Process Of Dna Methylation

Schematic Representation Of Dna Methylation The Process Starts With Dna methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the dna molecule. methylation can change the activity of a dna segment without changing the sequence. when located in a gene promoter, dna methylation typically acts to repress gene transcription. During development, the pattern of dna methylation in the genome changes as a result of a dynamic process involving both de novo dna methylation and demethylation. as a consequence, differentiated.

The Schematic Diagram For The Basic Process Of Dna Methylation Presently, the exact role of methylation in gene expression is unknown, but it appears that proper dna methylation is essential for cell differentiation and embryonic development. moreover, in. Dna methylation regulates gene expression by recruiting proteins involved in gene repression or by inhibiting the binding of transcription factor(s) to dna. during development, the pattern of dna methylation in the genome changes as a result of a dynamic process involving both de novo dna methylation and demethylation. Methylation is a first line essential biochemical process in the transmission of life, playing a critical role in modification of dna and histones. it is involved in regulating gametogenesis, embryonic and placental growth, as well as imprinting and epigenesis. Dna methylation is a process where methyl groups are added to dna by enzymes, leading to the formation of 5 methylcytosine. it is essential for various biological functions such as embryonic development, gene regulation, and maintaining cellular identity. ai generated definition based on: epigenetic mechanisms in cancer, 2018.
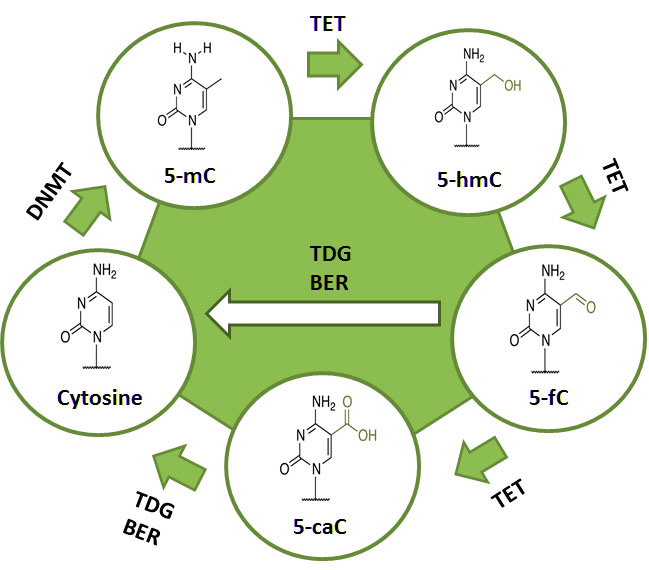
Dna Methylation What Is Epigenetics Methylation is a first line essential biochemical process in the transmission of life, playing a critical role in modification of dna and histones. it is involved in regulating gametogenesis, embryonic and placental growth, as well as imprinting and epigenesis. Dna methylation is a process where methyl groups are added to dna by enzymes, leading to the formation of 5 methylcytosine. it is essential for various biological functions such as embryonic development, gene regulation, and maintaining cellular identity. ai generated definition based on: epigenetic mechanisms in cancer, 2018. Dna methylation is an epigenetic process. unlike the sequence of dna, which is directly inherited intact from the parents, methylation patterns derived from the gametes are erased before implantation of the embryo and a new profile of methylation is established in each individual. 5,6 the resetting process takes place in two distinct stages. Dna methylation is a biochemical process where a dna base, usually cytosine, is enzymatically methylated at the 5 carbon position. an epigenetic modification associated with gene regulation, dna methylation is of paramount importance to biological health and disease.

