without them, the energy flow through the food chain would be disrupted, affecting the entire. Primary consumer definition. a primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food.
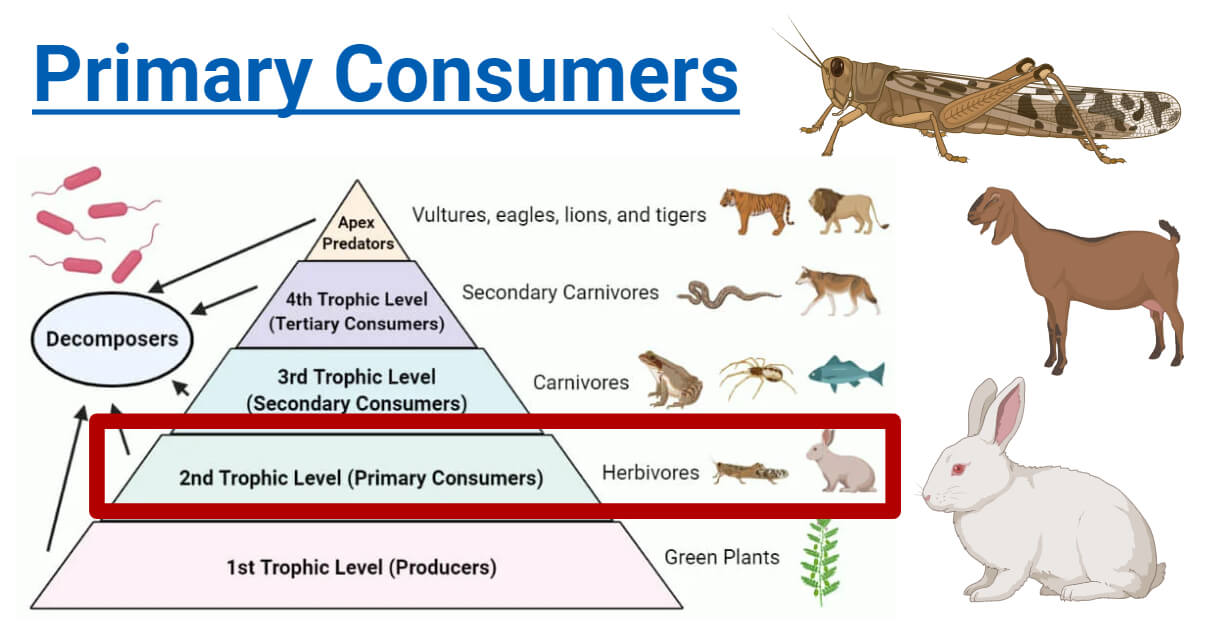
Primary Consumers Definition Food Chain Examples Roles Primary consumers play a pivotal role in ecological systems as the intermediary agents that transfer energy from producers, like plants and algae, to the higher trophic levels of the food chain. occupying the second trophic level, these organisms are primarily herbivores, although some may also be omnivores. Primary consumers can range from microscopic organisms like zooplankton to large creatures like elephants. here are some examples. 1. ruminants like giraffes and cows. primary herbivorous consumers such as cows, goats, zebras, giraffes are primary consumers. they consume plant material such as grass, branches, and roots. The different trophic levels in a typical food chain are: primary producers. they are the first biotic factor occupying the first tropic level or the bottom of the food chain. primary producers mainly produce their own food by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. plants, algae, and autotrophic bacteria are primary producers. consumers. Here is an example of a simple food chain: grass → cow → human. the grass is the producer. the cow and human are consumers. the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer.
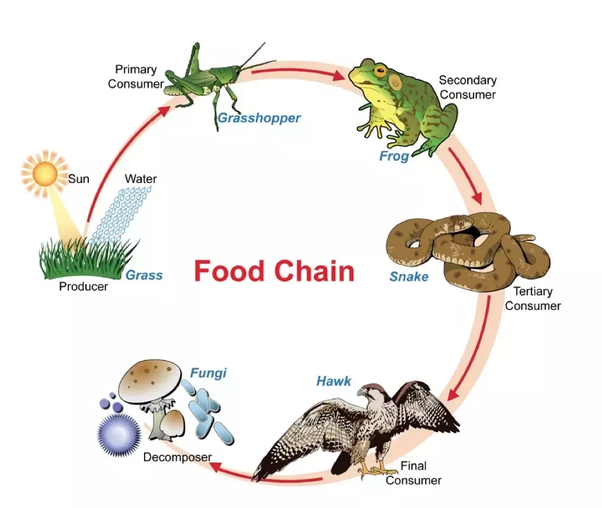
Food Chain Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary The different trophic levels in a typical food chain are: primary producers. they are the first biotic factor occupying the first tropic level or the bottom of the food chain. primary producers mainly produce their own food by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. plants, algae, and autotrophic bacteria are primary producers. consumers. Here is an example of a simple food chain: grass → cow → human. the grass is the producer. the cow and human are consumers. the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. Primary consumers are those members of a food chain that eat producers or plants. secondary and higher consumers may eat primary consumers as well as plants or lower level consumers. a food chain has at least three elements: a producer, a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. an example of a marine food chain is algae as producer plants. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Food Chain Pyramid Examples Primary consumers are those members of a food chain that eat producers or plants. secondary and higher consumers may eat primary consumers as well as plants or lower level consumers. a food chain has at least three elements: a producer, a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. an example of a marine food chain is algae as producer plants. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online

Food Chain Definition Examples Expii

Comments are closed.