Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Specific Therapies Approved By The Us

Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Specific Therapies Approved By The Us Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) carries a poor prognosis if not promptly diagnosed and appropriately treated. the development and approval of 14 medications over the last several decades have led to a rapidly evolving approach to therapy, and have necessitated periodic updating of evidence based treatment guidelines. this guideline statement, which now includes a visual algorithm to. Figure 2 united states recommendations for the use of pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah)–approved therapies. a combination therapy carries with it costs as well as multiple medications, including the potential for increased adverse events that may be undesirable for some patients. in these situations patients are unwilling or unable to.

Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Management Algorithm Modified With Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah, group 1 of the clinical classification) is characterized by intense pulmonary vascular remodeling, resulting in increased pulmonary vascular resistance (pvr) and ultimately leading to right heart failure and death. 1,2 pah encompasses a variety of different pathologies, such as idiopathic, heritable. Purpose of review: pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a disease that carries a significant mortality left untreated. this article aims to review pharmacotherapeutics for pah. recent findings: pah specific therapies have evolved over the last three decades and have expanded from one therapy in the 1990s to 14 fda approved medications. Abstract purpose of review. this review focuses on the therapeutic management and individualized approach to group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah), utilizing food and drug administration approved pah specific therapies and various interventional and surgical options for pah. Objective. choices of pharmacologic therapies for pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) are ideally guided by high level evidence. the objective of this guideline is to provide clinicians advice regarding pharmacologic therapy for adult patients with pah as informed by available evidence.
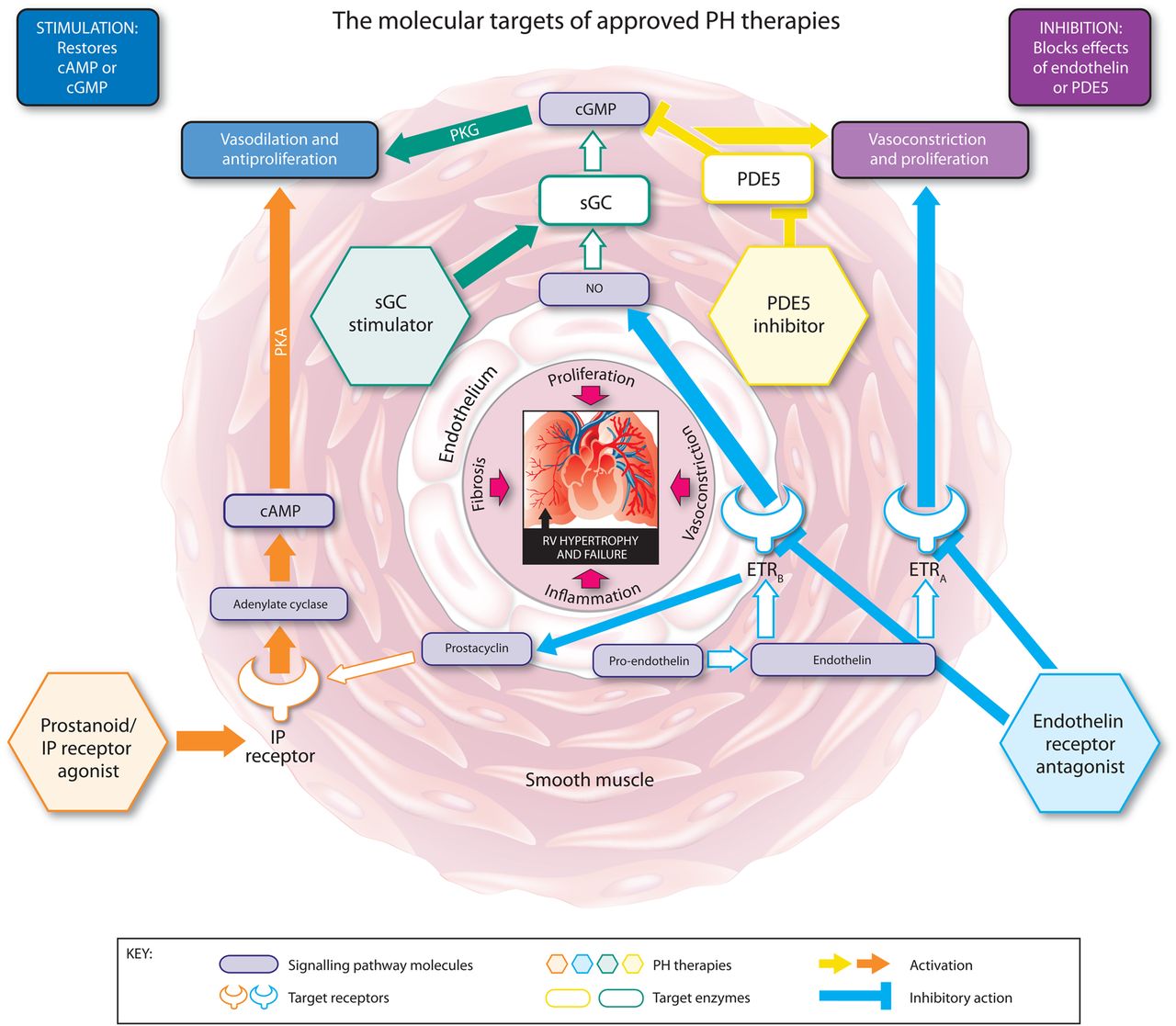
The Molecular Targets Of Approved Treatments For Pulmonary Arterial Abstract purpose of review. this review focuses on the therapeutic management and individualized approach to group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah), utilizing food and drug administration approved pah specific therapies and various interventional and surgical options for pah. Objective. choices of pharmacologic therapies for pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) are ideally guided by high level evidence. the objective of this guideline is to provide clinicians advice regarding pharmacologic therapy for adult patients with pah as informed by available evidence. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a life threatening disorder characterized by elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries due to increased pulmonary vascular resistance. 1 symptoms of pah are nonspecific but commonly include dyspnea on exertion and fatigue. 2 the estimated prevalence of pah is 10.6 per 1 million adults in the us. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a rare form of pulmonary hypertension characterized by a progressive obliterative vasculopathy of the distal pulmonary arterial circulation that usually leads to right ventricular failure and death. over the last 25 years, more than a dozen drugs representing five drug classes have been developed and approved for the treatment of this devastating.

Evidence Based Therapy With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a life threatening disorder characterized by elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries due to increased pulmonary vascular resistance. 1 symptoms of pah are nonspecific but commonly include dyspnea on exertion and fatigue. 2 the estimated prevalence of pah is 10.6 per 1 million adults in the us. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a rare form of pulmonary hypertension characterized by a progressive obliterative vasculopathy of the distal pulmonary arterial circulation that usually leads to right ventricular failure and death. over the last 25 years, more than a dozen drugs representing five drug classes have been developed and approved for the treatment of this devastating.

Emerging Therapeutics In Pulmonary Hypertension American Journal Of

Comments are closed.