Producer And Consumer Surplus Graph
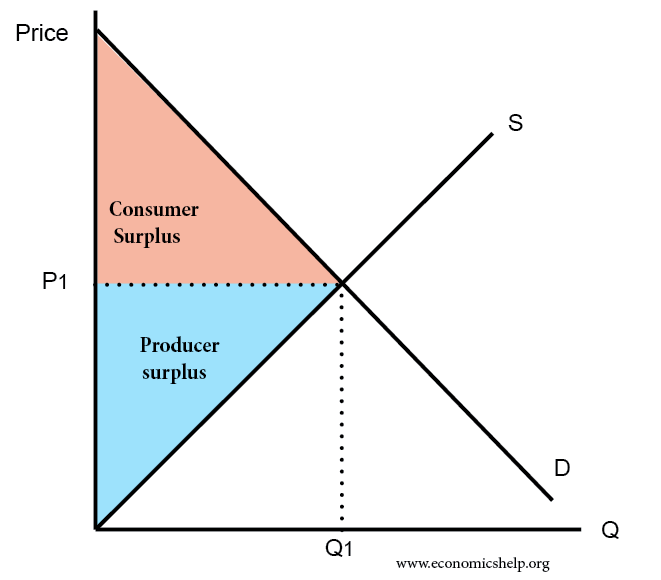
Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus School Of Economics Learn how to calculate and illustrate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and social surplus using demand and supply curves. see examples, videos, and practice problems on this topic. Microeconomics. course: microeconomics > unit 4. lesson 1: consumer and producer surplus. demand curve as marginal benefit curve. consumer surplus introduction. total consumer surplus as area. producer surplus. equilibrium, allocative efficiency and total surplus. lesson overview: consumer and producer surplus.

Write Short Notes On Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Forestrypedia In the context of welfare economics, consumer surplus and producer surplus measure the amount of value that a market creates for consumers and producers, respectively. consumer surplus is defined as the difference between consumers' willingness to pay for an item (i.e. their valuation, or the maximum they are willing to pay) and the actual. In the previous example, the total consumer surplus was $3, and the total producer surplus $4, respectively. the total surplus, therefore, will be $7 ($3 $4). below is the formula: total surplus = consumer surplus producer surplus. in the above example, the total surplus does not depict the equilibrium. there is a deadweight to shed off. Learn how to calculate and interpret consumer and producer surplus on a supply and demand diagram. see how changes in demand and supply affect the size and incidence of surplus. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers.
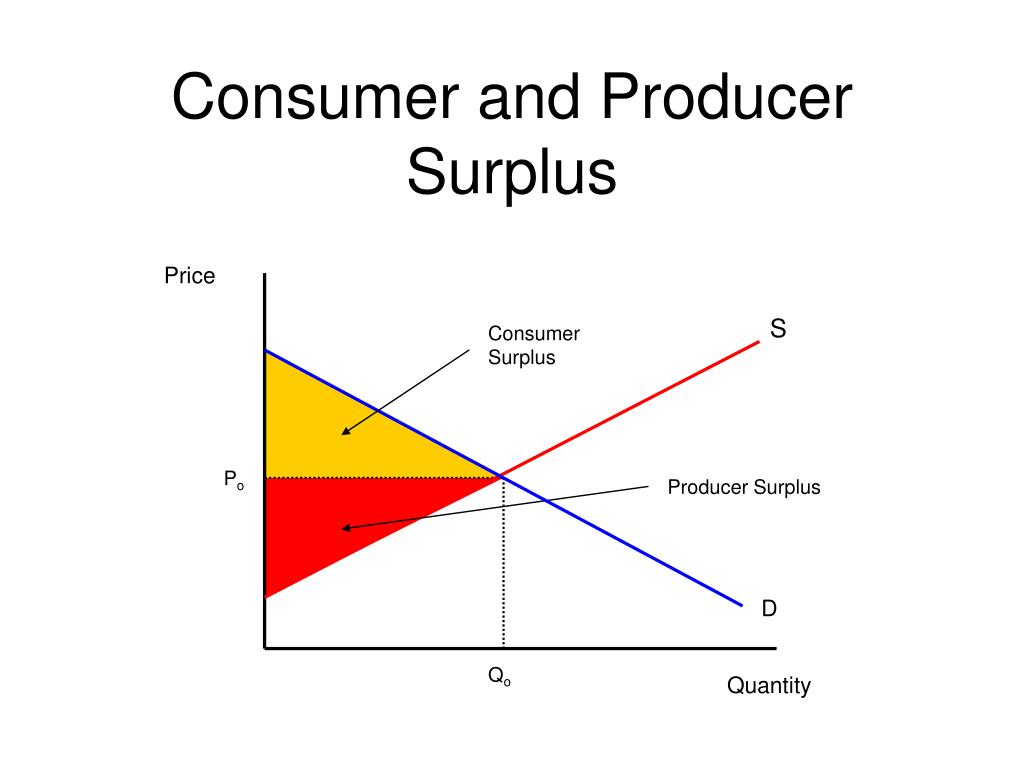
Consumer Producer Surplus Graph Learn how to calculate and interpret consumer and producer surplus on a supply and demand diagram. see how changes in demand and supply affect the size and incidence of surplus. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers. Learn the definitions, diagrams and examples of consumer and producer surplus in economics. find out how elasticity, monopolies, price discrimination and free trade affect surplus. Description. this lecture covers supply and demand curves, consumer surplus, and producer surplus. see handout 9 for relevant graphs for this lecture instructor: prof. jonathan gruber.

Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 3 Government Intervention Learn the definitions, diagrams and examples of consumer and producer surplus in economics. find out how elasticity, monopolies, price discrimination and free trade affect surplus. Description. this lecture covers supply and demand curves, consumer surplus, and producer surplus. see handout 9 for relevant graphs for this lecture instructor: prof. jonathan gruber.
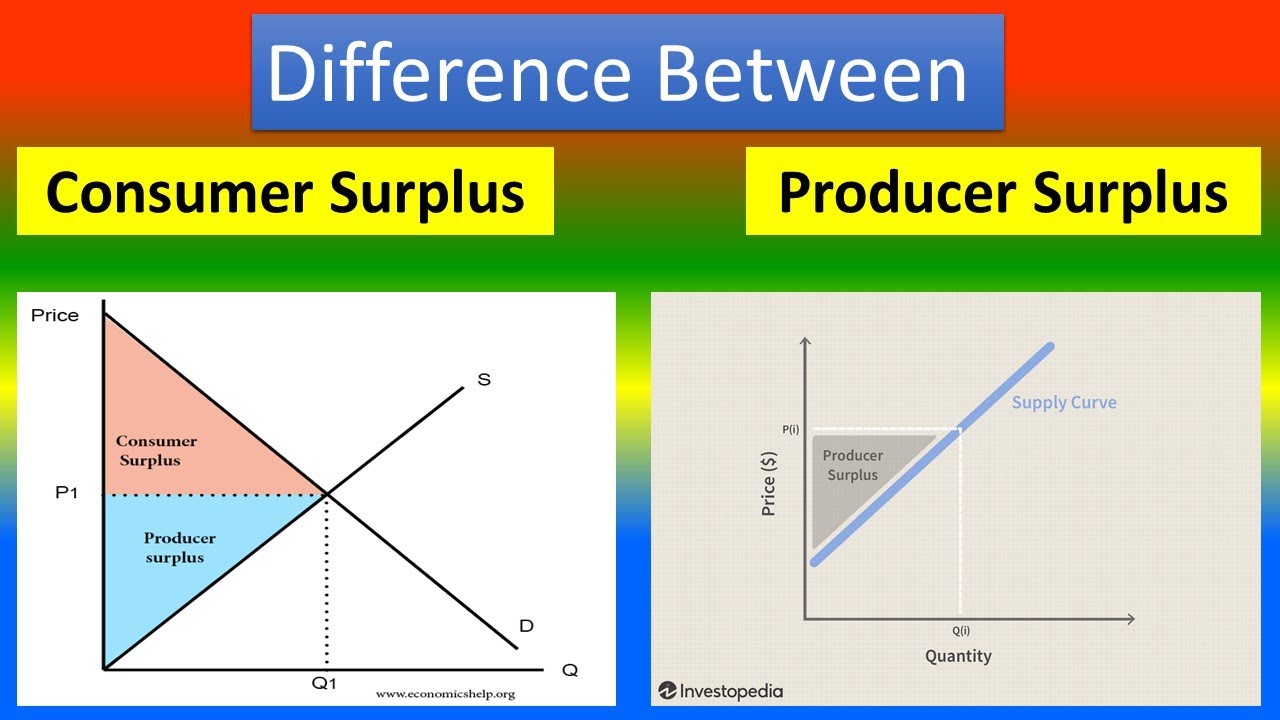
Difference Between Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Youtube

Comments are closed.