Quaternary Consumers Heterotrophs Top Predators Education Notes

Quaternary Consumers Heterotrophs Top Predators Education Notes Secondary consumer heterotroph—an animal that eats primary consumers. examples: blue claw crab, lobster, seastar, humpback whale, silverside; tertiary consumer heterotroph—an animal that eats secondary consumers. examples: shark, dolphin; apex predator heterotroph—an animal at the top of the food chain with no predators. examples: shark. Noun. aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle.

Energy Flow Diagram Biology Khan academy offers free educational resources on various topics, including biology, algebra, geometry, and more. Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. Noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. intermediate predator. noun. in a food chain or food web, an organism that eats (preys on) herbivores or other first order consumers, but is preyed upon by top predators. marine biology. noun. study of life in the ocean. nutrient. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems.
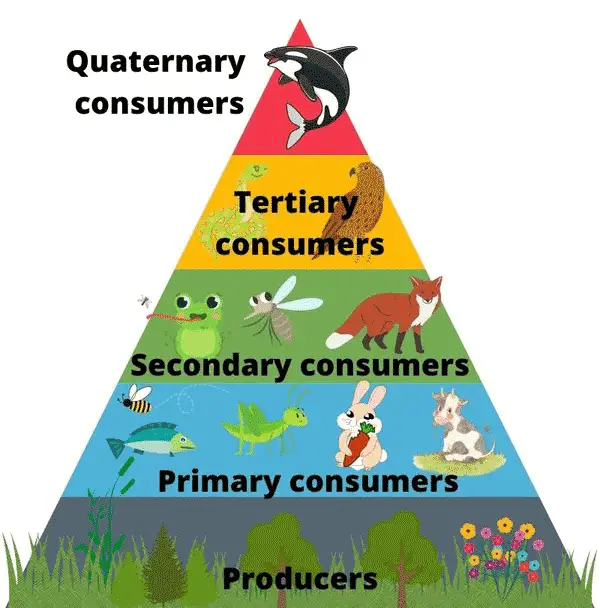
What Are Quaternary Consumers Answered With Examples Outlife Expert Noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. intermediate predator. noun. in a food chain or food web, an organism that eats (preys on) herbivores or other first order consumers, but is preyed upon by top predators. marine biology. noun. study of life in the ocean. nutrient. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. The final consumer at the top of the food chain is called a top (or apex) predator and is not eaten by anything else. image caption, nothing in this food chain eats the fox, which makes it the. Quaternary consumer. consumers found above the tertiary consumers in a food chain, or food web, are called quaternary consumers. they reside at the last trophic level in the food chain and have no natural predators. thus, in most cases, they are the top predators, or apex predators, in the ecosystem. in the ecological pyramid shown, the hawk is.

Food Chain Trophic Levels Worksheet The final consumer at the top of the food chain is called a top (or apex) predator and is not eaten by anything else. image caption, nothing in this food chain eats the fox, which makes it the. Quaternary consumer. consumers found above the tertiary consumers in a food chain, or food web, are called quaternary consumers. they reside at the last trophic level in the food chain and have no natural predators. thus, in most cases, they are the top predators, or apex predators, in the ecosystem. in the ecological pyramid shown, the hawk is.

Comments are closed.