Probiotics Vs Prebiotics For Gut Health Understanding The Differenc

Prebiotics And Probiotics Explained In An Easy To Understand Way The human gut is a complex ecosystem. a delicate balance of microorganisms plays a crucial role in our health and wellbeing. understanding the distinction between prebiotics and probiotics is fundamental to harnessing their benefits. both contribute to the nourishment and maintenance of this system. prebiotics are dietary fibers that the human body cannot digest. they serve as. Prebiotics. this is a food source for the friendly bacteria in your intestinal tract. our digestive system can’t break down prebiotics, so they survive the journey through the digestive tract.
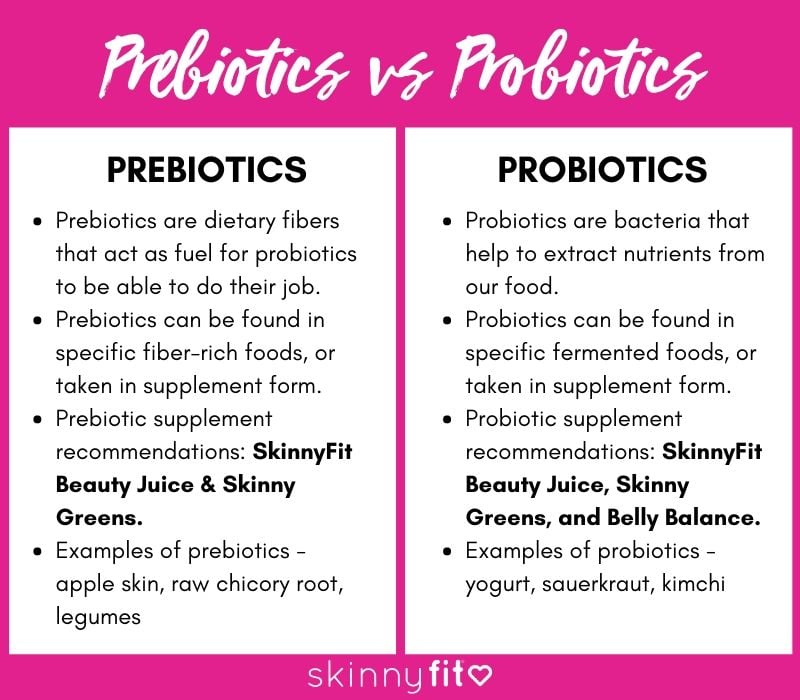
Prebiotics Vs Probiotics What S The Difference How To Use Probiotics vs prebiotics: the synergy for optimal gut health while probiotics and prebiotics have their unique roles, they work best together. this relationship, known as synbiotics , combines the live beneficial bacteria (probiotics) with the fuel they need to thrive (prebiotics), resulting in a synergistic effect that enhances the gut. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria, and prebiotics are food for these bacteria. eating foods or supplements containing both can help balance your gut. probiotics and prebiotics are both hot topics. Benefits of probiotics. probiotics have been associated with numerous health benefits, including: improved digestion and gut health. enhanced immune function. reduced bloating. maintenance of a healthy balance of gut bacteria and fungi. prebiotics: fuel for your gut microbiome. prebiotics, on the other hand, are non digestible fibers that serve. Probiotics are in foods such as yogurt and sauerkraut. prebiotics are in foods such as whole grains, bananas, greens, onions, garlic, soybeans and artichokes. in addition, probiotics and prebiotics are added to some foods and available as dietary supplements. research is ongoing into the relationship of the gut microflora to disease.

Comments are closed.