Dna Methylation Is Best Described As The Hudson Has Stone Dna methylation is an epigenetic process. unlike the sequence of dna, which is directly inherited intact from the parents, methylation patterns derived from the gametes are erased before implantation of the embryo and a new profile of methylation is established in each individual. 5,6 the resetting process takes place in two distinct stages. Dna methylation is a biochemical process where a dna base, usually cytosine, is enzymatically methylated at the 5 carbon position. an epigenetic modification associated with gene regulation, dna methylation is of paramount importance to biological health and disease.
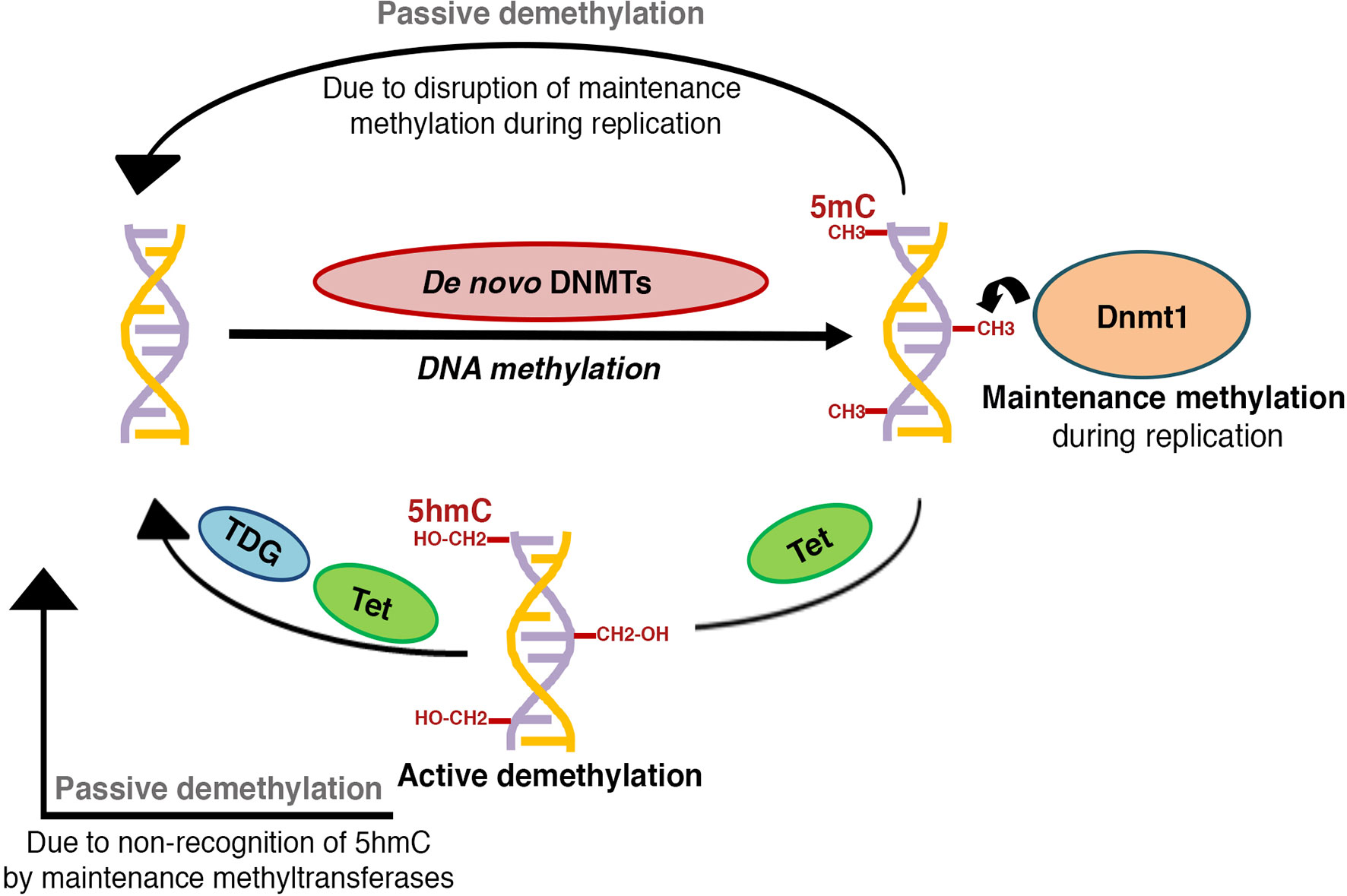
Process Of Dna Methylation

Comments are closed.