Radial Nerve Rehabilitation Part 1 Of 5 The Radial Nerve

Radial Nerve Rehabilitation Orthotic Intervention Part 1 Of 5 The Review of the anatomy of the radial nerve and different levels of injuryfor additional videos & clinical information visit: bracelab clinicians c. Video demonstration of step by step construction of radial nerve orthosis. an overview of the levels of radial nerve injury, the resulting clinical presentations, and the key goals of rehabilitation. a detailed radial palsy orthotic construction video is included.
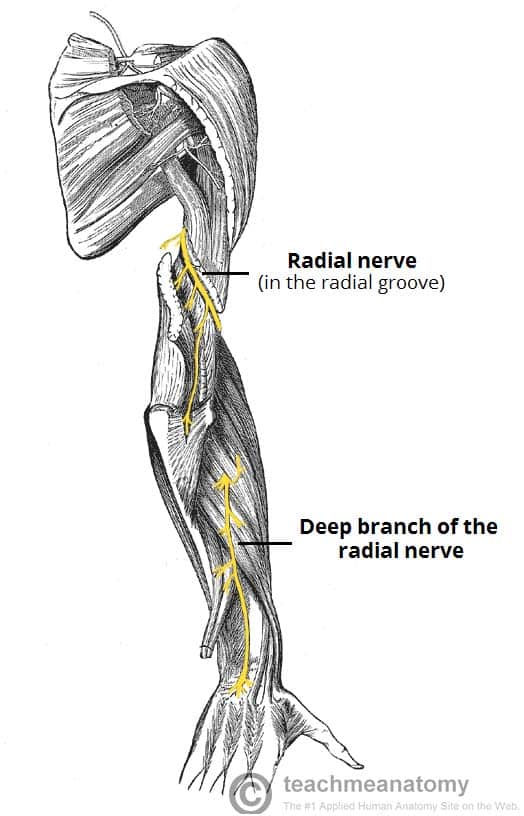
The Radial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy An overview of the levels of radial nerve injury, the resulting clinical presentations, and the key goals of rehabilitation. a detailed radial palsy orthotic. The radial nerve stems from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supplies the upper limb. it also supplies the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm (also known as the extensors), the wrist joint capsule, and aspects of the dorsal skin of the forearm and hand. the radial nerve proper innervates[1]:. Talk to your doctor or physical therapist about which exercises will best help you meet your rehabilitation goals. radial tunnel syndrome is a painful condition caused by pressure on the radial nerve – one of the three main nerves in your arm. the most common place for compression of the radial nerve is at the elbow where the nerve enters a tight. A radial nerve injury usually causes symptoms in the back of your hand, near your thumb, and in your index and middle fingers. symptoms may include a sharp or burning pain, as well as unusual.

Radial Nerve Rehabilitation Orthotic Intervention Preview Youtube Talk to your doctor or physical therapist about which exercises will best help you meet your rehabilitation goals. radial tunnel syndrome is a painful condition caused by pressure on the radial nerve – one of the three main nerves in your arm. the most common place for compression of the radial nerve is at the elbow where the nerve enters a tight. A radial nerve injury usually causes symptoms in the back of your hand, near your thumb, and in your index and middle fingers. symptoms may include a sharp or burning pain, as well as unusual. Including radial nerve palsy, a paresis or paralysis affecting muscles innervated by the radial nerve. wrist drop is a common indication of a radial nerve injury as the extensors of the wrist are all innervated by the radial nerve. what to look for as a patient comes in: patients may present with the inability to extend the wrist and digits. And an injury at the wrist can cause numbness through the thumb or pins and needles sensations in the hand. treatment for radial nerve injuries may include wrist splints, over the counter pain medication, physical therapy, or surgery. injuries can take a couple of weeks or up to six months to heal.

Comments are closed.